In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear force applied to them.

Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges,vacuum gauges or compound gauges. The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge.

Pressure is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure.
A viscometer is an instrument used to measure the viscosity of a fluid. For liquids with viscosities which vary with flow conditions, an instrument called a rheometer is used. Thus, a rheometer can be considered as a special type of viscometer. Viscometers can measure only constant viscosity, that is, viscosity that does not change with flow conditions.

A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries.

The pascal is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is a SI coherent derived unit defined as one newton per square metre (N/m2). It is also equivalent to 10 barye in the CGS system. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal, which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal, which is equal to one centibar.

In fluid dynamics, a vortex is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil.
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured using devices called flowmeters in various ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:
The A2W reactor is a naval nuclear reactor used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships. The A2W designation stands for:

Buoyancy, or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.
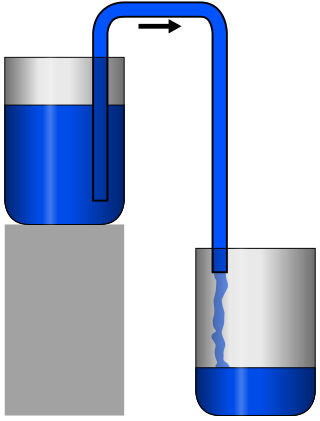
A siphon is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, with no pump, but powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, then discharging at a level lower than the surface of the reservoir from which it came.

Soil mechanics is a branch of soil physics and applied mechanics that describes the behavior of soils. It differs from fluid mechanics and solid mechanics in the sense that soils consist of a heterogeneous mixture of fluids and particles but soil may also contain organic solids and other matter. Along with rock mechanics, soil mechanics provides the theoretical basis for analysis in geotechnical engineering, a subdiscipline of civil engineering, and engineering geology, a subdiscipline of geology. Soil mechanics is used to analyze the deformations of and flow of fluids within natural and man-made structures that are supported on or made of soil, or structures that are buried in soils. Example applications are building and bridge foundations, retaining walls, dams, and buried pipeline systems. Principles of soil mechanics are also used in related disciplines such as geophysical engineering, coastal engineering, agricultural engineering, hydrology and soil physics.

A rheometer is a laboratory device used to measure the way in which a viscous fluid flows in response to applied forces. It is used for those fluids which cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity and therefore require more parameters to be set and measured than is the case for a viscometer. It measures the rheology of the fluid.

A landfill liner, or composite liner, is intended to be a low permeable barrier, which is laid down under engineered landfill sites. Until it deteriorates, the liner retards migration of leachate, and its toxic constituents, into underlying aquifers or nearby rivers, causing potentially irreversible contamination of the local waterway and its sediments.

The pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch, is a unit of measurement of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units. It is the pressure resulting from a force with magnitude of one pound-force applied to an area of one square inch. In SI units, 1 psi is approximately 6,895 pascals.

A tube, or tubing, is a long hollow cylinder used for moving fluids or to protect electrical or optical cables and wires.
This glossary of physics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to physics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including mechanics, materials science, nuclear physics, particle physics, and thermodynamics. For more inclusive glossaries concerning related fields of science and technology, see Glossary of chemistry terms, Glossary of astronomy, Glossary of areas of mathematics, and Glossary of engineering.
Most of the terms listed in Wikipedia glossaries are already defined and explained within Wikipedia itself. However, glossaries like this one are useful for looking up, comparing and reviewing large numbers of terms together. You can help enhance this page by adding new terms or writing definitions for existing ones.
This glossary of civil engineering terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts pertaining specifically to civil engineering, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. For a more general overview of concepts within engineering as a whole, see Glossary of engineering.
This glossary of engineering terms is a list of definitions about the major concepts of engineering. Please see the bottom of the page for glossaries of specific fields of engineering.











