Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometres (621 mi) west of the mainland. The capital and largest city is Quito.

Guayaquil, officially Santiago de Guayaquil, is the largest city in Ecuador. It is also the nation's main port. The city is the capital of Guayas Province and the seat of Guayaquil Canton.
Guayas is a coastal province in Ecuador. It is bordered to the west by Manabí, Santa Elena, and the Pacific Ocean ; to the east by Los Ríos, Bolívar, Chimborazo, Cañar, and Azuay; to the north by Los Ríos and Bolívar; and to the south by El Oro and the Pacific Ocean.

Tumbes is a coastal department and region in northwestern Peru bordering Ecuador. Due to the region's location near the Equator it has a warm climate, with beaches that are considered among the finest in Peru. Despite its small area, the region contains a wide variety of ecosystems. It is the smallest department in Peru and its third least populous department after Moquegua and Madre de Dios, but it is also its third most densely populated department, after La Libertad and Lambayeque.

Tumbes is a city in northwestern Peru, on the banks of the Tumbes River. It is the capital of the Tumbes Region, as well as of Tumbes Province and Tumbes District. Located near the border with Ecuador, Tumbes has 111,595 inhabitants as of 2015. It is served by the Cap. FAP Pedro Canga Rodriguez Airport. It is located on the Gulf of Guayaquil along with Zorritos.

The Ecuadorian–Peruvian War, known locally as the War of '41, was a South American border war fought between 5–31 July 1941. It was the first of three military conflicts between Ecuador and Peru during the 20th century. During the war, Peru occupied the western Ecuadorian province of El Oro and parts of the Andean province of Loja. Although the war took place during World War II, it is unrelated to that conflict; neither Ecuador nor Peru was supported by either the Allies or the Axis Powers.
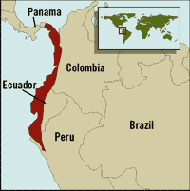
Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena is a biodiversity hotspot, which includes the tropical moist forests and tropical dry forests of the Pacific coast of South America and the Galapagos Islands. The region extends from easternmost Panama to the lower Magdalena Valley of Colombia, and along the Pacific coast of Colombia and Ecuador to the northwestern corner of Peru. Formerly called the Chocó-Darién-Western Ecuador Hotspot, it has been expanded to include several new areas, notably the Magdalena Valley in northern Colombia. It is bounded on the east by the Andes Mountains. The Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena Hotspot is 1,500 km long and encircles 274,597 km². Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena is near the Pacific Ocean. The factors that threaten Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena are farming encroachment, deforestation, illegal crops, and population growth. Whereas the Panamanian and Colombian portion of the hotspot are relatively intact, approximately 98% of native forest in coastal Ecuador has been cleared, rendering it the most threatened tropical forest in the world. The hotspot includes a wide variety of habitats, ranging from mangroves, beaches, rocky shorelines, and coastal wilderness to some of the world's wettest rain forests in the Colombian Chocó. The hotspot includes a number of ecoregions:

Zarumilla is one of the three provinces of the Tumbes Region in northwestern Peru. It borders the Pacific Ocean on the north, Ecuador on the south and east, and the Tumbes Province on the west.

Aguas Verdes, is a town in the Zarumilla Province of the Tumbes Region in northwestern Peru. It has a population of 2,390 (1999) and is capital of the Aguas Verdes District.

Zarumilla is a town in the Tumbes Region, in northwestern Peru. It has a population of 17,587 (1999) and is the capital of the Zarumilla Province. It is also the main settlement in the Zarumilla District.
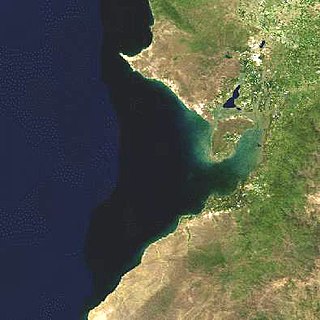
The Gulf of Guayaquil is a large body of water of the Pacific Ocean in western South America. Its northern limit is the city of Santa Elena, in Ecuador, and its southern limit is Cabo Blanco, in Peru.

The Tumbes River, is a river in South America. The river's sources are located between Ecuadorian El Oro and Loja provinces. It is the border between El Oro and Loja, and afterwards the border between Loja and the Tumbes Region in Peru. At its confluence with the Cazaderos stream, it enters the northern coastal region of Peru called the Tumbes Region, and flows into the Pacific Ocean outside the Gulf of Guayaquil. The largest city on its banks is Tumbes, Peru.

The Gulf of Guayaquil–Tumbes mangroves (NT1413) are an ecoregion located in the Gulf of Guayaquil in South America, in northern Peru and southern Ecuador. It has an area of 3,300 km².

The territorial dispute between Ecuador and Peru was the source of a long period of intermittent armed conflict between the two countries. This dispute was a consequence of each country's interpretation of what Real Cedulas Spain used to precisely define its colonial territories in the Americas. After independence, all of Spain's colonial territories signed and agreed to proclaim their limits in the basis of the principle uti possidetis juris which accepts the Spanish colonial borders of 1810 as the borders of the new republics. Thus the borders of Gran Colombia which included Ecuador, Colombia and Venezuela would follow the borders of the Viceroyalty of New Granada, and Peru the Viceroyalty of Peru in 1810. However, Peru was not satisfied with this and tried to set the date of her Uti Possitedis to 1824 – a time when Peru was officially independent with territories Peru militarily occupied since 1820.

Aguas Verdes is a district in the Zarumilla Province of the Tumbes Region in northwestern Peru. Its capital is the town of Aguas Verdes, which is on the banks of the Zarumilla River. Located on the border with Ecuador, Aguas Verdes serves as the largest international point of entry in Peru's northern border. This district is located right across the river from the Ecuadorian town of Huaquillas.
Tumbes National Reserve is a protected area established in 2006 and located in the region of Tumbes, Peru; near the border with Ecuador. It spans an area of 751 km2 (290 sq mi) and along with Cerros de Amotape National Park and El Angolo Game Preserve is part of the Noroeste Biosphere Reserve designated by UNESCO.

The Ecuadorian–Peruvian War took place between 1857 and 1860. The conflict began when Ecuador attempted to sell Amazon basin land claimed by Peru in order to settle a debt with British creditors. When diplomatic relations between the two countries broke down, prior to the fragmentation of the Ecuadorian government into several competing factions, the Peruvian government ordered a blockade of Ecuador's ports in order to force the cancellation of the sale, and the official acknowledgement of Peruvian ownership of the disputed territories. By late 1859, control of Ecuador was consolidated between General Guillermo Franco, in the city of Guayaquil, and a provisional government in Quito headed by Gabriel García Moreno. Peruvian President Ramón Castilla sailed to Guayaquil with several thousand soldiers in October 1859, and negotiated the Treaty of Mapasingue with General Franco in January 1860. The signing of the treaty indicated Ecuadorian compliance with all of Peru's demands, and temporarily marked the end of the territorial dispute between the two countries. However, in September 1860, the forces of the provisional government, commanded by García Moreno and General Juan José Flores defeated Franco's government at the Battle of Guayaquil, ending the civil war in Ecuador. The new government disavowed the Treaty of Mapasingue, followed shortly afterwards by its Peruvian counterpart; this re-opened the territorial dispute.
The military history of Ecuador spans hundreds of years.

The 1953 Tumbes earthquake occurred on December 12 at near the border between Peru and Ecuador. The shock had a moment magnitude of 7.5, a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VIII (Severe), and occurred in the northwestern offshore area of Tumbes, Peru.

The Tumbes–Piura dry forests (NT0232) is an arid tropical ecoregion along the Pacific coasts of southern Ecuador and northern Peru. The ecoregion contains many endemic species of flora and birds adapted to the short wet season followed by a long dry season. Threats include extraction of wood for fuel or furniture, and capture of wild birds for sale.