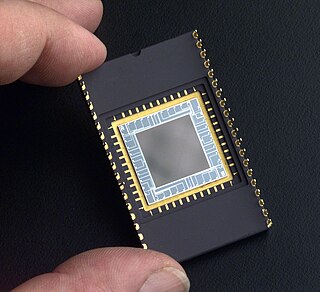
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.

Geodesy is the science of measuring and representing the geometry, gravity, and spatial orientation of the Earth in temporally varying 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical bodies, such as planets or circumplanetary systems.

In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north–south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and longitude are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth.

Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object was taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects outside of the visible spectrum of the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is accomplished through long time exposure as both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over long periods of time or using specialized optical filters which limit the photons to a certain wavelength.

The World Geodetic System (WGS) is a standard used in cartography, geodesy, and satellite navigation including GPS. The current version, WGS 84, defines an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system and a geodetic datum, and also describes the associated Earth Gravitational Model (EGM) and World Magnetic Model (WMM). The standard is published and maintained by the United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency.

Figure of the Earth is a term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A sphere is a well-known historical approximation of the figure of the Earth that is satisfactory for many purposes. Several models with greater accuracy have been developed so that coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns.

The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a United States federal agency based in Washington, D.C. that defines and manages a national coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication, mapping and charting, and a large number of science and engineering applications. Since its founding in 1970, it has been part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), a division within the United States Department of Commerce.
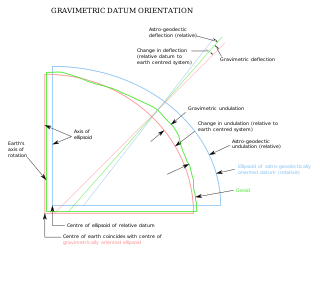
The vertical deflection (VD) or deflection of the vertical (DoV), also known as deflection of the plumb line and astro-geodetic deflection, is a measure of how far the gravity direction at a given point of interest is rotated by local mass anomalies such as nearby mountains. They are widely used in geodesy, for surveying networks and for geophysical purposes.

Satellite geodesy is geodesy by means of artificial satellites—the measurement of the form and dimensions of Earth, the location of objects on its surface and the figure of the Earth's gravity field by means of artificial satellite techniques. It belongs to the broader field of space geodesy. Traditional astronomical geodesy is not commonly considered a part of satellite geodesy, although there is considerable overlap between the techniques.
Geodetic astronomy or astronomical geodesy (astro-geodesy) is the application of astronomical methods into geodetic networks and other technical projects of geodesy.
The orthometric height is the vertical distance H along the plumb line from a point of interest to a reference surface known as the geoid, the vertical datum that approximates mean sea level. Orthometric height is one of the scientific formalizations of a laypersons' "height above sea level", along with other types of heights in Geodesy.
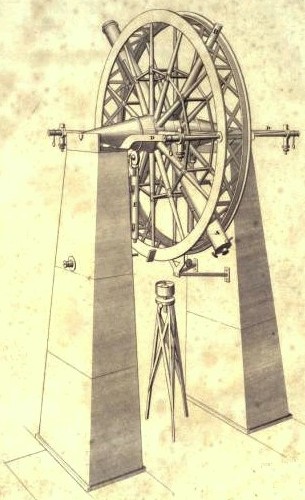
The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis.

Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure.
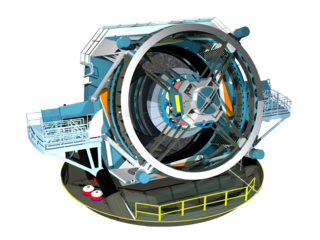
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, previously referred to as the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST), is an astronomical observatory currently under construction in Chile. Its main task will be carrying out a synoptic astronomical survey, the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). The word synoptic is derived from the Greek words σύν and ὄψις, and describes observations that give a broad view of a subject at a particular time. The observatory is located on the El Peñón peak of Cerro Pachón, a 2,682-meter-high mountain in Coquimbo Region, in northern Chile, alongside the existing Gemini South and Southern Astrophysical Research Telescopes. The LSST Base Facility is located about 100 kilometres (62 mi) away by road, in the town of La Serena. The observatory is named for Vera Rubin, an American astronomer who pioneered discoveries about galaxy rotation rates.

In astronomy, a transit instrument is a small telescope with extremely precisely graduated mount used for the precise observation of star positions. They were previously widely used in astronomical observatories and naval observatories to measure star positions in order to compile nautical almanacs for use by mariners for celestial navigation, and observe star transits to set extremely accurate clocks which were used to set marine chronometers carried on ships to determine longitude, and as primary time standards before atomic clocks. The instruments can be divided into three groups: meridian, zenith, and universal instruments.

An autoguider is an automatic electronic guidance tool used in astronomy to keep a telescope pointed precisely at an object being observed. This prevents the object from drifting across the field of view during long-exposures which would create a blurred or elongated image.

Afocal photography, also called afocal imaging or afocal projection is a method of photography where the camera with its lens attached is mounted over the eyepiece of another image forming system such as an optical telescope or optical microscope, with the camera lens taking the place of the human eye.
A3 Digital Mapping System consists of a digital airborne camera and an automatic ground processing system produced by VisionMap. The A3 camera captures imagery using a sweep mechanism, which collects high resolution vertical and oblique imagery simultaneously. The captured data is post-processed by the A3 LightSpeed ground processing system in order to create the final output products. The A3 System is used by numerous national and regional mapping agencies, as well as commercial mapping firms.

A star trail is a type of photograph that uses long exposure times to capture diurnal circles, the apparent motion of stars in the night sky due to Earth's rotation. A star-trail photograph shows individual stars as streaks across the image, with longer exposures yielding longer arcs. The term is used for similar photos captured elsewhere, such as on board the International Space Station and on Mars.















