Related Research Articles

A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures. A failure to pay, along with evasion of or resistance to taxation, is punishable by law. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labour equivalent. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC.
Pareto efficiency or Pareto optimality is a situation where no individual or preference criterion can be better off without making at least one individual or preference criterion worse off or without any loss thereof. The concept is named after Vilfredo Pareto (1848–1923), Italian civil engineer and economist, who used the concept in his studies of economic efficiency and income distribution. The following three concepts are closely related:

In neoclassical economics, market failure is a situation in which the allocation of goods and services by a free market is not Pareto efficient, often leading to a net loss of economic value. Market failures can be viewed as scenarios where individuals' pursuit of pure self-interest leads to results that are not efficient– that can be improved upon from the societal point of view. The first known use of the term by economists was in 1958, but the concept has been traced back to the Victorian philosopher Henry Sidgwick. Market failures are often associated with public goods, time-inconsistent preferences, information asymmetries, non-competitive markets, principal–agent problems, or externalities.
In microeconomics, economic efficiency is, roughly speaking, a situation in which nothing can be improved without something else being hurt. Depending on the context, it is usually one of the following two related concepts:
In economics, resource allocation is the assignment of available resources to various uses. In the context of an entire economy, resources can be allocated by various means, such as markets, or planning.
In law and economics, the Coase theorem describes the economic efficiency of an economic allocation or outcome in the presence of externalities. The theorem states that if trade in an externality is possible and there are sufficiently low transaction costs, bargaining will lead to a Pareto efficient outcome regardless of the initial allocation of property. In practice, obstacles to bargaining or poorly defined property rights can prevent Coasean bargaining. This 'theorem' is commonly attributed to Nobel Prize winner Ronald Coase.
Free-market environmentalism argues that the free market, property rights, and tort law provide the best means of preserving the environment, internalizing pollution costs, and conserving resources.
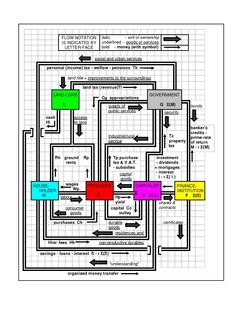
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community.
Algorithmic trading is a method of executing orders using automated pre-programmed trading instructions accounting for variables such as time, price, and volume. This type of trading attempts to leverage the speed and computational resources of computers relative to human traders. In the twenty-first century, algorithmic trading has been gaining traction with both retail and institutional traders. It is widely used by investment banks, pension funds, mutual funds, and hedge funds that may need to spread out the execution of a larger order or perform trades too fast for human traders to react to. A study in 2019 showed that around 92% of trading in the Forex market was performed by trading algorithms rather than humans.
In economics, a common-pool resource (CPR) is a type of good consisting of a natural or human-made resource system, whose size or characteristics makes it costly, but not impossible, to exclude potential beneficiaries from obtaining benefits from its use. Unlike pure public goods, common pool resources face problems of congestion or overuse, because they are subtractable. A common-pool resource typically consists of a core resource, which defines the stock variable, while providing a limited quantity of extractable fringe units, which defines the flow variable. While the core resource is to be protected or nurtured in order to allow for its continuous exploitation, the fringe units can be harvested or consumed.
The Lange model is a neoclassical economic model for a hypothetical socialist economy based on public ownership of the means of production and a trial-and-error approach to determining output targets and achieving economic equilibrium and Pareto efficiency. In this model, the state owns non-labor factors of production, and markets allocate final goods and consumer goods. The Lange model states that if all production is performed by a public body such as the state, and there is a functioning price mechanism, this economy will be Pareto-efficient, like a hypothetical market economy under perfect competition. Unlike models of capitalism, the Lange model is based on direct allocation, by directing enterprise managers to set price equal to marginal cost in order to achieve Pareto efficiency. By contrast, in a capitalist economy managers are instructed to maximize profits for private owners, while competitive pressures are relied on to indirectly lower the price to equal marginal cost.

A double auction is a process of buying and selling goods with multiple sellers and multiple buyers. Potential buyers submit their bids and potential sellers submit their ask prices to the market institution, and then the market institution chooses some price p that clears the market: all the sellers who asked less than p sell and all buyers who bid more than p buy at this price p. Buyers and sellers that bid or ask for exactly p are also included. A common example of a double auction is stock exchange.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:
Water trading is the process of buying and selling water access entitlements, also often called water rights. The terms of the trade can be either permanent or temporary, depending on the legal status of the water rights. Some of the western states of the United States, Chile, South Africa, Australia, Iran and Spain's Canary Islands have water trading schemes. Some consider Australia's to be the most sophisticated and effective in the world. Some other countries, especially in South Asia, also have informal water trading schemes. Water markets tend to be local and informal, as opposed to more formal schemes.
Property rights are constructs in economics for determining how a resource or economic good is used and owned. Resources can be owned by individuals, associations, collectives, or governments. Property rights can be viewed as an attribute of an economic good. This attribute has three broad components and is often referred to as a bundle of rights in the United States:
- the right to use the good
- the right to earn income from the good
- the right to transfer the good to others, alter it, abandon it, or destroy it
The genetic algorithm is an operational research method that may be used to solve scheduling problems in production planning.

Altreva Adaptive Modeler is a software application for creating agent-based financial market simulation models for the purpose of forecasting prices of real world market traded stocks or other securities. The technology it uses is based on the theory of agent-based computational economics (ACE), the computational study of economic processes modeled as dynamic systems of interacting heterogeneous agents.
The Spectrum Commons theory states that the telecommunication radio spectrum should be directly managed by its users rather than regulated by governmental or private institutions. Spectrum management is the process of regulating the use of radio frequencies to promote efficient use and gain a net social benefit. The theory of Spectrum Commons argues that there are new methods and strategies that will allow almost complete open access to this currently regulated commons with unlimited number of persons to share it without causing interference. This would eliminate the need for both a centralized, governmental management of the spectrum and the allocation of specific portions of the spectrum to private actors.

Shyam Sunder is an accounting theorist and experimental economist. He is the James L. Frank Professor of accounting, economics, and finance at the Yale School of Management; a professor in Yale University’s Department of Economics; and a Fellow of the Whitney Humanities Center.
Course allocation is the problem of allocating seats in university courses among students. Many universities impose an upper bound on the number of students allowed to register to each course, in order to ensure that the teachers can give sufficient attention to each individual student. Since the demand for some courses is higher than the upper bound, a natural question is which students should be allowed to register to each course.
References
- ↑ "Zero intelligence' trading closely mimics stock market". New Scientist. February 1, 2005.
- ↑ Gode, Dhananjay K.; Sunder, Shyam (1993). "Allocative Efficiency of Markets with Zero-Intelligence Traders: Market as a Partial Substitute for Individual Rationality". Journal of Political Economy. 101 (1): 119–137. doi:10.1086/261868. JSTOR 2138676. S2CID 11858620.
- ↑ Farmer, J. D.; Patelli, P.; Zovko, I. I. (2005). "The predictive power of zero intelligence in financial markets". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102 (6): 2254–2259. arXiv: cond-mat/0309233 . Bibcode:2005PNAS..102.2254F. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409157102 . PMC 548562 . PMID 15687505.
- ↑ Mark McBride (August 27, 2008). "Zero-Intelligence Trader Lab" (PDF). Miami University. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 27, 2008.