Harry Bernard Allen was one of Britain's last official executioners, officiating between 1941 and 1964. He was chief executioner at 41 executions and acted as assistant executioner at 53 others, at various prisons in England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, the Channel Islands and Cyprus. He acted as assistant executioner for 14 years, mostly to Albert Pierrepoint from 1941 to 1955.

Capital punishment in the United Kingdom predates the formation of the UK, having been used within the British Isles from ancient times until the second half of the 20th century. The last executions in the United Kingdom were by hanging, and took place in 1964; capital punishment for murder was suspended in 1965 and finally abolished in 1969. Although unused, the death penalty remained a legally defined punishment for certain offences such as treason until it was completely abolished in 1998; the last execution for treason took place in 1946. In 2004 the 13th Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights became binding on the United Kingdom; it prohibits the restoration of the death penalty as long as the UK is a party to the convention.

William Marwood was a British state hangman. He developed the technique of hanging known as the "long drop".

Charles Peace was an English burglar and murderer, who embarked on a life of crime after being maimed in an industrial accident as a boy.

San Quentin State Prison (SQ) is a California Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation state prison for men, located north of San Francisco in the unincorporated place of San Quentin in Marin County.

HM Prison Geelong was a maximum security Australia prison located on the corner of Myers Street and Swanston Street in Geelong, Victoria, Australia. The prison was built in stages from 1849 to 1864. Its panopticon design is based on Pentonville Prison in England. The prison was officially closed in 1991 and prisoners were moved to the newly built HM Prison Barwon in Lara. The building now functions as a museum for the history of the prison.

The Old Melbourne Gaol is a former jail and current museum on Russell Street, in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It consists of a bluestone building and courtyard, and is located next to the old City Police Watch House and City Courts buildings, and opposite the Russell Street Police Headquarters. It was first constructed starting in 1839, and during its operation as a prison between 1845 and 1924, it held and executed some of Australia's most notorious criminals, including bushranger Ned Kelly and serial killer Frederick Bailey Deeming. In total, 133 people were executed by hanging. Though it was used briefly during World War II, it formally ceased operating as a prison in 1924; with parts of the jail being incorporated into the RMIT University, and the rest becoming a museum.

Capital punishment in New Zealand – the process of sentencing convicted offenders to death for the most serious crimes and carrying out that sentence, as ordered by a legal system – first appeared in a codified form when New Zealand became a British colony in 1840. It was first carried out with a public hanging in Victoria Street, Auckland in 1842, while the last execution occurred in 1957 at Mount Eden Prison, also in Auckland. In total, 85 people have been executed in New Zealand.

The Maitland Gaol, also known as Maitland Correctional Centre, is a heritage-listed former Australian prison located in East Maitland, New South Wales. Its construction was started in 1844 and prisoners first entered the gaol in 1848. By the time of its closure, on 31 January 1998, it had become the longest continuously-run gaol in Australia. It has since been turned into a museum and is a popular tourist attraction. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.

HM Prison Leeds is a Category B men's prison, located at Gloucester Terrace in the Armley area of Leeds in West Yorkshire, England, which opened in 1847. Leeds Prison is operated by His Majesty's Prison Service, and is still known locally as Armley Gaol, the historical name for the prison.
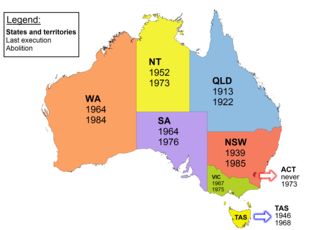
Capital punishment in Australia was a form of punishment in Australia that has been abolished in all jurisdictions. Queensland abolished the death penalty in 1922. Tasmania did the same in 1968. The Commonwealth abolished the death penalty in 1973, with application also in the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory. Victoria did so in 1975, South Australia in 1976, and Western Australia in 1984. New South Wales abolished the death penalty for murder in 1955, and for all crimes in 1985. In 2010, the Commonwealth Parliament passed legislation prohibiting the re-establishment of capital punishment by any state or territory. Australian law prohibits the extradition or deportation of a prisoner to another jurisdiction if they could be sentenced to death for any crime.
There is a long history of capital punishment in the Isle of Man. Until the 17th century, many convicted prisoners were executed at Hango Hill.

Leeds Combined Court Centre is a Crown Court venue, which deals with criminal cases, and a County Court venue, which deals with civil cases, in Oxford Row, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. It is adjacent to Leeds Magistrates Courts.

James Billington was a hangman for the British government from 1884 until 1901. He was the patriarch of the Billington family of executioners. Billington died at home from emphysema in the early hours of 13 December 1901, ten days after having executed Patrick McKenna, a man he knew well.
Thomas George Tattersall was an English plasterer who was convicted of murdering his wife.
The murder of William Plommer took place in Sheffield, England, on 27 April 1925. Plommer, a First World War veteran, was attacked in the street by a gang and died of his injuries shortly afterwards. Eleven men were placed under arrest in the aftermath of the murder, five of them eventually being convicted. Two of those convicted, the brothers Lawrence Fowler and Wilfred Fowler, were hanged at Armley Gaol, Leeds. The case was international news.
The Leeds dripping riot was an act of civil disorder that occurred in Leeds, England on 22 February 1865. The riot was a response to the imprisonment of a local woman for the theft of dripping. During the riot one person was seriously injured and subsequently died while five people were arrested and charged with riotous conduct.
Ann Husler (1803–1874), née Procter, was a quarry owner and stone merchant based in Weetwood, Leeds, in West Yorkshire. She ran a quarry business after the death of her husband, John Husler. She ran the business until her death at the age of 71, after which she left her share of the business to one of her sons.














