
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in which simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Another way to distinguish between the terms is to define simulation as experimentation with the help of a model. This definition includes time-independent simulations. Often, computers are used to execute the simulation.

Dassault Systèmes SE is a French multinational software corporation which develops software for 3D product design, simulation, manufacturing and other 3D related products.

Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer science and engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers.
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that provides software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and has offices worldwide. Its U.S. offices are located in the states of California, Oregon, Colorado, Texas, Michigan, New Hampshire and Massachusetts. Its Canada offices are located in the provinces of Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta.
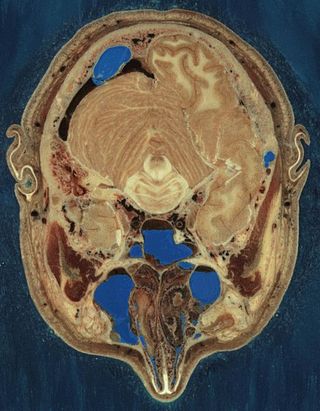
The Visible Human Project is an effort to create a detailed data set of cross-sectional photographs of the human body, in order to facilitate anatomy visualization applications. It is used as a tool for the progression of medical findings, in which these findings link anatomy to its audiences. A male and a female cadaver were cut into thin slices, which were then photographed and digitized. The project is run by the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM) under the direction of Michael J. Ackerman. Planning began in 1986; the data set of the male was completed in November 1994 and the one of the female in November 1995. The project can be viewed today at the NLM in Bethesda, Maryland. There are currently efforts to repeat this project with higher resolution images but only with parts of the body instead of a cadaver.
Poser is a figure posing and rendering 3D computer graphics program distributed by Bondware. Poser is optimized for the 3D modeling of human figures. It enables beginners to produce basic animations and digital images, along with the extensive availability of third-party digital 3D models.

Mixed reality (MR) is a term used to describe the merging of a real-world environment and a computer-generated one. Physical and virtual objects may co-exist in mixed reality environments and interact in real time.
Engineering Animation, Inc., or EAI, was a services and software company based in Ames, Iowa, United States. It remained headquartered there from its incorporation in 1990 until it was acquired in 2000 by Unigraphics Solutions, Inc., now a subsidiary of the German technology multinational Siemens AG. During its existence, EAI produced animations to support litigants in court, wrote and sold animation and visualization software, and developed a number of multimedia medical and computer game titles. Part of EAI's business now exists in a spin-off company, Demonstratives.

Bryan Brandenburg is a biophysicist, author, technology entrepreneur and former game programmer. Brandenburg is best known as co-founder of Zenerchi, Sculptured Software and Salt Lake Comic Con and Executive Producer at Engineering Animation, Inc.

An écorché is a figure drawn, painted, or sculpted showing the muscles of the body without skin, normally as a figure study for another work or as an exercise for a student artist. The Renaissance-era architect, theorist and all-around Renaissance man Leon Battista Alberti recommended that when painters intend to depict a nude, they should first arrange the muscles and bones, then depict the overlying skin.
Professor Paul Gerard McMenamin is an Australian academic and researcher specialising in the structure and immunology of the eye.

Synopsys Simpleware ScanIP is a 3D image processing and model generation software program developed by Synopsys Inc. to visualise, analyse, quantify, segment and export 3D image data from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), microtomography and other modalities for computer-aided design (CAD), finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and 3D printing. The software is used in the life sciences, materials science, nondestructive testing, reverse engineering and petrophysics.
ZygoteBody, formerly Google Body, is a web application by Zygote Media Group that renders manipulable 3D anatomical models of the human body. Several layers, from muscle tissues down to blood vessels, can be removed or made transparent to allow better study of individual body parts. Most of the body parts are labelled and are searchable.

In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based representation of a surface of an object in three dimensions via specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, and polygons in a simulated 3D space.

Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific-technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in art, printed media, simulators, videos and video games. These images are either static or dynamic. CGI both refers to 2D computer graphics and 3D computer graphics with the purpose of designing characters, virtual worlds, or scenes and special effects. The application of CGI for creating/improving animations is called computer animation, or CGI animation.
Computational human phantoms are models of the human body used in computerized analysis. Since the 1960s, the radiological science community has developed and applied these models for ionizing radiation dosimetry studies. These models have become increasingly accurate with respect to the internal structure of the human body.

Anatomography is an interactive website which supports generating anatomical diagrams and animations of the human body. The Anatomography website is maintained by the DBCLS non-profit research institute located at the University of Tokyo. Anatomical diagrams generated by Anatomography, and 3D polygon data used on the website, are freely available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license.

BioDigital is a New York-based biomedical visualization company that is often referred to as being "Google Earth for the Human Body". BioDigital offers an interactive, 3D software platform that enables individuals and businesses to explore and visualize health information. Their flagship product, the BioDigital Human, is a "searchable, customizable map of the human body".

An anatomical model is a three-dimensional representation of human or animal anatomy, used for medical and biological education.












