Related Research Articles

A classical Kuiper belt object, also called a cubewano ( "QB1-o"), is a low-eccentricity Kuiper belt object (KBO) that orbits beyond Neptune and is not controlled by an orbital resonance with Neptune. Cubewanos have orbits with semi-major axes in the 40–50 AU range and, unlike Pluto, do not cross Neptune's orbit. That is, they have low-eccentricity and sometimes low-inclination orbits like the classical planets.
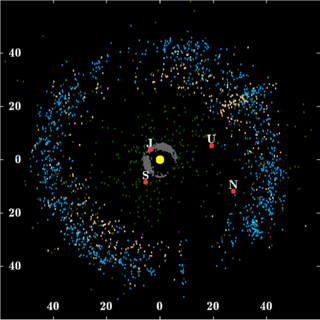
The Kuiper belt is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles, such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, may have originated in the region.

Following the discovery of the planet Neptune in 1846, there was considerable speculation that another planet might exist beyond its orbit. The search began in the mid-19th century and continued at the start of the 20th with Percival Lowell's quest for Planet X. Lowell proposed the Planet X hypothesis to explain apparent discrepancies in the orbits of the giant planets, particularly Uranus and Neptune, speculating that the gravity of a large unseen ninth planet could have perturbed Uranus enough to account for the irregularities.
In astronomy, the plutinos are a dynamical group of trans-Neptunian objects that orbit in 2:3 mean-motion resonance with Neptune. This means that for every two orbits a plutino makes, Neptune orbits three times. The dwarf planet Pluto is the largest member as well as the namesake of this group. The next largest members are Orcus, (208996) 2003 AZ84, and Ixion. Plutinos are named after mythological creatures associated with the underworld.

In planetary astronomy, a centaur is a small Solar System body that orbits the Sun between Jupiter and Neptune and crosses the orbits of one or more of the giant planets. Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because they cross or have crossed the orbits of the giant planets; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one known centaur, 514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, which may be in a stable orbit. Centaurs typically exhibit the characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000.

28978 Ixion (, provisional designation 2001 KX76) is a large trans-Neptunian object and a possible dwarf planet. It is located in the Kuiper belt, a region of icy objects orbiting beyond Neptune in the outer Solar System. Ixion is classified as a plutino, a dynamical class of objects in a 2:3 orbital resonance with Neptune. It was discovered in May 2001 by astronomers of the Deep Ecliptic Survey at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, and was announced in July 2001. The object is named after the Greek mythological figure Ixion, who was a king of the Lapiths.

38628 Huya ( hoo-YAH), provisional designation 2000 EB173, is a binary trans-Neptunian object located in the Kuiper belt, a region of icy objects orbiting beyond Neptune in the outer Solar System. Huya is classified as a plutino, a dynamical class of trans-Neptunian objects with orbits in a 3:2 orbital resonance with Neptune. It was discovered by the Quasar Equatorial Survey Team and was identified by Venezuelan astronomer Ignacio Ferrín in March 2000. It is named after Juyá, the mythological rain god of the Wayuu people native to South America.

The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small Solar System bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc objects (SDOs) have orbital eccentricities ranging as high as 0.8, inclinations as high as 40°, and perihelia greater than 30 astronomical units (4.5×109 km; 2.8×109 mi). These extreme orbits are thought to be the result of gravitational "scattering" by the gas giants, and the objects continue to be subject to perturbation by the planet Neptune.

Neptune trojans are bodies that orbit the Sun near one of the stable Lagrangian points of Neptune, similar to the trojans of other planets. They therefore have approximately the same orbital period as Neptune and follow roughly the same orbital path. Thirty-one Neptune trojans are currently known, of which 27 orbit near the Sun–Neptune L4 Lagrangian point 60° ahead of Neptune and four orbit near Neptune's L5 region 60° behind Neptune. The Neptune trojans are termed 'trojans' by analogy with the Jupiter trojans.
(309239) 2007 RW10, provisionally known as 2007 RW10, is a temporary quasi-satellite of Neptune. Observed from Neptune, it would appear to go around it during one Neptunian year but it actually orbits the Sun, not Neptune.
83982 Crantor, prov. designation: 2002 GO9, is a centaur in a 1:1 resonance with Uranus, approximately 60 kilometers (37 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 12 April 2002, by astronomers of the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. This minor planet was named for Crantor from Greek mythology.
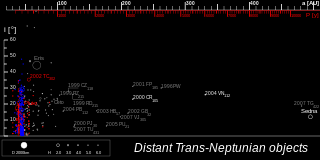
Detached objects are a dynamical class of minor planets in the outer reaches of the Solar System and belong to the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs). These objects have orbits whose points of closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) are sufficiently distant from the gravitational influence of Neptune that they are only moderately affected by Neptune and the other known planets: This makes them appear to be "detached" from the rest of the Solar System, except for their attraction to the Sun.
(55638) 2002 VE95, prov. designation: 2002 VE95, is a trans-Neptunian object from the outermost region of the Solar System. It was discovered on 14 November 2002, by astronomers with the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking program at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. This resonant trans-Neptunian object is a member of the plutino population, locked in a 2:3 resonance with Neptune. The object is likely of primordial origin with a heterogeneous surface and a notably reddish color (RR) attributed to the presence of methanol and tholins. It has a poorly defined rotation period of 6.8 hours and measures approximately 250 kilometers (160 miles) in diameter, too small to be a dwarf planet candidate. As of 2021, it has not yet been named.
(445473) 2010 VZ98, provisional designation 2010 VZ98, is a trans-Neptunian object of the scattered disc, orbiting the Sun in the outermost region of the Solar System. It has a diameter of approximately 400 kilometers.
(310071) 2010 KR59, provisional designation 2010 KR59, is a trans-Neptunian object, approximately 110 kilometers in diameter. The object is trapped in a 1:1 mean motion resonance with Neptune, and rotates nearly every 9 hours around its axis. It was discovered on May 18, 2010 at 7:45 UT by the WISE spacecraft. The WISE telescope scanned the entire sky in infrared light from January 2010 to February 2011.

(316179) 2010 EN65 is a trans-Neptunian object orbiting the Sun. However, with a semi-major axis of 30.8 AU, the object is actually a jumping Neptune trojan, co-orbital with Neptune, as the giant planet has a similar semi-major axis of 30.1 AU. The body is jumping from the Lagrangian point L4 into L5 via L3. As of 2016, it is 54 AU from Neptune. By 2070, it will be 69 AU from Neptune.
2012 GX17, also written as 2012 GX17, is a minor body classified as Centaur and Trans-Neptunian object by the Minor Planet Center. The object was once considered a promising Neptune L5 trojan candidate.
2010 EU65 is a centaur, approximately 64 kilometers (40 miles) in diameter, orbiting the Sun in the outer Solar System. The object is also a promising Uranus horseshoe librator candidate. It was first observed on 13 March 2010, by American astronomers David Rabinowitz and Suzanne Tourtellotte, observing from Cerro Tololo and La Silla Observatory in Chile. As of 2021, it has neither been numbered nor named.
2014 FZ71 is a trans-Neptunian object, a scattered disc classified as a scattered and detached object, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. It was first observed on 24 March 2014, by a team led by American astronomer Scott Sheppard at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile. With its perihelion of almost 56 AU, it belongs to a small and poorly understood group of very distant objects with moderate eccentricities. The object is not a dwarf planet candidate as it only measures approximately 150 kilometers (93 miles) in diameter.
2015 FJ345 is a trans-Neptunian object and detached object, located in the scattered disc, the outermost region of the Solar System. It was first observed on 17 March 2015, by a team led by American astronomer Scott Sheppard at the Mauna Kea Observatories, in Hawaii, United States. With its perihelion of almost 51 AU, it belongs to a small and poorly understood group of very distant objects with moderate eccentricities. The object is not a dwarf planet candidate as it only measures approximately 120 kilometers (75 miles) in diameter.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "148975 (2001 XA255)". JPL Small-Body Database . NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 7 April 2016.
- 1 2 Jewitt, David C. (2009). "The Active Centaurs". The Astronomical Journal . 137 (5): 4296–4312. arXiv: 0902.4687 . Bibcode:2009AJ....137.4296J. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/137/5/4296. S2CID 18877930.
- 1 2 3 Johnston, Wm. Robert (18 August 2020). "List of Known Trans-Neptunian Objects". Johnston's Archive. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ↑ Jewitt, David C.; Sheppard, S. S.; Kleyna, J.; Marsden, B. G. "2001 XA255". Minor Planet Electronic Circular .
- 1 2 de la Fuente Marcos, C.; de la Fuente Marcos, R. (2012). "Four temporary Neptune co-orbitals: (148975) 2001 XA255, (310071) 2010 KR59, (316179) 2010 EN65, and 2012 GX17". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 547: L2. arXiv: 1210.3466 . Bibcode:2012A&A...547L...2D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201220377. S2CID 118622987.
- ↑ ADS link Gallardo, T. (2006) Atlas of the mean-motion resonances in the Solar System