
1998 WW31, is a non-resonant trans-Neptunian object and binary system from the Kuiper belt located in the outermost region of the Solar System, approximately 148 kilometers (92 miles) in diameter. It was first observed on 18 November 1998, by American astronomer Marc Buie and Robert Millis at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, United States. In December 2000, a minor-planet moon, designated S/2000 (1998 WW31) 1 with a diameter of 123 kilometers (76 miles), was discovered in its orbit. After Charon in 1978, it was the first of nearly 100 satellites since discovered in the outer Solar System.
53311 Deucalion (provisional designation 1999 HU11) is a trans-Neptunian object from the classical Kuiper belt, with a diameter of approximately 130–210 kilometers (81–130 miles), located in the outermost region of the Solar System. The cubewano belongs to the cold population and was discovered on 18 April 1999, by the Deep Ecliptic Survey at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, United States. It was named after Deucalion, from Greek mythology.

(48639) 1995 TL8 is a binary trans-Neptunian object from the scattered disc in the outermost regions of the Solar System. It was discovered by Arianna Gleason in 1995 and measures approximately 176 kilometers in diameter. Its 80-kilometer minor-planet moon, provisionally designated S/2002 (48639) 1, was discovered on 9 November 2002.

58534 Logos, or as a binary system (58534) Logos-Zoe, is a trans-Neptunian object and binary system from the classical Kuiper belt, approximately 77 kilometers (48 miles) in diameter. The bright cubewano belongs to the cold population and has a 66-kilometer sized companion named Zoe. The system mass is (4.58±0.07)×1017 kg.

(208996) 2003 AZ84 (provisional designation 2003 AZ84) is a trans-Neptunian object with a possible moon located in the outer regions of the Solar System. It is approximately 940 kilometers across its longest axis, as it has an elongated shape. It belongs to the plutinos – a group of minor planets named after its largest member Pluto – as it orbits in a 2:3 resonance with Neptune in the Kuiper belt. It is the third-largest known plutino, after Pluto and Orcus. It was discovered on 13 January 2003, by American astronomers Chad Trujillo and Michael Brown during the NEAT survey using the Samuel Oschin telescope at Palomar Observatory.

174567 Varda (provisional designation 2003 MW12) is a binary trans-Neptunian planetoid of the resonant hot classical population of the Kuiper belt, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. Its moon, Ilmarë, was discovered in 2009.
(24835) 1995 SM55 (provisional designation 1995 SM55) is a trans-Neptunian object and member of the Haumea family that resides in the Kuiper belt, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. It was discovered on 19 September 1995, by American astronomer Nichole Danzl of the Spacewatch program at Kitt Peak National Observatory near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. It measures approximately 200 kilometers in diameter and was the second-brightest known object in the Kuiper belt, after Pluto, until 1996 TO66 was discovered.
(79983) 1999 DF9 (provisional designation 1999 DF9) is a trans-Neptunian object of the Kuiper belt, classified as a non-resonant cubewano, that measures approximately 270 kilometers in diameter.
(35671) 1998 SN165 (provisional designation 1998 SN165) is a trans-Neptunian object from the Kuiper belt located in the outermost region of the Solar System. It was discovered on 23 September 1998, by American astronomer Arianna Gleason at the Kitt Peak National Observatory near Tucson, Arizona. The cold classical Kuiper belt object is a dwarf planet candidate, as it measures approximately 400 kilometers (250 miles) in diameter. It has a grey-blue color (BB) and a rotation period of 8.8 hours. As of 2021, it has not been named.

(40314) 1999 KR16 is a trans-Neptunian object on an eccentric orbit in the outermost region of the Solar System, approximately 254 kilometers (158 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 16 May 1999, by French astronomer Audrey Delsanti and Oliver Hainaut at ESO's La Silla Observatory in northern Chile. The very reddish object is a dwarf planet candidate and has a rotation period of 11.7 hours.
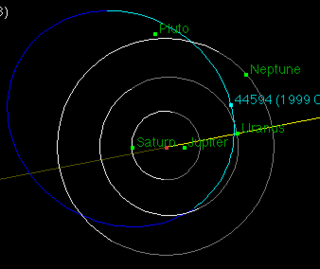
(44594) 1999 OX3 is an eccentric trans-Neptunian object with a centaur-like orbit from the outer Solar System, approximately 150 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 21 July 1999, by astronomers John Kavelaars, Brett Gladman, Matthew Holman and Jean-Marc Petit at Mauna Kea Observatories, Hawaii, United States.
(144897) 2004 UX10 (provisional designation 2004 UX10) is a Kuiper-belt object. It has a diameter of about 360 kilometres (220 mi) and was discovered by Andrew Becker, Andrew Puckett and Jeremy Kubica on 20 October 2004 at Apache Point Observatory in Sunspot, New Mexico. The object is classified as a cubewano. It is near a 2:3 resonance with Neptune.
(469306) 1999 CD158 (provisional designation 1999 CD158) is a trans-Neptunian object from the circumstellar disc of the Kuiper belt, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. The relatively bright hot classical Kuiper belt object measures approximately 310 kilometers (190 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 10 February 1999, by American astronomers Jane Luu, David Jewitt and Chad Trujillo at Mauna Kea Observatories on the Big Island of Hawaii, United States.

(82158) 2001 FP185 (provisional designation 2001 FP185) is a highly eccentric trans-Neptunian object from the scattered disc in the outermost part of the Solar System, approximately 330 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 26 March 2001, by American astronomer Marc Buie at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, United States.
2014 OS393, unofficially designated e31007AI, e3 and PT2, is a binary trans-Neptunian object in the classical Kuiper belt, the outermost region of the Solar System. It was first observed by the New Horizons KBO Search using the Hubble Space Telescope on 30 July 2014. Until 2015, when the object 486958 Arrokoth was selected, it was a potential flyby target for the New Horizons probe. Estimated to be approximately 42 kilometres (26 mi) in diameter, the object has a poorly determined orbit as it had been observed for only a few months.
(508869) 2002 VT130, provisional designation 2002 VT130, is a trans-Neptunian object and binary system from the classical Kuiper belt, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. It was discovered by American astronomer Marc Buie at Kitt Peak Observatory on 7 November 2002. The primary measures approximately 324 kilometers (201 miles) in diameter.

(524366) 2001 XR254, provisional designation 2001 XR254, is a trans-Neptunian object and binary system from the classical Kuiper belt, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. The cubewano belongs to the cold population and measures approximately 171 kilometers (110 miles). It was first observed on 10 December 2001, by astronomers at the Mauna Kea Observatory, Hawaii. Its 140-kilometer sized companion was discovered by the Hubble Space Telescope in June 2006.

(275809) 2001 QY297 is a trans-Neptunian object from the classical Kuiper belt, located in the outermost region of the Solar System. The binary classical Kuiper belt object belongs to the cold population.

(416400) 2003 UZ117 (provisional designation 2003 UZ117) is a trans-Neptunian object and suspected member of the Haumea family, located in the Kuiper belt in the outermost region of the Solar System. It was discovered on 24 October 2003, by astronomers of the Spacewatch survey project at Kitt Peak Observatory, Arizona. The object may also be a non-resonant cubewano.














