Azulene is an organic compound and an isomer of naphthalene. Whereas naphthalene is colourless, azulene is dark blue. Two terpenoids, vetivazulene (4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) and guaiazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene), that feature the azulene skeleton are found in nature as constituents of pigments in mushrooms, guaiac wood oil, and some marine invertebrates.

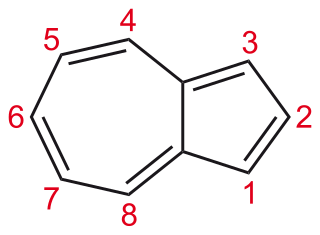
Pentalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon composed of two fused cyclopentadiene rings. It has chemical formula C8H6. It is antiaromatic, because it has 4n π electrons where n is any integer. For this reason it dimerizes even at temperatures as low as −100 °C. The derivative 1,3,5-tri-tert-butylpentalene was synthesized in 1973. Because of the tert-butyl substituents this compound is thermally stable. Pentalenes can also be stabilized by benzannulation for example in the compounds benzopentalene and dibenzopentalene.
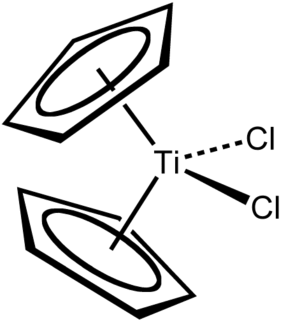
Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic covalent bonds to two arene ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives (for example Cn(CH3)n) and heterocyclic derivatives (for example BCnHn+1). Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond.

Dicarbonylbis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium is the chemical compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2Ti(CO)2, abbreviated Cp2Ti(CO)2. This maroon-coloured, air-sensitive species is soluble in aliphatic and aromatic solvents. It has been used for the deoxygenation of sulfoxides, reductive coupling of aromatic aldehydes and reduction of aldehydes.
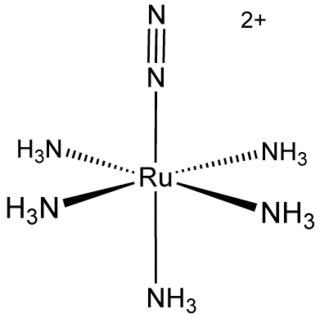
Transition metal dinitrogen complexes are coordination compounds that contain transition metals as ion centers the dinitrogen molecules (N2) as ligands.

Organozirconium compounds are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to zirconium chemical bond. Organozirconium chemistry is the corresponding science exploring properties, structure, and reactivity of these compounds. Organozirconium compounds have been widely studied, in part because they are useful catalysts in Ziegler-Natta polymerization.
Zirconocene dichloride is an organozirconium compound composed of a zirconium central atom, with two cyclopentadienyl and two chloro ligands. It is a colourless diamagnetic solid that is somewhat stable in air.
Organoscandium chemistry is an area with organometallic compounds focused on compounds with at least on carbon to scandium chemical bond. The interest in organoscandium compounds is mostly academic but motivated by potential practical applications in catalysis, especially in polymerization. A common precursor is scandium chloride, especially its THF complex.
Organovanadium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to vanadium (V) chemical bond. Organovanadium compounds find only minor use as reagents in organic synthesis but are significant for polymer chemistry as catalysts.
In organometallic chemistry, bent metallocenes are a subset of metallocenes. In bent metallocenes, the ring systems coordinated to the metal are not parallel, but are tilted at an angle. A common example of a bent metallocene is Cp2TiCl2. Several reagents and much research is based on bent metallocenes.

Vanadium(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula VF5. It is a colorless volatile liquid. It is a highly reactive compound, as indicated by its ability to fluorinate organic substances.
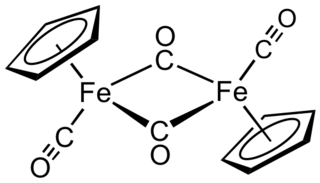
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(η5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2]2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, [CpFe(CO)2]2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below).

Bis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium(III) chloride, also known as the Nugent–RajanBabu reagent, is the organotitanium compound which exists as a dimer with the formula [(C5H5)2TiCl]2. It is an air sensitive green solid. The complex finds specialized use in synthetic organic chemistry as a single electron reductant.
Organoniobium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing niobium-carbon (Nb-C) bonds. Compared to the other group 5 transition metal organometallics, the chemistry of organoniobium compounds most closely resembles that of organotantalum compounds. Organoniobium compounds of oxidation states +5, +4, +3, +2, +1, 0, -1, and -3 have been prepared, with the +5 oxidation state being the most common.

(Cyclopentadienyl)zirconium trichloride is an organozirconium compound with the formula (C5H5)ZrCl3. It a moisture-sensitive white solid. The compound adopts a polymeric structure. The compound has been well studied spectroscopically.

A lanthanocene is a type of metallocene compound that contains an element from the lanthanide series. The most common lanthanocene complexes contain two cyclopentadienyl anions and an X type ligand, usually hydride or alkyl ligand.
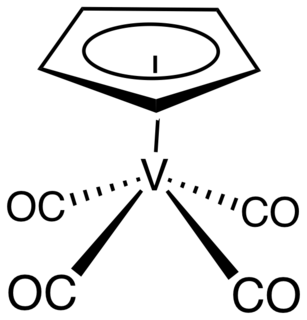
Cyclopentadienylvanadium tetracarbonyl is the organovanadium compound with the formula (C5H5)V(CO)4. An orange, diamagnetic solid, it is the principal cyclopentadienyl carbonyl of vanadium. It can be prepared by heating a solution of vanadocene under high pressure of carbon monoxide. As confirmed by X-ray crystallography, the coordination sphere of vanadium consists of η5-cyclopentadienyl and four carbonyl ligands. The molecule is a four-legged piano stool complex. The compound is soluble in common organic solvents. The compound has no commercial applications.

(Cycloheptatrienyl)(cyclopentadienyl)titanium is an organotitanium compound with the formula Ti(C7H7)(C5H5). It is a blue, diamagnetic, sublimable solid that is sensitive toward air. The structure has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. This sandwich complex features cyclopentadienyl and cycloheptatrienyl ligands bound to titanium. The Ti-C distances are all within a narrow range near 2.35 Å.
















