
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database.

An object database or object-oriented database is a database management system in which information is represented in the form of objects as used in object-oriented programming. Object databases are different from relational databases which are table-oriented. A third type, object–relational databases, is a hybrid of both approaches. Object databases have been considered since the early 1980s.
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e., data incorporating relations among entities and variables.
Object–relational mapping in computer science is a programming technique for converting data between a relational database and the memory of an object-oriented programming language. This creates, in effect, a virtual object database that can be used from within the programming language.

An object–relational database (ORD), or object–relational database management system (ORDBMS), is a database management system (DBMS) similar to a relational database, but with an object-oriented database model: objects, classes and inheritance are directly supported in database schemas and in the query language. Also, as with pure relational systems, it supports extension of the data model with custom data types and methods.
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve information. A well known example is the Structured Query Language (SQL).
Datalog is a declarative logic programming language. While it is syntactically a subset of Prolog, Datalog generally uses a bottom-up rather than top-down evaluation model. This difference yields significantly different behavior and properties from Prolog. It is often used as a query language for deductive databases. Datalog has been applied to problems in data integration, networking, program analysis, and more.
Hibernate ORM is an object–relational mapping tool for the Java programming language. It provides a framework for mapping an object-oriented domain model to a relational database. Hibernate handles object–relational impedance mismatch problems by replacing direct, persistent database accesses with high-level object handling functions.

MonetDB is an open-source column-oriented relational database management system (RDBMS) originally developed at the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) in the Netherlands. It is designed to provide high performance on complex queries against large databases, such as combining tables with hundreds of columns and millions of rows. MonetDB has been applied in high-performance applications for online analytical processing, data mining, geographic information system (GIS), Resource Description Framework (RDF), text retrieval and sequence alignment processing.
Object–relational impedance mismatch is a set of difficulties going between data in relational data stores and data in domain-driven object models. Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) is the standard method for storing data in a dedicated database, while object-oriented (OO) programming is the default method for business-centric design in programming languages. The problem lies in neither relational databases nor OO programming, but in the conceptual difficulty mapping between the two logic models. Both logical models are differently implementable using database servers, programming languages, design patterns, or other technologies. Issues range from application to enterprise scale, whenever stored relational data is used in domain-driven object models, and vice versa. Object-oriented data stores can trade this problem for other implementation difficulties.
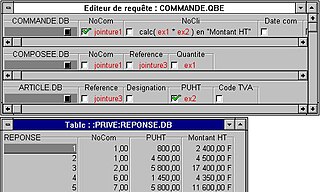
Query by Example (QBE) is a database query language for relational databases. It was devised by Moshé M. Zloof at IBM Research during the mid-1970s, in parallel to the development of SQL. It is the first graphical query language, using visual tables where the user would enter commands, example elements and conditions. Many graphical front-ends for databases use the ideas from QBE today. Originally limited only for the purpose of retrieving data, QBE was later extended to allow other operations, such as inserts, deletes and updates, as well as creation of temporary tables.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to software engineering.

JADE is a proprietary object-oriented software development and deployment platform product from the New Zealand-based Jade Software Corporation, first released in 1996. It consists of the JADE programming language, Integrated development environment and debugger, integrated application server and object database management system.
Semmle Inc is a code-analysis platform; Semmle was acquired by GitHub on 18 September 2019 for an undisclosed amount. Semmle's LGTM technology automates code review, tracks developer contributions, and flags software security issues. The LGTM platform leverages the CodeQL query engine to perform semantic analysis on software code bases. GitHub aims to integrate Semmle technology to provide continuous vulnerability detection services. In November 2019, use of CodeQL was made free for research and open source. CodeQL either shares a direct pedigree with .QL (dot-que-ell), which derives from the Datalog family tree, or is an evolution of similar technology.

db4o was an embeddable open-source object database for Java and .NET developers. It was developed, commercially licensed and supported by Actian. In October 2014, Actian declined to continue to actively pursue and promote the commercial db4o product offering for new customers.
Apache Empire-db is a Java library that provides a high level object-oriented API for accessing relational database management systems (RDBMS) through JDBC. Apache Empire-db is open source and provided under the Apache License 2.0 from the Apache Software Foundation.
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application programming interface (API) for the Java programming language which defines how a client may access a database. It is a Java-based data access technology used for Java database connectivity. It is part of the Java Standard Edition platform, from Oracle Corporation. It provides methods to query and update data in a database, and is oriented toward relational databases. A JDBC-to-ODBC bridge enables connections to any ODBC-accessible data source in the Java virtual machine (JVM) host environment.

TypeDB is an open-source, distributed database management system that relies on a user-defined type system to model, manage, and query data.







