
The San Andreas Fault is a continental right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly 1,200 kilometers (750 mi) through the U.S. state of California. It forms part of the tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. Traditionally, for scientific purposes, the fault has been classified into three main segments, each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The average slip rate along the entire fault ranges from 20 to 35 mm per year.

The 1994 Northridge earthquake was a moment magnitude 6.7, blind thrust earthquake that occurred on January 17, 1994, at 4:30:55 a.m. PST in the San Fernando Valley region of the City of Los Angeles. The quake had a duration of approximately 10–20 seconds, and its peak ground acceleration of 1.82 g was the highest ever instrumentally recorded in an urban area in North America. Shaking was felt as far away as San Diego, Turlock, Las Vegas, Richfield, Phoenix, and Ensenada. The peak ground velocity at the Rinaldi Receiving Station was 183 cm/s, the fastest ever recorded.

Parkfield is an unincorporated community in Monterey County, California. It is located on Little Cholame Creek 21 miles (34 km) east of Bradley, at an elevation of 1,529 feet (466 m). As of 2007, road signs announce the population as 18.

The Hayward Fault Zone is a right-lateral strike-slip geologic fault zone capable of generating destructive earthquakes. The fault was first named in the Lawson Report of the 1906 San Francisco Earthquake in recognition of its involvement in the earthquake of 1868. This fault is about 119 km (74 mi) long, situated mainly along the western base of the hills on the east side of San Francisco Bay. It runs through densely populated areas, including Richmond, El Cerrito, Berkeley, Oakland, San Leandro, Castro Valley, Hayward, Union City, Fremont, and San Jose.

The Cascadia subduction zone is a 960 km (600 mi) fault at a convergent plate boundary, about 110–160 km (70–100 mi) off the Pacific coast, that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is capable of producing 9.0+ magnitude earthquakes and tsunamis that could reach 30 m (98 ft). The Oregon Department of Emergency Management estimates shaking would last 5–7 minutes along the coast, with strength and intensity decreasing further from the epicenter. It is a very long, sloping subduction zone where the Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates move to the east and slide below the much larger mostly continental North American Plate. The zone varies in width and lies offshore beginning near Cape Mendocino, Northern California, passing through Oregon and Washington, and terminating at about Vancouver Island in British Columbia.

The Newport–Inglewood Fault is a right-lateral strike-slip fault in Southern California. The fault extends for 47 mi (76 km) from Culver City southeast through Inglewood and other coastal communities to Newport Beach at which point the fault extends east-southeast into the Pacific Ocean where it is known as the Rose Canyon Fault. The fault can be inferred on the Earth's surface as passing along and through a line of hills extending from Signal Hill to Culver City. The fault has a slip rate of approximately 0.6 mm (0.024 in)/year and is predicted to be capable of a 6.0–7.4 magnitude earthquake on the moment magnitude scale. A 2017 study concluded that, together, the Newport–Inglewood Fault and Rose Canyon Fault could produce an earthquake of 7.3 or 7.4 magnitude.

10.5: Apocalypse is a 2006 television miniseries written and directed by John Lafia. A sequel to 2004's 10.5, the show follows a series of catastrophic seismic disasters including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and sinkholes, all triggered by an apocalyptic earthquake. The series was produced in Canada. It received primarily negative reviews.

The Calaveras Fault is a major branch of the San Andreas Fault System that is located in northern California in the San Francisco Bay Area. Activity on the different segments of the fault includes moderate and large earthquakes as well as aseismic creep. The last large event was the magnitude 6.2 1984 Morgan Hill event. The most recent moderate earthquakes were the magnitude 5.1 event on 25 October 2022, and the magnitude 5.6 2007 Alum Rock event.

The 2008 Chino Hills earthquake occurred at 11:42:15 am PDT on July 29 in Southern California. The epicenter of the magnitude 5.4 earthquake was in Chino Hills, c. 28 miles (45 km) east-southeast of downtown Los Angeles. Movement on an oblique-slip fault resulted in a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong). Though there were no deaths, eight people were injured, and it caused considerable damage in numerous structures throughout the area and caused some amusement park facilities to shut down their rides. The earthquake led to increased discussion regarding the possibility of a stronger earthquake in the future.
The 2007 Alum Rock earthquake occurred on in Alum Rock Park in San Jose, in the U.S. state of California. It measured 5.6 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong). The event was then the largest in the San Francisco Bay Area since the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake, which measured 6.9 on the moment magnitude scale, but was later surpassed by the 2014 South Napa earthquake. Ground shaking from the Alum Rock quake reached San Francisco and Oakland and other points further north. Sixty thousand felt reports existed far beyond Santa Rosa, as far north as Eugene, Oregon.
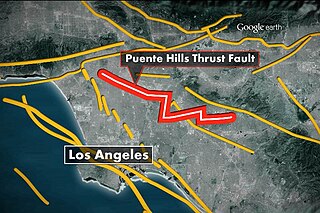
The Puente Hills Fault is an active geological fault that is located in the Los Angeles Basin in California. The thrust fault was discovered in 1999 and runs about 40 km (25 mi) in three discrete sections from the Puente Hills region in the southeast to just south of Griffith Park in the northwest. The fault is known as a blind thrust fault, as the fault plane does not extend to the surface. Large earthquakes on the fault are relatively infrequent but computer modeling has indicated that a major event could have substantial impact in the Los Angeles area. The fault is now thought to be responsible for one moderate earthquake in 1987 and another light event that took place in 2010, with the former causing considerable damage and deaths.

The 2010 Baja California earthquake occurred on April 4 with a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The shock originated at south of Guadalupe Victoria, Baja California, Mexico.
Seismicity of the New York City area is relatively low. New York is less seismically active than California because it is far from any plate boundaries. Large and damaging intraplate earthquakes are relatively rare but when they do occur in the northeastern United States the areas affected by them are much larger than for earthquakes of similar magnitude on the West Coast. The largest known earthquake in the greater New York City area occurred in 1884, probably somewhere between Brooklyn and Sandy Hook, and had a magnitude of approximately 5. The New York quakes in 2023 and 2024 were shallow quakes.
Shoreline Fault is a 25 km long vertical strike-slip fault discovered in 2008 that lies less than a mile from the Diablo Canyon Nuclear Power Plant in California. It is thought to be able to produce quakes up to 6.8 magnitude. The San Luis Obispo County Board of Supervisors claims that it may potentially pose a threat to the nuclear plant despite the plant's operator, Pacific Gas and Electric, claiming that the facility is able to withstand a 7.5 magnitude quake.
Diablo Canyon (Nuclear) Power Plant, located in San Luis Obispo County California, was originally designed to withstand a 6.75 magnitude earthquake from four faults, including the nearby San Andreas and Hosgri faults, but was later upgraded to withstand a 7.5 magnitude quake. It has redundant seismic monitoring and a safety system designed to shut it down promptly in the event of significant ground motion.

San Andreas is a 2015 American disaster film directed by Brad Peyton and written by Carlton Cuse, with Andre Fabrizio and Jeremy Passmore receiving story credit. The film stars Dwayne Johnson, in the lead role, Carla Gugino, Alexandra Daddario, Ioan Gruffudd, Archie Panjabi and Paul Giamatti. Its plot centers on a massive earthquake caused by the San Andreas Fault, devastating the West Coast of the United States.

The 2014 South Napa earthquake occurred in the North San Francisco Bay Area on August 24 at . At 6.0 on the moment magnitude scale and with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), the event was the largest in the San Francisco Bay Area since the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake. The epicenter of the earthquake was located to the south of Napa and to the northwest of American Canyon on the West Napa Fault.
The 2016 Oklahoma earthquake occurred on September 3, 2016 near Pawnee, Oklahoma. Measuring 5.8 on the moment magnitude scale, it is the strongest in state history. At 5.8 magnitude, this ties it with the 2011 Virginia earthquake, which was determined after it struck to be the most powerful quake in the eastern United States in the preceding 70 years.
The 2019 Ridgecrest earthquakes of July 4 and 5 occurred north and northeast of the town of Ridgecrest, California located in Kern County and west of Searles Valley. They included three initial main shocks of magnitudes 6.4, 5.4, and 7.1, and many perceptible aftershocks, mainly within the area of the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake. Eleven months later, a Mw 5.5 aftershock took place to the east of Ridgecrest. The first main shock occurred on Thursday, July 4 at 10:33 a.m. PDT, approximately 18 km (11.2 mi) ENE of Ridgecrest, and 13 km (8.1 mi) WSW of Trona, on a previously unnoticed NE-SW trending fault where it intersects the NW-SE trending Little Lake Fault Zone. This quake was preceded by several smaller earthquakes, and was followed by more than 1,400 detected aftershocks. The M 5.4 and M 7.1 quakes struck on Friday, July 5 at 4:08 a.m. and 8:19 p.m. PDT approximately 10 km (6 miles) to the northwest. The latter, now considered the mainshock, was the most powerful earthquake to occur in the state in 20 years. Subsequent aftershocks extended approximately 50 km (~30 miles) along the Little Lake Fault Zone.
The 2020 Sparta earthquake was a relatively uncommon intraplate earthquake that occurred near the small town of Sparta, North Carolina, on August 9, 2020 at 8:07 am local time. The earthquake had a moment magnitude of 5.1, and a shallow depth of 7.6 kilometers (4.7 mi). Shaking was reported throughout the Southern, Midwestern, and Northeastern United States. It was the strongest earthquake recorded in North Carolina in 104 years, the second-strongest in the state's history, and the largest to strike the East Coast since the 2011 Virginia earthquake.













