
Harlem–125th Street station is a commuter rail stop serving the Metro-North Railroad's Hudson, Harlem, and New Haven Lines. It is located at East 125th Street and Park Avenue in East Harlem, Manhattan, New York City. The station also serves as an important transfer point between the Metro-North trains and the New York City Subway's IRT Lexington Avenue Line for access to the Upper East Side of Manhattan. It is the only station besides Grand Central Terminal that serves all three lines east of the Hudson River. Trains leave for Grand Central Terminal, as well as to the Bronx and the northern suburbs, regularly.

The IRT Ninth Avenue Line, often called the Ninth Avenue Elevated or Ninth Avenue El, was the first elevated railway in New York City. It opened in July 1868 as the West Side and Yonkers Patent Railway, as an experimental single-track cable-powered elevated railway from Battery Place, at the south end of Manhattan Island, northward up Greenwich Street to Cortlandt Street. By 1879 the line was extended to the Harlem River at 155th Street. It was electrified and taken over by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company in 1903.
The IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line is a New York City Subway line. It is one of several lines that serves the A Division, stretching from South Ferry in Lower Manhattan north to Van Cortlandt Park–242nd Street in Riverdale, Bronx. The Brooklyn Branch, known as the Wall and William Streets Branch during construction, from the main line at Chambers Street southeast through the Clark Street Tunnel to Borough Hall in Downtown Brooklyn, is also part of the Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line. The IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line is the only line to have elevated stations in Manhattan, with two short stretches of elevated track at 125th Street and between Dyckman and 225th Streets.
The Lenox Avenue Line is a line of the New York City Subway, part of the A Division, mostly built as part of the first subway line. Located in Manhattan, New York City, it consists of six stations between Central Park North–110th Street and Harlem–148th Street, all of which are situated within the neighborhood of Harlem in Upper Manhattan.

The 125th Street station is a local station on the IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 125th Street and Broadway, at the border of the Manhattanville and Morningside Heights neighborhoods of Manhattan, it is served by the 1 train at all times.

The Harlem Line is an 82-mile (132 km) commuter rail line owned and operated by the Metro-North Railroad in the U.S. state of New York. It runs north from New York City to Wassaic, in eastern Dutchess County. The lower 53 miles (85 km) from Grand Central Terminal to Southeast, in Putnam County, is electrified with a third rail and has at least two tracks. The section north of Southeast is a non-electrified single-track line served by diesel locomotives. The diesel trains usually run as a shuttle on the northern end of the line, except for rush-hour express trains in the peak direction and one train in each direction on weekends.
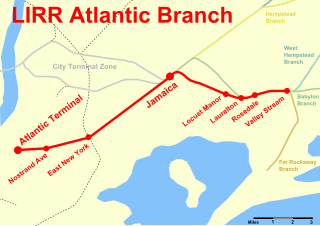
The Atlantic Branch is an electrified rail line owned and operated by the Long Island Rail Road in the U.S. state of New York. It is the only LIRR line with revenue passenger service in the borough of Brooklyn.
The BMT Fourth Avenue Line is a rapid transit line of the New York City Subway, mainly running under Fourth Avenue in Brooklyn. The line is served by the D, N, and R at all times; the R typically runs local, while the D and N run express during the day and local at night. During rush hours, select W and northbound Q trains also serve the line. Northbound D and N trains run local along the line after 6:45 p.m. during weekdays as well. The line was originally built by the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company and is now internally operated as part of the New York City Subway's B Division.

The 135th Street station is a station on the IRT Lenox Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 135th Street and Lenox Avenue in Harlem, it is served by the 2 and 3 trains at all times.

110th Street is a street in the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is commonly known as the boundary between Harlem and Central Park, along which it is known as Central Park North. In the west, between Central Park West/Frederick Douglass Boulevard and Riverside Drive, it is co-signed as Cathedral Parkway.

The 238th Street station is a local station on the IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 238th Street and Broadway in the Kingsbridge neighborhood of the Bronx, it is served by the 1 train at all times.

The 116th Street station is a station on the IRT Lenox Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 116th Street and Lenox Avenue in Harlem, it is served by the 2 and 3 trains at all times.

The Central Park North–110th Street station is a station on the IRT Lenox Avenue Line of the New York City Subway, located at the intersection of 110th Street and Lenox Avenue at the southern edge of Harlem, Manhattan. It is served by the 2 and 3 trains at all times.

86th Street is a major two-way street in the Upper East Side and Upper West Side of the New York City borough of Manhattan. It runs in two major sections: between East End and Fifth Avenue on the Upper East Side, and between Central Park West and Riverside Drive on the Upper West Side. The western segment feeds into the 86th Street transverse across Central Park, which connects to East 84th and 85th Streets on the eastern side.

The first regularly operated subway in New York City was opened on October 27, 1904, and was operated by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT). The early IRT system consisted of a single trunk line running south from 96th Street in Manhattan, with a southern branch to Brooklyn. North of 96th Street, the line had three northern branches in Upper Manhattan and the Bronx. The system had four tracks between Brooklyn Bridge–City Hall and 96th Street, allowing for local and express service. The original line and early extensions consisted of:

The Park Avenue main line, which consists of the Park Avenue Tunnel and the Park Avenue Viaduct, is a railroad line in the New York City borough of Manhattan, running entirely along Park Avenue. The line carries four tracks of the Metro-North Railroad as a tunnel from Grand Central Terminal at 42nd Street to a portal at 97th Street, where it rises to a viaduct north of 99th Street and continues over the Harlem River into the Bronx over the Park Avenue Bridge. During rush hours, Metro-North uses three of the four tracks in the peak direction.

The 86th Street Crosstown Line is a bus line in Manhattan, New York City, running mostly along 86th Street on the Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. Originally a streetcar line, it now comprises the M86 Select Bus Service bus line.

The 59th Street station is a never-opened station in the Park Avenue Tunnel used by the Metro-North Railroad for all of its trains. The station was built by the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad as part of an agreement with the government of New York City during the late 1870s, although trains never stopped here. The station is used as an emergency exit for the Metro-North Railroad.

The 72nd Street station is an abandoned station located in the Park Avenue Tunnel used by Metro-North Railroad for all of its trains. The station has two side platforms and is located in between 72nd Street and 73rd Street underneath Park Avenue on the Upper East Side of Manhattan. The station was built by the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad as part of an agreement with New York City.

The 86th Street station is an abandoned station located in the Park Avenue Tunnel used by Metro-North Railroad for all of its trains. The station was built by the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad as part of an agreement with New York City. The station was built during the late 19th century. It was located at Park Avenue and 86th Street on the Upper East Side of Manhattan.


















