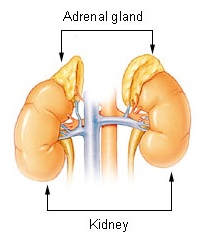
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.

The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of the adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. It is also a secondary site of androgen synthesis.
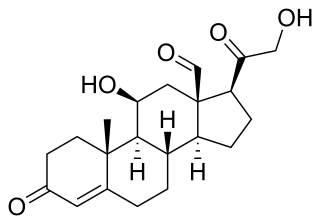
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a central role in the homeostatic regulation of blood pressure, plasma sodium (Na+), and potassium (K+) levels. It does so primarily by acting on the mineralocorticoid receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron. It influences the reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium (from and into the tubular fluids, respectively) of the kidney, thereby indirectly influencing water retention or loss, blood pressure, and blood volume. When dysregulated, aldosterone is pathogenic and contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular and kidney disease. Aldosterone has exactly the opposite function of the atrial natriuretic hormone secreted by the heart.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17α-hydroxylase deficiency is an uncommon form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) resulting from a mutation in the gene CYP17A1, which produces the enzyme 17α-hydroxylase. It causes decreased synthesis of cortisol and sex hormones, with resulting increase in mineralocorticoid production. Thus, common symptoms include mild cortisol deficiency, ambiguous genitalia in men or amenorrhea at puberty in women, and hypokalemic hypertension. However, partial (incomplete) deficiency often has inconsistent symptoms between patients, and affected women may be asymptomatic except for infertility.

5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes of 5α-reductase encoded by the genes SRD5A1, SRD5A2, and SRD5A3.

The zona glomerulosa of the adrenal gland is the most superficial layer of the adrenal cortex, lying directly beneath the renal capsule. Its cells are ovoid and arranged in clusters or arches.
11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzymes catalyze the conversion of inert 11 keto-products (cortisone) to active cortisol, or vice versa, thus regulating the access of glucocorticoids to the steroid receptors.

11-Deoxycorticosterone (DOC), or simply deoxycorticosterone, also known as 21-hydroxyprogesterone, as well as desoxycortone (INN), deoxycortone, and cortexone, is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland that possesses mineralocorticoid activity and acts as a precursor to aldosterone. It is an active (Na+-retaining) mineralocorticoid. As its names indicate, 11-deoxycorticosterone can be understood as the 21-hydroxy-variant of progesterone or as the 11-deoxy-variant of corticosterone.

Aldosterone synthase, also called steroid 18-hydroxylase, corticosterone 18-monooxygenase or P450C18, is a steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone and other steroids. The enzyme catalyzes sequential hydroxylations of the steroid angular methyl group at C18 after initial 11β-hydroxylation. It is encoded by the CYP11B2 gene in humans.

Steroid 11β-hydroxylase, also known as steroid 11β-monooxygenase, is a steroid hydroxylase found in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. Named officially the cytochrome P450 11B1, mitochondrial, it is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP11B1 gene. The enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of adrenal corticosteroids by catalyzing the addition of hydroxyl groups during oxidation reactions.
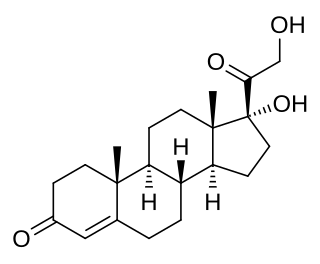
11-Deoxycortisol, also known as cortodoxone (INN), cortexolone as well as 17α,21-dihydroxyprogesterone or 17α,21-dihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is an endogenous glucocorticoid steroid hormone, and a metabolic intermediate toward cortisol. It was first described by Tadeusz Reichstein in 1938 as Substance S, thus has also been referred to as Reichstein's Substance S or Compound S.
Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism also describable as aldosterone synthase hyperactivity, is an autosomal dominant disorder in which the increase in aldosterone secretion produced by ACTH is no longer transient.
A steroidogenesis inhibitor, also known as a steroid biosynthesis inhibitor, is a type of drug which inhibits one or more of the enzymes that are involved in the process of steroidogenesis, the biosynthesis of endogenous steroids and steroid hormones. They may inhibit the production of cholesterol and other sterols, sex steroids such as androgens, estrogens, and progestogens, corticosteroids such as glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, and neurosteroids. They are used in the treatment of a variety of medical conditions that depend on endogenous steroids.

21-Deoxycortisol, also known as 11β,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone or as 11β,17α-dihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a naturally occurring, endogenous steroid related to cortisol (11β,17α,21-trihydroxyprogesterone) which is formed as a metabolite from 17α-hydroxyprogesterone via 11β-hydroxylase.

11β-Hydroxyprogesterone (11β-OHP), also known as 21-deoxycorticosterone, as well as 11β-hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a naturally occurring, endogenous steroid and derivative of progesterone. It is a potent mineralocorticoid. Syntheses of 11β-OHP from progesterone is catalyzed by the steroid 11β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) enzyme, and, to a lesser extent, by the aldosterone synthase enzyme (CYP11B2).
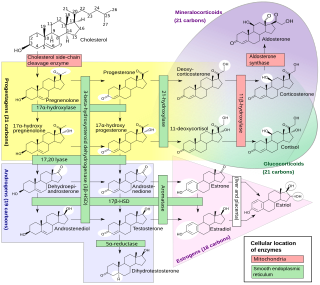
Steroidogenic enzymes are enzymes that are involved in steroidogenesis and steroid biosynthesis. They are responsible for the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones, including sex steroids and corticosteroids, as well as neurosteroids, from cholesterol. Steroidogenic enzymes are most highly expressed in classical steroidogenic tissues, such as the testis, ovary, and adrenal cortex, but are also present in other tissues in the body.

5α-Pregnan-17α-ol-3,20-dione, also known as 17α-hydroxy-dihydroprogesterone (17‐OH-DHP) is an endogenous steroid, a metabolite of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone.

5α-Pregnane-3α,17α-diol-20-one, also known as 17α-hydroxyallopregnanolone (17-OH-allo) is an endogenous steroid.
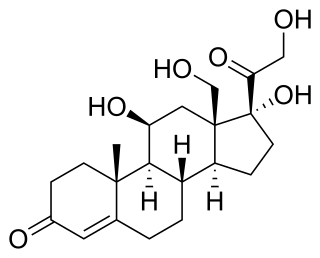
18-Hydroxycortisol is an endogenous steroid, a metabolite of cortisol.

18-Oxocortisol is an endogenous steroid, a metabolite of cortisol.

















