
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Western Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is 242,495 square kilometres (93,628 sq mi), with an estimated 2023 population of over 68 million people.
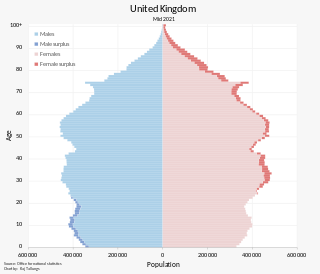
The population of the United Kingdom was estimated at over 67.0 million in 2020. It is the 21st most populated country in the world and has a population density of 270 people per square kilometre, with England having significantly greater density than Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland. Almost a third of the population lives in south east England, which is predominantly urban and suburban, with about 9 million in the capital city, London, whose population density is just over 5,200 per square kilometre.

The United Kingdom has four legal systems, each of which derives from a particular geographical area for a variety of historical reasons: English and Welsh law, Scots law, Northern Ireland law, and, since 2007, purely Welsh law as a result of Welsh devolution, with further calls for a Welsh justice system.

The administrative geography of the United Kingdom is complex, multi-layered and non-uniform. The United Kingdom, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe, consists of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. For local government in the United Kingdom, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each have their own system of administrative and geographic demarcation. Consequently, there is "no common stratum of administrative unit encompassing the United Kingdom".

A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194.

Religion in the United Kingdom, and in the countries that preceded it, has been dominated for over 1,400 years by various forms of Christianity, replacing Romano-British religions, Celtic and Anglo-Saxon paganism as the primary religion. Religious affiliations of United Kingdom citizens are recorded by regular surveys, the four major ones being the national decennial census, the Labour Force Survey, the British Social Attitudes survey and the European Social Survey.

Coincident full censuses have taken place in the different jurisdictions of the United Kingdom every ten years since 1801, with the exceptions of 1941, Ireland in 1921/Northern Ireland in 1931, and Scotland in 2021. In addition to providing detailed information about national demographics, the results of the census play an important part in the calculation of resource allocation to regional and local service providers by the UK government.
The United Kingdom Census of 1841 recorded the occupants of every United Kingdom household on the night of Sunday 6 June 1841. The enactment of the Population Act 1840 meant a new procedure was adopted for taking the 1841 census. It was described as the "first modern census" as it was the first to record information about every member of the household, and administered as a single event, under central control, rather than being devolved to a local level. It formed the model for all subsequent UK censuses, although each went on to refine and expand the questions asked of householders.

White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population was 49,997,686, 81.5% of Great Britain's total population. For the United Kingdom entirely, due to different reporting measures within Northern Ireland which includes all those who identified as British with those who identified as Irish, an amalgamated total of 52,320,080 including those who identified as White Irish in Great Britain is given making up 82.8% of the population.

Deborah Alcock was a late-Victorian author of historical fiction focused on religious, evangelical themes.

Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe. With an area of 209,331 km2 (80,823 sq mi), it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The island of Ireland, with an area 40 per cent that of Great Britain, is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago.

Since 1922, the United Kingdom comprises four constituent countries: England, Scotland, and Wales, as well as Northern Ireland. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom. Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the UK, refer to Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales as "regions". With regard to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales particularly, the descriptive name one uses "can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one's political preferences".
Claude Martin Blagden was an eminent Anglican bishop in the first half of the 20th century.
Francis Loraine Petre was a British civil servant in India and a military historian upon his retirement. He wrote a two-volume regimental history of the Norfolk Regiment, but is best known for his works on the Napoleonic Wars. The grandson of the 11th Baron Petre, he was educated at Oscott College and joined the Bar in 1880. He took the civil service exam and subsequently joined the Indian Civil Service. He retired as Commissioner of Allahabad in 1900.
The United Kingdom Census of 1881 recorded the people residing in every household on the night of Sunday 3 April 1881, and was the fifth of the UK censuses to include details of household members.

The 2021 United Kingdom census is the 23rd official census of the United Kingdom. Beginning in 1801, they have been recorded every 10 years. The decadal 2021 censuses of England, Wales, and Northern Ireland took place on 21 March 2021, and the census of Scotland took place 365 days later on 20 March 2022. The censuses were administered by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) in England and Wales, by the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) in Northern Ireland, and by the National Records of Scotland in Scotland. These were the first British censuses for which most of the data was gathered online. Two of them went ahead despite the COVID-19 pandemic, in part because the information obtained would assist government and public understanding of the pandemic's impact. The census-taking in Scotland was postponed, and took place in 2022 because of the pandemic.
The United Kingdom Census 1911 of 2 April 1911 was the 12th nationwide census conducted in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The total population of the United Kingdom was approximately 45,221,000, with 36,070,000 recorded in England and Wales, 4,761,000 in Scotland, and 4,390,000 in Ireland.
The United Kingdom Census 1931 was a census of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland that was carried out on 26 April 1931. A census in Northern Ireland had been taken in April 1926, so no census was taken there in 1931. The questions asked were similar to those in 1921, with the addition of a question about everyone's usual place of residence, as opposed to where they actually were on that night.

The 1841 Census of Ireland was a census that covered the whole island of Ireland. It was conducted as part of the broader 1841 United Kingdom census, which was the first modern census undertaken in the UK. The census is of particular note in Ireland as it was taken shortly before the Great Famine (1845-1852), which resulted in over 1 million deaths and spurred decades of mass emigration. The total population of the island in 1841 was estimated to be just under 8.2 million, which remains the highest recorded population Ireland has ever had. During this year, Ireland also held about 45% of the UK's population. As of the latest censuses - 2022 in the Republic of Ireland and 2021 in Northern Ireland - the island's population stood at just over 7 million, roughly 16% lower than its pre-famine peak.











