
The 1918 Irish general election was the part of the 1918 United Kingdom general election which took place in Ireland. It is a key moment in modern Irish history because it saw the overwhelming defeat of the moderate nationalist Irish Parliamentary Party (IPP), which had dominated the Irish political landscape since the 1880s, and a landslide victory for the radical Sinn Féin party. Sinn Féin had never previously stood in a general election, but had won six seats in by-elections in 1917–18. The party had vowed in its manifesto to establish an independent Irish Republic. In Ulster, however, the Unionist Party was the most successful party.

The 1906 United Kingdom general election was held from 12 January to 8 February 1906.

South Antrim is a parliamentary constituency in the United Kingdom House of Commons. The current MP is Paul Girvan of the Democratic Unionist Party.

Belfast South is a parliamentary constituency in the United Kingdom House of Commons. The current MP is Claire Hanna of the SDLP.

North Down is a parliamentary constituency in the United Kingdom House of Commons. The current MP is Stephen Farry of the Alliance Party. Farry was elected to the position in the 2019 general election, replacing the incumbent Sylvia Hermon. Hermon had held the position since being elected to it in the 2001 general election, but chose not to contest in 2019.

The Irish Unionist Alliance (IUA), also known as the Irish Unionist Party, Irish Unionists or simply the Unionists, was a unionist political party founded in Ireland in 1891 from a merger of the Irish Conservative Party and the Irish Loyal and Patriotic Union (ILPU) to oppose plans for home rule for Ireland within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The party was led for much of its existence by Colonel Edward James Saunderson and later by St John Brodrick, 1st Earl of Midleton. In total, eighty-six members of the House of Lords affiliated themselves with the Irish Unionist Alliance, although its broader membership among Irish voters outside Ulster was relatively small.
The Unionist Party was a pre-apartheid South African political party, which contested elections to the Union of South Africa parliament from the 1910 South African general election until its merger into the South African Party just before the 1921 South African general election.

General elections were held in South Africa on 15 September 1910 to elect the 121 members of the House of Assembly. They were the first general election after the Union of South Africa was created on 31 May 1910.

General elections were held in South Africa on 17 June 1924, electing 135 members of the House of Assembly. Considered a realigning election, rising discontent with the government of Jan Smuts led to the defeat of his government by a coalition of the pro-Afrikaner National Party and the South African Labour Party, a socialist party representing the interests of the white proletariat.

General elections were held in South Africa on 12 June 1929. The National Party under J. B. M. Hertzog won an outright majority in the House of Assembly. Hertzog had the opportunity to form a government without the aid of the Labour Party. In fact the Pact government continued, with two ministers from the Creswell Labour faction remaining in office. The National Party remained the dominant party, for its second consecutive term.

General elections were held in South Africa on 18 October 1961. They were the first general elections after South Africa became a republic following the 1960 South African referendum. The National Party under H. F. Verwoerd won a majority in the House of Assembly.

General elections were held in South Africa on 15 April 1953. The elections consolidated the position of the National Party under D. F. Malan, which won an absolute majority of the 156 elected seats in the House of Assembly, also receiving the most votes. Its first-time majority of the white electorate would be retained until the 1989 elections.

General elections were held in South Africa on 16 April 1958. The result was a victory for the National Party, now under the leadership of J. G. Strijdom after the retirement of D. F. Malan in 1954. The opposition United Party campaigned for the first time under De Villiers Graaff, who would remain party leader for two decades.
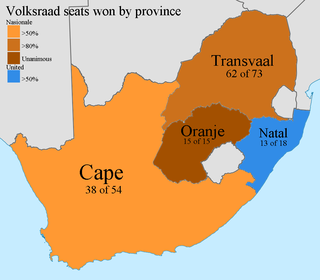
General elections were held in South Africa on 30 March 1966. The result was another comprehensive victory for the National Party under H. F. Verwoerd.

General elections were held in South Africa on 20 October 1915 to elect the 130 members of the House of Assembly. This was the second Union Parliament. The governing South African Party (SAP) of General Louis Botha emerged from the elections as the largest party, but did not receive an overall majority.

General elections were held in South Africa on 10 March 1920 to elect the 134 members of the House of Assembly. This was for the third Union Parliament.

General elections were held in South Africa on 17 May 1933 to elect the 150 members of the House of Assembly. The National Party won half the seats in the House, but the coalition with the South African Party continued.

General elections were held in South Africa on 18 May 1938 to elect the 150 members of the House of Assembly. The United Party won an absolute majority.

General elections were held in South Africa on 7 July 1943 to elect the 150 members of the House of Assembly. The United Party of Jan Smuts won an absolute majority.

The 1982 Northern Ireland Assembly elections were held on 20 October 1982 in an attempt to re-establish devolution and power-sharing in Northern Ireland. Although the Northern Ireland Assembly officially lasted until 1986 it met infrequently and achieved very little.
























