
Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning 10,990 square kilometres (4,240 sq mi) in area, it is the third largest island — after Cuba and Hispaniola — of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about 145 km (90 mi) south of Cuba, and 191 km (119 mi) west of Hispaniola ; the British Overseas Territory of the Cayman Islands lies 215 km (134 mi) to the north-west.

The Caribbean Island of Jamaica was initially inhabited in approximately 600 AD or 650 AD by the Redware people, often associated with redware pottery. By roughly 800 AD, a second wave of inhabitance occurred by the Arawak tribes, including the Tainos, prior to the arrival of Columbus in 1494. Early inhabitants of Jamaica named the land "Xaymaca", meaning "land of wood and water". The Spanish enslaved the Arawak, who were ravaged further by diseases that the Spanish brought with them. Early historians believe that by 1602, the Arawak-speaking Taino tribes were extinct. However, some of the Taino escaped into the forested mountains of the interior, where they mixed with runaway African slaves, and survived free from first Spanish, and then English, rule.

Politics in Jamaica takes place in the framework of a representative parliamentary democratic constitutional monarchy. The 1962 Constitution of Jamaica established a parliamentary system whose political and legal traditions closely follow those of the United Kingdom. As the head of state, King Charles III - on the advice of the Prime Minister of Jamaica - appoints a governor-general as his representative in Jamaica. The governor-general has a largely ceremonial role. Jamaica constitutes an independent Commonwealth realm.

Michael Norman Manley was a Jamaican politician who served as the fourth Prime Minister of Jamaica from 1972 to 1980 and from 1989 to 1992. Manley championed a democratic socialist program, and has been described as a populist. He remains one of Jamaica's most popular prime ministers.

The People's National Party (PNP) is a social-democratic political party in Jamaica, founded in 1938 by Norman Washington Manley who served as party president until his death in 1969. It holds 14 of the 63 seats in the House of Representatives, as 96 of the 227 local government divisions. The party is democratic socialist by constitution.

Percival Noel James Patterson,, popularly known as P.J. Patterson, is a Jamaican former politician who served as the sixth Prime Minister of Jamaica from 1992 to 2006. He served in office for 14 years, making him the longest-serving prime minister in Jamaica's history. He was the leader of the People's National Party from 1992 to 2006.

Sir William Alexander Clarke Bustamante was a Jamaican politician and labour leader, who, in 1962, became the first prime minister of Jamaica.
The Jamaica Labour Party (JLP) is one of the two major political parties in Jamaica, the other being the People's National Party (PNP). While its name might suggest that it is a social democratic party, the JLP is actually a conservative party.

Edward Philip George Seaga was a Jamaican politician. He was the fifth Prime Minister of Jamaica, from 1980 to 1989, and the leader of the Jamaica Labour Party from 1974 to 2005. He served as leader of the opposition from 1974 to 1980, and again from 1989 until January 2005.

Portia Lucretia Simpson-Miller is a former Jamaican politician. She served as Prime Minister of Jamaica from March 2006 to September 2007 and again from 5 January 2012 to 3 March 2016. She was the leader of the People's National Party from 2005 to 2017 and the Leader of the Opposition twice, from 2007 to 2012 and from 2016 to 2017.

Juliet Cuthbert-Flynn is a Jamaican politician and retired track and field sprinter who competed in the 100 metres and 200 metres. As an athlete, Cuthbert-Flynn competed at four Olympic Games, winning two silver medals at the 1992 games held in Barcelona.
General elections were held in Jamaica on 3 September 2007. They had originally been scheduled for 27 August 2007 but were delayed due to Hurricane Dean. The preliminary results indicated a slim victory for the opposition Jamaican Labour Party (JLP) led by Bruce Golding, which grew by two seats from 31–29 to 33-27 after official recounts. The JLP defeated the People's National Party after eighteen years of unbroken governance.

General elections were held in Jamaica on 30 October 1980. The balance of power in the 60-seat Jamaican House of Representatives was dramatically-shifted. Prior to the vote, the People's National Party (PNP), led by Prime Minister Michael Manley, had a 47 to 13 majority over the Jamaica Labour Party (JLP), led by Edward Seaga. With the loss by 38 PNP incumbents to their JLP challengers, Seaga's party captured a 51 to 9 majority and Seaga replaced Manley as Prime Minister of Jamaica. Voter turnout was 87%.

General elections were held in Jamaica on 18 December 1997. The ruling People's National Party of Prime Minister P. J. Patterson won 50 of the 60 seats defeating the main opposition Jamaica Labour Party.

General elections were held in Jamaica on 29 December 2011. The elections were contested mainly between the nation's two major political parties, the governing Jamaica Labour Party (JLP), led by Andrew Holness, and the Portia Simpson-Miller-led opposition People's National Party (PNP). The result was a landslide victory for the PNP which won 42 of the 63 seats, a two-thirds majority.
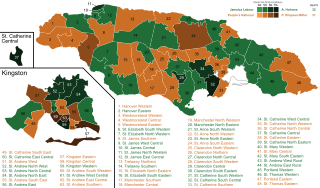
General elections were held in Jamaica on 25 February 2016. The elections were largely a contest between the governing People's National Party (PNP) and the opposition Jamaica Labour Party (JLP). The result was a narrow victory for the JLP, which won 32 of the 63 seats. One political commentator described the poll as "the closest election Jamaica has ever had".

Federal elections were held in the West Indies Federation for the first and only time on 25 March 1958. The result was a victory for the West Indies Federal Labour Party, which won 25 of the 45 seats in the House of Representatives.

The House of Assembly was the legislature of the British colony of Jamaica. It held its first meeting on 20 January 1664 at Spanish Town. As a result of the Morant Bay Rebellion, the Assembly voted to abolish self-governance in 1865. Jamaica then became a direct-ruled crown colony.
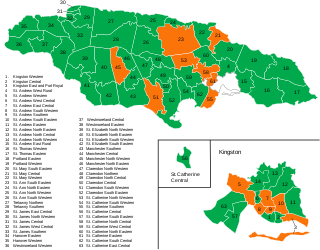
General elections were held in Jamaica on Thursday, 3 September 2020 to elect 63 members of Parliament. As the constitution stipulates a five-year parliamentary term, the next elections were not expected until between 25 February and 10 June 2021. However, Prime Minister Andrew Holness called early elections to ensure a united response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. On the advice of Holness, Governor General Patrick Allen dissolved Parliament on 13 August 2020.
The Jamaican political conflict is a long-standing feud between right-wing and left-wing elements in the country, often exploding into violence. The Jamaican Labour Party (JLP) and the People's National Party (PNP) have fought for control of the island for years and the rivalry has encouraged urban warfare in Kingston. Each side believes the other to be controlled by foreign elements, the JLP is said to be backed by the American Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and the PNP is said to have been backed by the Soviet Union and Cuba.















