
The war-responsibility trials in Finland were trials of the Finnish wartime leaders held responsible for "definitely influencing Finland in getting into a war with the Soviet Union and United Kingdom in 1941 or preventing peace" during the Continuation War, the Finnish term for their participation in the Second World War from 1941–1944. Unlike other World War II war-responsibility trials, the Finnish trials were not international. The trials were conducted from November 1945 through February 1946 by a special court consisting of the presidents of the Supreme Court of Finland, the Supreme Administrative Court of Finland, a professor from the University of Helsinki and twelve MPs appointed by the Parliament of Finland. The accused were convicted and were imprisoned until they were eventually paroled and then pardoned.

Varsinais-Suomi is one of the 13 electoral districts of the Parliament of Finland, the national legislature of Finland. The district was established as Turku and Pori Province South in 1907 when the Diet of Finland was replaced by the Parliament of Finland. It was renamed Varsinais-Suomi in 1997. It is conterminous with the region of Southwest Finland. The district currently elects 17 of the 200 members of the Parliament of Finland using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 parliamentary election it had 398,903 registered electors.

Central Finland is one of the 13 electoral districts of the Parliament of Finland, the national legislature of Finland. The district was established as Vaasa Province East in 1907 when the Diet of Finland was replaced by the Parliament of Finland. It was renamed Central Finland Province in 1960 and Central Finland in 1997. It is conterminous with the region of Central Finland. The district currently elects 10 of the 200 members of the Parliament of Finland using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 parliamentary election it had 226,335 registered electors.
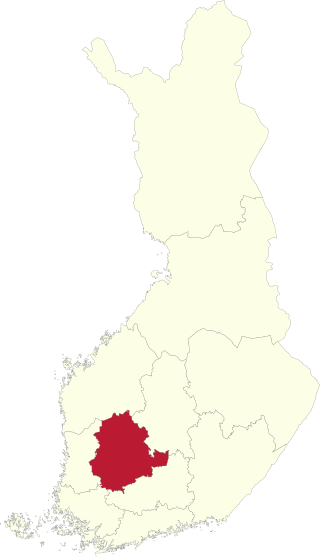
Pirkanmaa is one of the 13 electoral districts of the Parliament of Finland, the national legislature of Finland. The district was established as Häme Province North in 1907 when the Diet of Finland was replaced by the Parliament of Finland. It was renamed Pirkanmaa in 1997. It is conterminous with the region of Pirkanmaa. The district currently elects 20 of the 200 members of the Parliament of Finland using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 parliamentary election it had 437,155 registered electors.

Satakunta is one of the 13 electoral districts of the Parliament of Finland, the national legislature of Finland. The district was established as Turku and Pori Province North in 1907 when the Diet of Finland was replaced by the Parliament of Finland. It was renamed Satakunta in 1997. It is conterminous with the region of Satakunta. The district currently elects eight of the 200 members of the Parliament of Finland using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 parliamentary election it had 176,653 registered electors.

Häme is one of the 13 electoral districts of the Parliament of Finland, the national legislature of Finland. The district was established as Häme Province South in 1907 when the Diet of Finland was replaced by the Parliament of Finland. It was renamed Häme in 1997. It is conterminous with the regions of Kanta-Häme and Päijät-Häme. The district currently elects 14 of the 200 members of the Parliament of Finland using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 parliamentary election it had 310,047 registered electors.

Uusimaa is one of the 13 electoral districts of the Parliament of Finland, the national legislature of Finland. The district was established as Uusimaa Province in 1907 when the Diet of Finland was replaced by the Parliament of Finland. It was renamed Uusimaa in 1997. It is conterminous with the region of Uusimaa but excludes the municipality of Helsinki which has its own electoral district. The district currently elects 37 of the 200 members of the Parliament of Finland using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 parliamentary election it had 801,205 registered electors.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 6 and 7 July 1958. The communist Finnish People's Democratic League emerged as the largest party, but was unable to form a government.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 1 and 2 October 1930. The Social Democratic Party emerged as the largest in Parliament with 66 of the 200 seats. Voter turnout was 65.9%.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 1 and 2 July 1936. Following the election Prime Minister Toivo Mikael Kivimäki of the National Progressive Party was defeated in a confidence vote in September 1936 and resigned in October. Kyösti Kallio of the Agrarian League formed a centrist minority government after Pehr Evind Svinhufvud refused to allow the Social Democrats to join the government. After Svinhufvud's defeat in the February 1937 presidential election, Kallio took office as the new President in March 1937, and he allowed the Social Democrats, Agrarians and Progressives to form the first centre-left or "red soil" Finnish government. Aimo Cajander (Progressive) became Prime Minister, although the real strong men of the government were Finance Minister Väinö Tanner and Defence Minister Juho Niukkanen (Agrarian).
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 1 and 2 July 1939. Following the elections, the National Progressive Party-led government of Aimo Cajander continued in office. However, he was replaced by Risto Ryti's Progressive-led war government in December 1939.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 1 and 2 July 1948.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 1 and 2 July 1951.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 7 and 8 March 1954.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 4 and 5 February 1962.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 20 and 21 March 1966. The Social Democratic Party (SDP) overtook the Centre Party as the largest faction in Parliament. Rafael Paasio of the SDP subsequently became Prime Minister and formed a popular front government consisting of the SDP, the Centre Party, the People's Democratic League (SKDL), and the Social Democratic Union of Workers and Smallholders (TPSL) in May 1966.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 15 and 16 March 1970.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 21 and 22 September 1975.
Two-stage presidential elections were held in Finland in 1925. On 15 and 16 January the public elected presidential electors to an electoral college. They in turn elected the president. The result was a victory for Lauri Kristian Relander, who won on the third ballot. The turnout for the popular vote was just 39.7%. The outgoing president, K.J. Ståhlberg, had refused to seek a second term. According to the late Agrarian and Centrist politician, Johannes Virolainen, he stepped down after one term because he believed that an incumbent president would be too likely to win re-election. President Ståhlberg claimed that he had already completed his political service to Finland as president. Moreover, he wanted to step down because many right-wing Finns opposed him. According to Pentti Virrankoski, a Finnish historian, President Ståhlberg hoped that his retirement would advance parliamentary politics in Finland. Ståhlberg's party, the Progressives, chose Risto Ryti, the governor of the Bank of Finland, as their presidential candidate. The Agrarians only chose Lauri Kristian Relander as their presidential candidate in early February 1925. The National Coalitioners originally chose former Regent and Prime Minister Pehr Evind Svinhufvud as their presidential candidate, but before the presidential electors met, they replaced Svinhufvud with Hugo Suolahti, an academician working as the rector (principal) of the University of Helsinki. Relander surprised many politicians by defeating Ryti as a dark-horse presidential candidate, although he had served as the Speaker of the Finnish Parliament, and as Governor of the Province of Viipuri. Ståhlberg had quietly favoured Ryti as his successor, because he considered Ryti a principled and unselfish politician. He was disappointed with Relander's victory, and told one of his daughters that if he had known beforehand that Relander would be elected as his successor, he would have considered seeking a second term.

Early and indirect presidential elections were held in Finland in 1940 after President Kyösti Kallio resigned on 27 November following a stroke on 27 August. The 1937 electoral college was recalled and elected Prime Minister Risto Ryti, who received 288 of the 300 votes. Most other Finnish politicians considered Ryti a principled, unselfish, intelligent and patriotic man, who could lead Finland effectively enough during World War II. His leadership qualities had been tested already during the Winter War. Also the outgoing President Kallio considered him the best available presidential candidate. In early December 1940, the Soviet Foreign Minister, Vyacheslav Molotov, interfered with the Finnish presidential elections by claiming to the Finnish Ambassador to the Soviet Union, Juho Kusti Paasikivi, that if potential presidential candidates such as Marshal Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim, former President Pehr Evind Svinhufvud, or former Prime Minister Toivo Mikael Kivimäki were elected President, the Soviet government would consider Finland unwilling to fulfill its peace treaty with the Soviet Union. Due to the lingering threat of another war and the Karelian refugees' dispersal throughout Finland, regular presidential elections were cancelled, and instead the 1937 presidential electors were summoned to elect the President. Under these tense political circumstances, Ryti had no problem winning these exceptional presidential elections by a landslide. The same day, former president Kallio died.
















