
Brazilian Integralism was a political movement in Brazil, created in October 1932. Founded and led by Plínio Salgado, a literary figure who was somewhat famous for his participation in the 1922 Modern Art Week. The movement had adopted some characteristics of European mass movements of those times, specifically of Italian fascism, but distancing itself from Nazism because Salgado himself did not support racism. He believed that every person of every race should unite under the Integralist flag. Despite the movement's slogan "Union of all races and all peoples", members and leaders like Gustavo Barroso held anti-Semitic views. The name of the party created to support its doctrine was Brazilian Integralist Action. The reference to Integralism mirrored a traditionalist movement in Portugal, the Lusitanian Integralism. For its symbol, the AIB used a flag with a white disk on a royal blue background, with an uppercase sigma (Σ) in its center.

The president of Brazil, officially the president of the Federative Republic of Brazil or simply the President of the Republic, is the head of state and head of government of Brazil. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the Brazilian Armed Forces.

The military dictatorship in Brazil was established on 1 April 1964, after a coup d'état by the Brazilian Armed Forces, with support from the United States government, against President João Goulart. The Brazilian dictatorship lasted for 21 years, until 15 March 1985. The military coup was fomented by José de Magalhães Pinto, Adhemar de Barros, and Carlos Lacerda, then governors of the states of Minas Gerais, São Paulo, and Guanabara, respectively. The coup was planned and executed by the most senior commanders of the Brazilian Army and received the support of almost all high-ranking members of the military, along with conservative elements in society, like the Catholic Church and anti-communist civil movements among the Brazilian middle and upper classes. Internationally, it was supported by the US State Department through its embassy in Brasilia.

Augusto Hamann Rademaker Grünewald was a Brazilian admiral, of German and Danish descent, in the Brazilian Navy. Rademaker was one of the leaders of the Military Junta that ruled Brazil between the illness of Artur da Costa e Silva in August 1969 and the investiture ceremony of Emílio Garrastazu Médici in October of that same year, elected by fellow officer generals and confirmed by the Congress. In the same occasions Rademaker was picked and "elected" as vice president for the same term as Medici's (1969–1974).

Emílio Garrastazu Médici was a Brazilian military leader and politician who was the president of Brazil from 1969 to 1974. His authoritarian rule marked the apex of the Brazilian military regime.

Geraldo José Rodrigues Alckmin Filho is a Brazilian politician who has served as the 26th vice president of Brazil since 1 January 2023. He previously served as the Governor of São Paulo from 2001 to 2006, and then again from 2011 to 2018, the longest term served in that state since the end of the Military dictatorship in Brazil. He was the Brazilian Social Democracy Party (PSDB) presidential nominee for the 2018 Brazilian presidential election, when he finished in fourth place, as well for the 2006 Brazilian presidential election, when he came in second place, losing in the runoff to then president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva.

A Military Junta or Junta Militar ruled Brazil from August 31 to October 30, 1969, between the sudden illness of President Artur da Costa e Silva and the swearing-in of Emílio Garrastazu Médici as his successor.

Artur da Costa e Silva was a Brazilian Army Marshal and the second president of the Brazilian military government that came to power after the 1964 coup d'état. He reached the rank of Marshal of the Brazilian Army, and held the post of Minister of War in the military government of President Castelo Branco.
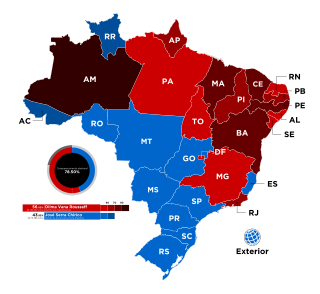
General elections were held in Brazil on 3 October 2010 to elect the president, National Congress and state governors. As no presidential candidate received more than 50% in the first round of voting, a second round was held on 31 October to choose a successor to Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva of the Workers' Party (PT), who was constitutionally ineligible to run for a third term as he has already served two terms after winning the elections in 2002 and being re-elected in 2006.

The Ato Institucional Número Cinco – AI-5 was the fifth of seventeen major decrees issued by the military dictatorship in the years following the 1964 coup d'état in Brazil. Institutional Acts were the highest form of legislation during the military regime, given that they overruled even the highly authoritarian Constitution, and were enforced without the possibility of judicial review. They were issued on behalf of the "Supreme Command of the Revolution".
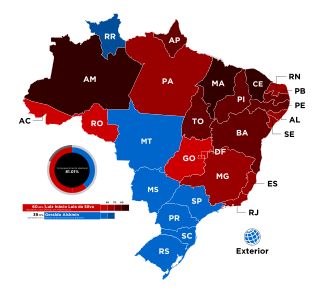
General elections were held in Brazil on 1 October 2006 to elect the president, National Congress and state governors, with a second round of the presidential election on 29 October as no candidate received more than 50% of the vote in the first round.

The National Renewal Alliance was a far-right political party that existed in Brazil between 1966 and 1979. It was the official party of the military dictatorship that ruled Brazil from 1964 to 1985.

Indirect presidential elections were held in Brazil on 15 October 1978. The opposition Brazilian Democratic Movement (MDB) chose an anti-candidate to fill the spot and denounce the restrictive democracy. The MDB chose General Euler Bentes Monteiro to run against João Figueiredo from the National Renewal Alliance Party. Figueiredo won with 355 electoral votes against 226 votes for Euler Monteiro.

Indirect presidential elections were held in Brazil on 15 January 1974. They were the fourth presidential elections held under the military government and were carried out through an electoral college.

Indirect presidential elections were held in Brazil on 3 October 1966 through an electoral college system. It was the second election during the Brazilian military government, with Artur da Costa e Silva as the sole candidate. Costa e Silva was elected with 295 votes from the ruling National Renewal Alliance Party (ARENA).

Events in the year 1969 in Brazil.

General elections were held in Brazil on 7 October 2018 to elect the president, National Congress and state governors. As no candidate in the presidential election received more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a runoff round was held on 28 October.
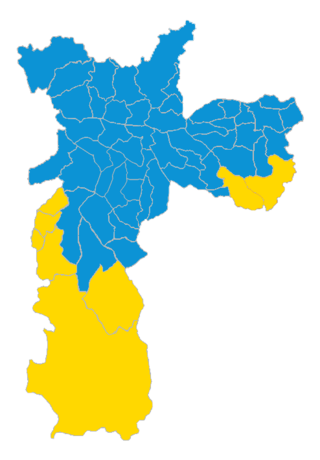
The 2020 São Paulo municipal election took place in the city of São Paulo, Brazil, with the first round taking place on 15 November 2020 and the second round taking place on 29 November 2020. Voters voted to elect the Mayor, the Vice Mayor and 55 city councillors for the administration of the city. The result was a 2nd round victory for incumbent Mayor Bruno Covas of the Brazilian Social Democratic Party (PSDB), winning 3,169,121 votes and a share of 59,38% of the popular vote, defeating political activist Guilherme Boulos of the Socialism and Liberty Party (PSOL), who took 2,168,109 votes and a share of 40.62% of the popular vote.

Municipal elections took place in Brazil on 15 November 2020. Electors chose Mayors, Vice-Mayors and City Councillors of all 5,568 cities of the country. The partisan conventions took place between 31 August and 16 September. They were the first elections since Bolsonaro's election as President.
General elections will be held in Brazil on 4 October 2026 to elect the president, vice president, members of the National Congress, the governors, vice governors, and legislative assemblies of all federative units, and the district council of Fernando de Noronha. If no candidate for president—or for governor in some states—received more than half of the valid votes in the first round, a runoff election for these offices will be held on 31 October.

















