
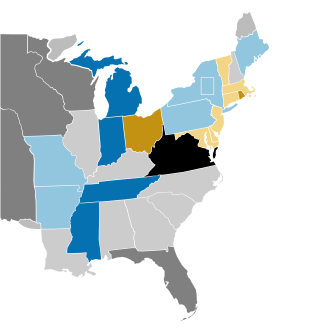
The 1972 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of Republican President Richard Nixon. Despite Nixon's landslide victory, Democrats increased their majority by two seats. The Democrats picked up open seats in Kentucky and South Dakota, and defeated four incumbent senators: Gordon Allott of Colorado, J. Caleb Boggs of Delaware, Jack Miller of Iowa, and Margaret Chase Smith of Maine. The Republicans picked up open seats in New Mexico, North Carolina, and Oklahoma, and defeated one incumbent, William B. Spong Jr. of Virginia.

The 1960 United States Senate elections coincided with the election of John F. Kennedy as president on November 8, 1960. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. A special election was also held on June 28, 1960, for a mid-term vacancy in North Dakota. The Republicans gained two seats at the expense of the Democrats. However, Republican Senator-elect Edwin Keith Thomson of Wyoming died December 9, 1960, and was replaced by appointee Democratic John J. Hickey at the beginning of the Congress, reducing Republican gains to one seat.

The 1916 United States Senate elections were elections that coincided with the re-election of President Woodrow Wilson. This was the first election since the enactment of the Seventeenth Amendment that all 32 Class 1 Senators were selected by direct or popular elections instead of state legislatures. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. Republicans gained a net of two seats from the Democrats.

The 2000 United States Senate election in Missouri was held on November 7, 2000, to select the next U.S. Senator from Missouri. Incumbent Republican Senator John Ashcroft ran for reelection to a second term, but he was defeated by Democratic Governor Mel Carnahan despite Carnahan's death in a plane crash three weeks before election day. Roger B. Wilson, the newly inaugurated Governor, appointed Mel Carnahan's widow Jean Carnahan to fill the seat. As of 2023, this is the first and only time a deceased person has won a U.S. Senate election.
The 1844–45 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with James K. Polk's election. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1844 and 1845, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1890–91 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1890 and 1891, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.
The 1842–43 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1842 and 1843, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.

The 1840–41 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1840 and 1841, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.
The 1832–33 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1832 and 1833, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1972 United States Senate election in Alabama was held on November 7, 1972.

The 1972 United States Senate election in Idaho took place on November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican Senator Leonard B. Jordan did not run for re-election. Republican U.S. Representative James A. McClure was elected to succeed him over Democrat Bud Davis.

The 1972 United States Senate special election in Vermont took place on January 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican Robert Stafford, appointed in September 1971 to fill the vacancy created by the death of Winston L. Prouty, successfully ran for election to the remainder of Prouty's term in the United States Senate. Stafford defeated Democratic candidate Randolph T. Major. Liberty Union candidate Bernie Sanders received 2% of the vote and was later elected to this seat in 2006 as an independent.

The 1972 United States Senate election in Oregon took place on November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican Senator Mark Hatfield was re-elected to a second term in office, defeating Democrat Wayne Morse.

The 1972 United States Senate election in Arkansas took place on November 7, 1972. Incumbent U.S. Senator John L. McClellan was re-elected to a sixth term in office, defeating U.S. Representative David Pryor in a hotly contested primary. In the general election, McClellan easily defeated Republican physician Wayne Babbitt. This was McClellan's final campaign; he died in his sleep in 1977. Pryor was elected Governor of Arkansas in 1974 and won the race to succeed McClellan in 1978.

The 1972 United States Senate election in Colorado took place on November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Gordon Allott ran for re-election to a fourth term, but was narrowly defeated by Democratic former State Representative Floyd Haskell. This would be the last time until 2008 that a Democrat was elected to the Class 2 Senate seat from Colorado.

The 1972 United States Senate election in Iowa took place on November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Jack Miller ran for re-election to a third term but was defeated by Democrat Dick Clark.
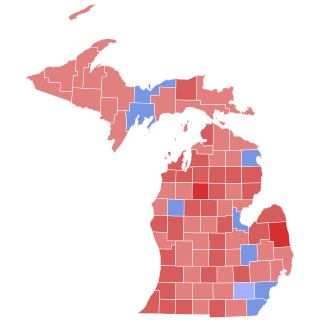
The 1972 United States Senate election in Michigan was held on November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator and Senate Minority Whip Robert P. Griffin ran for re-election to a second term, won reelection defeating the Democratic candidate, and Michigan Attorney General Frank J. Kelley by 6%. Despite President Richard Nixon’s landslide victory in Michigan and the rest of the country, Griffin’s margin of victory decreased from the previous election.

The 1974 United States Senate election in Illinois took place on November 5, 1974. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Adlai Stevenson III, who was first elected in a special election in 1970, was re-elected to a full term in office, defeating Republican George Burditt by a large margin of nearly 800,000 votes.

The 1974 United States Senate election in Kansas took place on November 5, 1974. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Bob Dole was narrowly re-elected to a second term in office.




















