| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1987 in Sri Lanka .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1987 in Sri Lanka .

The history of Sri Lanka is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions, comprising the areas of South Asia, Southeast Asia and Indian Ocean.

Sri Lankabhimanya Ranasinghe Premadasa was the third President of Sri Lanka from 2 January 1989 to 1 May 1993. Before that, he served as the prime minister in the government headed by J. R. Jayewardene from 6 February 1978 to 1 January 1989. He was awarded Sri Lanka's highest award to a civilian Sri Lankabhimanya in 1986 by President Junius Richard Jayewardene, the first to receive in Sri Lankan history.

Junius Richard Jayewardene, commonly abbreviated in Sri Lanka as J.R., was the leader of Sri Lanka from 1977 to 1989, serving as Prime Minister from 1977 to 1978 and as the second President of Sri Lanka from 1978 to 1989. He was a leader of the nationalist movement in Ceylon who served in a variety of cabinet positions in the decades following independence. A longtime member of the United National Party, he led it to a landslide victory in 1977 and served as Prime Minister for half a year before becoming the country's first executive president under an amended constitution.
The Indo-Sri Lanka Peace Accord was an accord signed in Colombo on 29 July 1987, between Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi and Sri Lankan President J. R. Jayewardene. The accord was expected to resolve the Sri Lankan Civil War by enabling the thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution of Sri Lanka and the Provincial Councils Act of 1987. Under the terms of the agreement, Colombo agreed to a devolution of power to the provinces, the Sri Lankan troops were to be withdrawn to their barracks in the north and the Tamil rebels were to surrender their arms.

Indian Peace Keeping Force (IPKF) was the Indian military contingent performing a peacekeeping operation in Sri Lanka between 1987 and 1990. It was formed under the mandate of the 1987 Indo-Sri Lankan Accord that aimed to end the Sri Lankan Civil War between Sri Lankan Tamil militant groups such as the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) and the Sri Lankan military.

The Eastern Province is one of the nine provinces of Sri Lanka, the first level administrative division of the country. The provinces have existed since the 19th century but did not have any legal status until 1987 when the 13th Amendment to the Constitution of Sri Lanka established provincial councils. Between 1988 and 2006 the province was temporarily merged with the Northern Province to form the North Eastern Province. The capital of the province is Trincomalee.

Black July was an anti-Tamil genocide that occurred in Sri Lanka during July 1983. The genocide was premeditated, and was finally triggered by a deadly ambush on 23 July 1983, which caused the death of 13 Sri Lanka Army soldiers, by the Tamil militant group Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). Although initially orchestrated by members of the ruling UNP, the genocide soon escalated into mass violence with significant public participation.
Eelam War I is the name given to the initial phase of the armed conflict between the government of Sri Lanka and the LTTE.
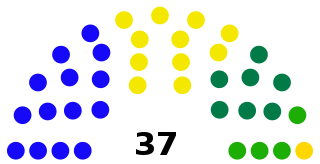
The Eastern Provincial Council is the provincial council for the Eastern Province in Sri Lanka. In accordance with the Sri Lankan constitution, EPC has legislative power over a variety of matters including agriculture, education, health, housing, local government, planning, road transport and social services. The constitution also gives it powers over police and land but successive central governments have refused to devolve these powers to the provinces. EPC has 37 members elected using the open list proportional representation system.
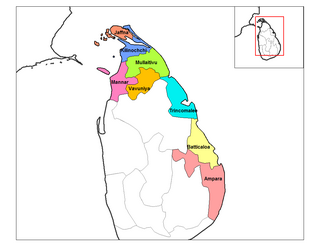
Provincial Council elections were held on 19 November 1988 to elect members to Sri Lanka’s North Eastern Provincial Council.
The 1987 grenade attack in the Sri Lankan Parliament is an attack that took place on August 18, 1987, when an assailant hurled two grenades into a room where Members of Parliament were meeting. The grenades bounced off the table at which Sri Lankan President J. R. Jayawardene and Prime Minister Ranasinghe Premadasa were sitting, and rolled away. A Member of Parliament and a ministry secretary were killed by the explosions.

The history of Sri Lanka from 1948 to the present is marked by the independence of the country through to Dominion and becoming a Republic. The main factor has been conflict and civil war regarding the status of minority Tamils.

Northern Provincial Council is the provincial council for the Northern Province in Sri Lanka. In accordance with the Sri Lankan constitution, NPC has legislative power over a variety of matters including agriculture, education, health, housing, local government, planning, road transport and social services. The constitution also gives it powers over police and land but successive central governments have refused to devolve these powers to the provinces. NPC has 38 members elected using the open list proportional representation system.
The Indian intervention in the Sri Lankan Civil War was the deployment of the Indian Peace Keeping Force in Sri Lanka intended to perform a peacekeeping role. The deployment followed the Indo-Sri Lankan Accord between India and Sri Lanka of 1987 which was intended to end the Sri Lankan Civil War between militant Sri Lankan Tamil nationalists, principally the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE), and the Sri Lankan military.
The Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution of Sri Lanka (13A) is amendment to the Constitution of Sri Lanka, passed in 1987, which created Provincial Councils in Sri Lanka.
Provincial governments of Sri Lanka are the devolved governments of the nine Provinces of Sri Lanka. In accordance with the Sri Lankan constitution, provinces have legislative power over a variety of matters including agriculture, education, health, housing, local government, planning, road transport and social services. The constitution also gives them powers over police and land but successive central governments have refused to devolve these powers to the provinces.
The following lists events that happened during 1985 in Sri Lanka.
The following lists events that happened during 1983 in Sri Lanka.

Sri Lanka–Turkey relations are the foreign relations between Sri Lanka and Turkey. Turkey has an embassy in Colombo since 2013. Sri Lanka has an embassy in Ankara since 2012.
Patriotic People's Armed troops was a militant organization in Sri Lanka. The organization was recognized as a military arm of the Marxist Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna, which was attempting to overthrow the government of Sri Lanka.