The Mars program was a series of uncrewed spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1973. The spacecraft were intended to explore Mars, and included flyby probes, landers and orbiters.
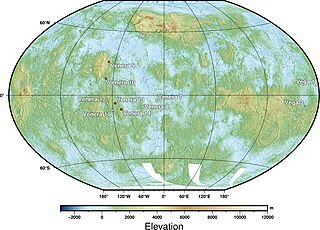
The Venera program was a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus.
Tyazhely Sputnik, also known by its development name as Venera 1VA No. 1, and in the West as Sputnik 7, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was intended to be the first spacecraft to explore Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit. In order to avoid acknowledging the failure, the Soviet government instead announced that the entire spacecraft, including the upper stage, was a test of a "Heavy Satellite" which would serve as a launch platform for future missions. This resulted in the upper stage being considered a separate spacecraft, from which the probe was "launched", on several subsequent missions.
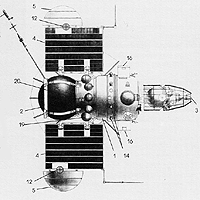
Venera 2MV-1 No.1, also known as Sputnik 19 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme.
Venera 2MV-1 No.2, also known as Sputnik 20 in the Western world, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the second of two Venera 2MV-1 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit. The previous mission, Venera 2MV-1 No.1, was launched several days earlier.

Mars 1, also known as 1962 Beta Nu 1, Mars 2MV-4 and Sputnik 23, was an automatic interplanetary station launched in the direction of Mars on November 1, 1962, the first of the Soviet Mars probe program, with the intent of flying by the planet at a distance of about 11,000 km (6,800 mi). It was designed to image the surface and send back data on cosmic radiation, micrometeoroid impacts and Mars' magnetic field, radiation environment, atmospheric structure, and possible organic compounds.
Mars 2MV-3 No.1 also known as Sputnik 24 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Mars program, and was intended to land on the surface of Mars. Due to a problem with the rocket which launched it, it did not depart low Earth orbit, and it decayed several days later. It was the only Mars 2MV-3 spacecraft to be launched.

S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation "Energia" is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. Its name is derived from the Russian word for energy and is also named for Sergei Pavlovich Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau and the driving force behind early Soviet accomplishments in space exploration.

Venera 3 was a Venera program space probe that was built and launched by the Soviet Union to explore the surface of Venus. It was launched on 16 November 1965 at 04:19 UTC from Baikonur, Kazakhstan, USSR. The probe comprised an entry probe, designed to enter the Venus atmosphere and parachute to the surface, and a carrier/flyby spacecraft, which carried the entry probe to Venus and also served as a communications relay for the entry probe.

Mars 1M was a series of two uncrewed spacecraft which were used in the first Soviet missions to explore Mars. They were the earliest missions of the Mars program. The Western media dubbed the spacecraft "Marsnik", a portmanteau of Mars and Sputnik.

The Soviet space program was the state space program of the Soviet Union, active from 1951 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Contrary to its American, European, and Chinese competitors, which had their programs run under single coordinating agencies, the Soviet space program was divided between several internally competing design bureaus led by Korolev, Kerimov, Keldysh, Yangel, Glushko, Chelomey, Makeyev, Chertok and Reshetnev. Several of these bureaus were subordinated to the Ministry of General Machine-Building. The Soviet space program served as an important marker of claims by the Soviet Union to its superpower status.
Venera 2MV-2 No.1, also known as Sputnik 21 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to make a flyby of Venus. Due to a problem with the rocket which launched it, it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the second Venera 2MV-2 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit.

The 3MV planetary probe is a designation for a common design used by early Soviet unmanned probes to Mars and Venus. It was an incremental improvement of earlier 2MV probes and was used for Zond 1, Zond 2 and Zond 3 missions to Mars as well as several Venera probes. It was standard practice of the Soviet space program to use standardized components as much as possible. All probes shared the same typical characteristics and differed usually in equipment necessary for specific missions. Each probe also incorporated improvements based on experience with earlier missions.

Mars 1M No.1, designated Mars 1960A by NASA analysts and dubbed Marsnik 1 by the Western media, was the first spacecraft launched as part of the Soviet Union's Mars programme. A Mars 1M spacecraft, it was intended for conducting flight testing system and to study the interplanetary environment between Earth and Mars, however it was lost in a launch failure before it could begin its mission.
Kosmos 167, or 4V-1 No.311, was a 1967 Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Venus. A spacecraft launched as part of the Venera programme, Kosmos 167 was intended to land on Venus but never departed low Earth orbit due to a launch failure.

The 4MV planetary probe is a designation for a common design used for Soviet unmanned probes to Mars and Venus.

The 2MV planetary probe is a designation for a common design used by early Soviet uncrewed probes to Mars and Venus.

The Mars-69/M-69 or 2M was the designation given to 2 Soviet Mars probes that were to be sent in 1969. Based on the Luna E-8 landers used for Luna 15-24, they were the first attempted Mars and Interplanetary Orbiters. The probes, however, were both destroyed in separate launches in early 1969.











