
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", or arenes, are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule.

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.
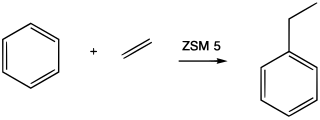
Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene. Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.

A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.

Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a yellow-orange salt with the formula [C5H5NH]+[CrO3Cl]−. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity. PCC offers the advantage of the selective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones, whereas many other reagents are less selective.

Oxalyl chloride is an organic chemical compound with the formula Cl−C(=O)−C(=O)−Cl. This colorless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacyl chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.
Fenton's reagent is a solution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and an iron catalyst (typically iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4). It is used to oxidize contaminants or waste water as part of an advanced oxidation process. Fenton's reagent can be used to destroy organic compounds such as trichloroethylene and tetrachloroethylene (perchloroethylene). It was developed in the 1890s by Henry John Horstman Fenton as an analytical reagent.
As the name suggests, a non-nucleophilic base is a sterically hindered organic base that is a poor nucleophile. Normal bases are also nucleophiles, but often chemists seek the proton-removing ability of a base without any other functions. Typical non-nucleophilic bases are bulky, such that protons can attach to the basic center but alkylation and complexation is inhibited.

A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications.
Xylenols are organic compounds with the formula (CH3)2C6H3OH. They are volatile colorless solids or oily liquids. They are derivatives of phenol with two methyl groups at various positions relative to the hydroxyl group. Six isomers exist, of which 2,6-xylenol with both methyl groups in an ortho position with respect to the hydroxyl group is the most important. The name xylenol is a portmanteau of the words xylene and phenol.

A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.

2,6-Dichlorophenolindophenol is a chemical compound used as a redox dye. When oxidized, DCPIP is blue with a maximal absorption at 600 nm; when reduced, DCPIP is colorless.
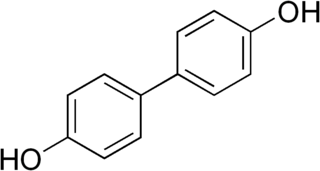
4,4′-Biphenol is an organic compound which is a phenolic derivative of biphenyl. It is a colorless solid.

A boronic acid is an organic compound related to boric acid in which one of the three hydroxyl groups is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group. As a compound containing a carbon–boron bond, members of this class thus belong to the larger class of organoboranes.

The Folin–Ciocâlteu reagent (FCR) or Folin's phenol reagent or Folin–Denis reagent, is a mixture of phosphomolybdate and phosphotungstate used for the colorimetric in vitro assay of phenolic and polyphenolic antioxidants, also called the gallic acid equivalence method (GAE). It is named after Otto Folin, Vintilă Ciocâlteu, and Willey Glover Denis. The Folin-Denis reagent is prepared by mixing sodium tungstate and phosphomolybdic acid in phosphoric acid. The Folin–Ciocalteu reagent is just a modification of the Folin-Denis reagent. The modification consisted of the addition of lithium sulfate and bromine to the phosphotungstic-phosphomolybdic reagent.

Indophenol is an organic compound with the formula OC6H4NC6H4OH. It is deep blue dye that is the product of the Berthelot's reaction, a common test for ammonia. The indophenol group, with various substituents in place of OH and various ring substitutions, is found in many dyes used in hair coloring and textiles.

Organobismuth chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to bismuth chemical bond. Applications are few. The main bismuth oxidation states are Bi(III) and Bi(V) as in all higher group 15 elements. The energy of a bond to carbon in this group decreases in the order P > As > Sb > Bi. The first reported use of bismuth in organic chemistry was in oxidation of alcohols by Frederick Challenger in 1934 (using Ph3Bi(OH)2). Knowledge about methylated species of bismuth in environmental and biological media is limited.

2,6-Di-tert-butylpyridine is an organic compound with the formula (Me3C)2C5H3N. This colourless, oily liquid is derived from pyridine by replacement of the two H atoms with tert-butyl groups. It is a hindered base. For example, it can be protonated, but it does not form an adduct with boron trifluoride.

2,4,6-Tri-tert-butylphenol (2,4,6-TTBP) is a phenol symmetrically substituted with three tert-butyl groups and thus strongly sterically hindered. 2,4,6-TTBP is a readily oxidizable aromatic compound and a weak acid. It oxidizes to give the deep-blue 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenoxy radical. 2,4,6-TTBP is related to 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, which is widely used as an antioxidant in industrial applications. These compounds are colorless solids.


















