Zinc chloride is the name of chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl2 and its hydrates. Zinc chlorides, of which nine crystalline forms are known, are colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water. This white salt is hygroscopic and even deliquescent. Samples should therefore be protected from sources of moisture, including the water vapor present in ambient air. Zinc chloride finds wide application in textile processing, metallurgical fluxes, and chemical synthesis. No mineral with this chemical composition is known aside from the very rare mineral simonkolleite, Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O.
Sodium amide, commonly called sodamide, is the inorganic compound with the formula NaNH2. It is a salt composed of the sodium cation and the azanide anion. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is white, but commercial samples are typically gray due to the presence of small quantities of metallic iron from the manufacturing process. Such impurities do not usually affect the utility of the reagent. NaNH2 conducts electricity in the fused state, its conductance being similar to that of NaOH in a similar state. NaNH2 has been widely employed as a strong base in organic synthesis.

Indazole, also called isoindazole, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and pyrazole.
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: total synthesis, semisynthesis, and methodology.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

Chloro(triphenylphosphine)gold(I) or triphenylphosphinegold(I) chloride is a coordination complex with the formula (Ph3P)AuCl. This colorless solid is a common reagent for research on gold compounds.

Organozirconium compounds are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to zirconium chemical bond. Organozirconium chemistry is the corresponding science exploring properties, structure, and reactivity of these compounds. Organozirconium compounds have been widely studied, in part because they are useful catalysts in Ziegler-Natta polymerization.
The Davis–Beirut reaction is N,N-bond forming heterocyclization that creates numerous types of 2H-indazoles and indazolones in both acidic and basic conditions The Davis–Beirut reaction is named after Mark Kurth and Makhluf Haddadin's respective universities; University of California, Davis and American University of Beirut, and is utilized for its lack of expensive materials and toxic metals.

4-Methylpentedrone, is a stimulant drug of the cathinone class that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a higher homolog of 4-methylmethcathinone (mephedrone) and 4-methylbuphedrone (4-MeMABP), and the p-methyl derivative of pentedrone. It can also be viewed as the methylamino analog of pyrovalerone.
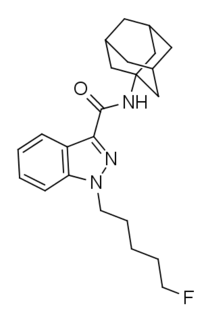
5F-APINACA is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. Structurally it closely resembles cannabinoid compounds from patent WO 2003/035005 but with a 5-fluoropentyl chain on the indazole 1-position, and 5F-APINACA falls within the claims of this patent, as despite not being disclosed as an example, it is very similar to the corresponding pentanenitrile and 4-chlorobutyl compounds which are claimed as examples 3 and 4.
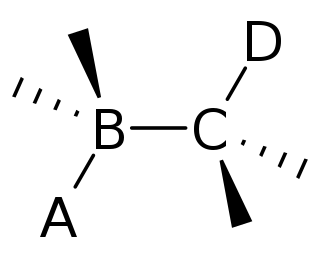
In organic chemistry, anti-periplanar, or antiperiplanar, describes the A–B–C–D bond angle in a molecule. In this conformer, the dihedral angle of the A–B bond and the C–D bond is greater than +150° or less than −150°. Anti-periplanar is often used in textbooks to mean strictly anti-coplanar, with an A-B C-D dihehedral angle of 180°. In a Newman projection, the molecule will be in a staggered arrangement with the anti-periplanar functional groups pointing up and down, 180° away from each other. Figure 5 shows 2-chloro-2,3-dimethylbutane in a sawhorse projection with chlorine and a hydrogen anti-periplanar to each other.

DMTMM is an organic triazine derivative commonly used for activation of carboxylic acids, particularly for amide synthesis. Amide coupling is one of the most common reactions in organic chemistry and DMTMM is one reagent used for that reaction. The mechanism of DMTMM coupling is similar to other common amide coupling reactions involving activated carboxylic acids. Its precursor, 2-chloro-4,6,-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine (CDMT), has also been used for amide coupling. DMTMM has also been used to synthesize other carboxylic functional groups such as esters and anhydrides. DMTMM is usually used in the chloride form but the tetrafluoroborate salt is also commercially available.

CUMYL-4CN-BINACA (also known as CUMYL-CYBINACA or SGT-78) is an indazole-3-carboxamide based synthetic cannabinoid that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a potent agonist for cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, with in vitro EC50 values of 0.58 nM and 6.12 nM, respectively. In mice, CUMYL-4CN-BINACA produces hypothermic and pro-convulsant effects via the CB1 receptor, and anecdotal reports suggest it has an active dose of around 0.1 mg in humans.

16-Methylene-17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate is a progestin of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was never marketed. Given orally, it shows about 2.5-fold the progestogenic activity of parenteral progesterone in animal bioassays. It is a parent compound of the following clinically used progestins:

Yttrium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the formula Y(NO3)3. The hexahydrate is the most common form commercially available.

α-Pyrrolidinoheptaphenone is a designer drug of the pyrrolidinophenone class of cathinones. It is the higher homolog of α-pyrrolidinohexiophenone (α-PHP).
The Cadogan–Sundberg indole synthesis, or simply Cadogan indole synthesis, is a name reaction in organic chemistry that allows for the generation of indoles from o-nitrostyrenes with the use of trialkyl phosphites, such as triethyl phosphite.
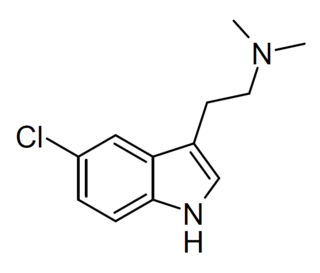
5-Chloro-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-chloro-DMT) is a tryptamine derivative related to compounds such as 5-bromo-DMT and 5-fluoro-DMT. It acts as a serotonin receptor agonist and has primarily sedative effects in animal studies. It has been sold as a designer drug.
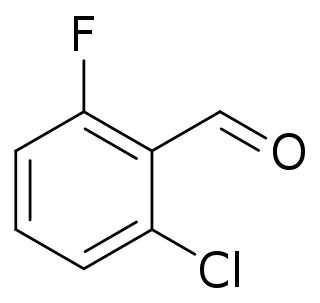
2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde is a halogenated benzaldhyde derivative with the formula C6H3ClFCHO. It is an intermediate in the synthesis of other halogenated hetrocyclic compounds.