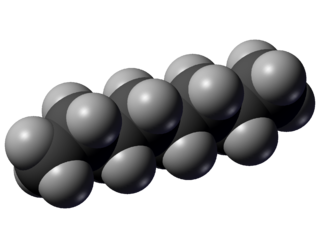
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
Monomethylhydrazine (mono-methyl hydrazine, MMH) is a highly toxic, volatile hydrazine chemical with the chemical formula CH3(NH)NH2. It is used as a rocket propellant in bipropellant rocket engines because it is “hypergolic” with various oxidizers such as nitrogen tetroxide (N
2O
4) and nitric acid (HNO
3). As a propellant, it is described in specification MIL-PRF-27404.
Cyanogen chloride is a toxic chemical compound with the formula NCCl. This linear, triatomic pseudohalogen is an easily condensed colorless gas. More commonly encountered in the laboratory is the related compound cyanogen bromide, a room-temperature solid that is widely used in biochemical analysis and preparation.

The term immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) is defined by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as exposure to airborne contaminants that is "likely to cause death or immediate or delayed permanent adverse health effects or prevent escape from such an environment." Examples include smoke or other poisonous gases at sufficiently high concentrations. It is calculated using the LD50 or LC50. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulation defines the term as "an atmosphere that poses an immediate threat to life, would cause irreversible adverse health effects, or would impair an individual's ability to escape from a dangerous atmosphere."

tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.
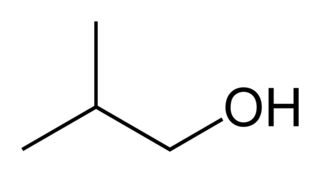
Isobutanol (IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropan-1-ol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2OH (sometimes represented as i-BuOH). This colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic smell is mainly used as a solvent either directly or as its esters. Its isomers are 1-butanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol, all of which are important industrially.
1,1-Dichloroethane is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colorless oily liquid with a chloroform-like odor. It is not easily soluble in water, but miscible with most organic solvents.
1,2-Dichlorotetrafluoroethane, or R-114, also known as cryofluorane (INN), is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) with the molecular formula ClF2CCF2Cl. Its primary use has been as a refrigerant. It is a non-flammable gas with a sweetish, chloroform-like odor with the critical point occurring at 145.6 °C and 3.26 MPa. When pressurized or cooled, it is a colorless liquid. It is listed on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's list of ozone depleting chemicals, and is classified as a Montreal Protocol Class I, group 1 ozone depleting substance.
Tellurium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound of tellurium and fluorine with the chemical formula TeF6. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an unpleasant odor.
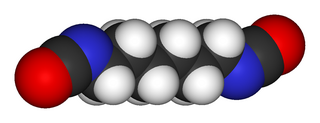
Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI or HMDI) is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)6(NCO)2. It is classified as an diisocyanate. It is a colorless liquid.

2-Ethoxyethanol, also known by the trademark Cellosolve or ethyl cellosolve, is a solvent used widely in commercial and industrial applications. It is a clear, colorless, nearly odorless liquid that is miscible with water, ethanol, diethyl ether, acetone, and ethyl acetate.
Carbonyl fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula COF2. This gas, like its analog phosgene, is colourless and highly toxic. The molecule is planar with C2v symmetry.

1,2-Dichlorobenzene, or orthodichlorobenzene (ODCB), is an organic compound with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colourless liquid is poorly soluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents. It is a derivative of benzene, consisting of two adjacent chlorine atoms.

An occupational hazard is a hazard experienced in the workplace. This encompasses many types of hazards, including chemical hazards, biological hazards (biohazards), psychosocial hazards, and physical hazards. In the United States, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) conduct workplace investigations and research addressing workplace health and safety hazards resulting in guidelines. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes enforceable standards to prevent workplace injuries and illnesses. In the EU, a similar role is taken by EU-OSHA.

Dibromodifluoromethane is a mixed halomethane. It is a colorless non-flammable liquid.
A recommended exposure limit (REL) is an occupational exposure limit that has been recommended by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The REL is a level that NIOSH believes would be protective of worker safety and health over a working lifetime if used in combination with engineering and work practice controls, exposure and medical monitoring, posting and labeling of hazards, worker training and personal protective equipment. To formulate these recommendations, NIOSH evaluates all known and available medical, biological, engineering, chemical, trade, and other information. Although not legally enforceable limits, RELS are transmitted to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) or the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) of the U.S. Department of Labor for use in promulgating legal standards.
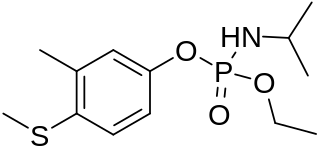
Fenamiphos is an organophosphate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide.

Diethylethanolamine (DEAE) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H15NO. It is used as a precursor in the production of a variety of chemical commodities such as the local anesthetic procaine. It can be reacted with 4-aminobenzoic acid to make procaine. DEAE can be used as a precursor for DEAE-cellulose resin, which is commonly used in ion exchange chromatography. DEAE can also be conveniently obtained from renewable sources. It is chemically stable and able to absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from its surroundings. In solution, it can decrease the surface tension of water when the temperature is increased.
Fonofos is an organothiophosphate insecticide primarily used on corn. It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance.

Parathion methyl, or methyl parathion, is an organophosphate insecticide, possessing an organothiophosphate group. It is structurally very similar to parathion-ethyl. It is not allowed for sale and import in nearly all countries around the world, while a few allow it under subject to specified conditions only.
















