
Amyl alcohols are alcohols with the formula C5H11OH. Eight are known. A mixture of amyl alcohols (also called amyl alcohol) can be obtained from fusel alcohol. Amyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification, by which is produced amyl acetate and other products. The name amyl alcohol without further specification applies to the normal (straight-chain) form, 1-pentanol.

Methyl nitrite is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH
3ONO. It is a gas, and is the simplest alkyl nitrite.

"Lucas' reagent" is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid. This solution is used to classify alcohols of low molecular weight. The reaction is a substitution in which the chloride replaces a hydroxyl group. A positive test is indicated by a change from clear and colourless to turbid, signalling formation of a chloroalkane. Also, the best results for this test are observed in tertiary alcohols, as they form the respective alkyl halides fastest due to higher stability of the intermediate tertiary carbocation. The test was reported in 1930 and became a standard method in qualitative organic chemistry. The test has since become somewhat obsolete with the availability of various spectroscopic and chromatographic methods of analysis. It was named after Howard Lucas (1885–1963).
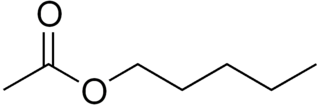
Amyl acetate (pentyl acetate) is an organic compound and an ester with the chemical formula CH3COO[CH2]4CH3 and the molecular weight 130.19 g/mol. It is colorless and has a scent similar to bananas and apples. The compound is the condensation product of acetic acid and 1-pentanol. However, esters formed from other pentanol isomers (amyl alcohols), or mixtures of pentanols, are often referred to as amyl acetate. The symptoms of exposure to amyl acetate in humans are dermatitis, central nervous system depression, narcosis and irritation to the eyes and nose.

Mesityl oxide is a α,β-unsaturated ketone with the formula CH3C(O)CH=C(CH3)2. This compound is a colorless, volatile liquid with a honey-like odor.

Isoamyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with the formula C
5H
12O, specifically (H3C–)2CH–CH2–CH2–OH. It is one of several isomers of amyl alcohol (pentanol). It is also known as isopentyl alcohol, isopentanol, or (in the IUPAC recommended nomenclature) 3-methyl-butan-1-ol. An obsolete name for it was isobutyl carbinol.
The molecular formula C5H12O (molar mass: 88.15 g/mol, exact mass: 88.088815) may refer to:

tert-Amyl alcohol (TAA) or 2-methylbutan-2-ol (2M2B), is a branched pentanol.

3-Pentanol is one of the eight isomers of amyl alcohol. It is found naturally and has a role as a pheromone.

2-Pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the manufacturing of other chemicals. 2-Pentanol is a component of many mixtures of amyl alcohols sold industrially. 2-Pentanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(−)-2-pentanol and (S)-(+)-2-pentanol.

3-Methyl-1-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It occurs naturally in Capsicum frutescens, the tabasco pepper.

2-Methyl-1-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.

Isohexanol is an organic chemical compound. It is found in longan fruit.
Methylpentanol may refer to:

2-Methyl-2-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It can be added to a gas chromatograph to help distinguish between branched compounds, especially alcohols. Its presence in urine can be used to test for exposure to 2-methylpentane. As with many other short-chain alcohols, 2-methyl-2-pentanol can produce intoxication and sedative effects similar to those of ethanol, though it is more irritating to mucous membranes and generally more toxic to the body.
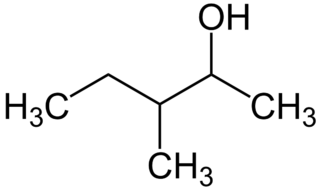
3-Methyl-2-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It has been identified as a component of hops. Its presence in urine can be used to test for exposure to 3-methylpentane.

4-Methyl-2-pentanol or methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) is an organic chemical compound used primarily as a frother in mineral flotation and in the production of lubricant oil additives such as Zinc dithiophosphate. It is also used as a solvent, in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of brake fluid and as a precursor to some plasticizers. It is an acetone derivative in liquid state, with limited solubility in water but generally miscible with most organic solvents.
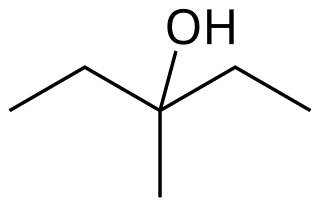
3-Methyl-3-pentanol is an organic chemical compound and a tertiary hexanol. It is used in the synthesis of the tranquilizer emylcamate, and has similar sedative and anticonvulsant actions itself.
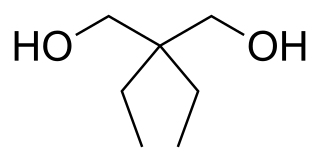
Prenderol (Diethylpropanediol) is a simple alkyl diol which has sedative, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects. It is closely related in structure to meprobamate and numerous other alkyl alcohols and diols with generally comparable activity.


















