
The politics of Trinidad and Tobago function within the framework of a unitary state regulated by a parliamentary democracy modelled on that of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, from which the country gained its independence in 1962. Under the 1976 republican Constitution, the monarch was replaced as head of state by a President chosen by an electoral college composed of the members of the bicameral Parliament, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives.

Patrick Augustus Mervyn Manning was a Trinidadian politician who was the fourth prime minister of Trinidad and Tobago; his terms ran from 17 December 1991 to 9 November 1995 and from 24 December 2001 to 26 May 2010. He was also the political leader of the People's National Movement (PNM) from 1987 to 2010. A geologist by training, Manning served as Member of Parliament for the San Fernando East constituency from 1971 until 2015 when he was replaced by Randall Mitchell and was the longest-serving member of the House of Representatives. He was the Leader of the Opposition from 1986 to 1990 and again from 1995 to 2001.

The United National Congress is one of two major political parties in Trinidad and Tobago and the current parliamentary opposition. The UNC is a centre-left party. It was founded in 1989 by Basdeo Panday, a Trinidadian lawyer, economist, trade unionist, and actor after a split in the ruling National Alliance for Reconstruction (NAR). After spending six years in opposition, the UNC won control of the government in 1995, initially in coalition with the NAR and later on its own. In the 2000 general election, the UNC won an absolute majority in the Parliament. In 2001, a split in the party caused the UNC to lose its parliamentary majority and control of the government. From 2001 to 2010, the UNC was once again Parliamentary Opposition party. In May 2010, the UNC returned to government as the majority party in the People's Partnership. The UNC's Political Leader, Kamla Persad-Bissessar, was sworn in as the first female Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago. Kamla Persad-Bissessar was Prime Minister from 2010 until 2015.

The People's National Movement (PNM) is the longest-serving and oldest active political party in Trinidad and Tobago. The party has dominated national and local politics for much of Trinidad and Tobago's history, contesting all elections since 1956 serving as the nation's governing party or on four occasions, the main opposition. It is one out of the country's two main political parties. There have been four PNM Prime Ministers and multiple ministries. The party espouses the principles of liberalism and generally sits at the centre to centre-left of the political spectrum.

The National Alliance for Reconstruction (NAR) was the governing party in Trinidad and Tobago between 1986 and 1991. The party has been inactive since 2005.
Ralph Maraj is a Trinidad and Tobago politician, actor, playwright, and teacher. He served as Minister of Foreign Affairs under a People's National Movement (PNM) administration, Minister of Communication and Information Technology under a United National Congress (UNC) administration, and was a founding member of National Team Unity before returning to the PNM to work as a speech writer for Prime Minister Patrick Manning. Prior to entering politics in 1991, Maraj worked as a teacher at Naparima College in San Fernando. He also attended that school. He wrote several plays, the most successful being Cynthia Sweetness. Maraj also starred in the movies The Right and The Wrong (1969) and Bim (1974), described by Bruce Paddington as "one of the most important films to be produced in Trinidad and Tobago".

Basdeo Panday was a Trinidadian and Tobagonian statesman, lawyer, politician, trade unionist, economist, and actor who served as the fifth Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago from 1995 to 2001. He was the first person of Indian descent along with being the first Hindu to hold the office of Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago. He was first elected to Parliament in 1976 as the Member for Couva North, Panday served as Leader of the Opposition four times between 1976 and 2010 and was a founding member of the United Labour Front (ULF), the National Alliance for Reconstruction (NAR), and the United National Congress (UNC). He served as leader of the ULF and UNC, and was President General of the All Trinidad Sugar and General Workers' Trade Union from 1973 to 1995.

The Congress of the People (COP) is a political party in Trinidad and Tobago. Its current political leader is Kirt Sinnette. Its symbol is the "Circle of Circles".

Early general elections were held in Trinidad and Tobago on 10 December 2001, after the ruling United National Congress lost its majority in the House of Representatives following four defections. However, the election results saw the UNC and the People's National Movement both win 18 seats. Although the UNC received the most votes, President A. N. R. Robinson nominated PNM leader Patrick Manning as Prime Minister. Voter turnout was 66.1%.

General elections were held in Trinidad and Tobago on 24 May 2010. The date of the general elections was announced by Prime Minister Patrick Manning on April 16, 2010, via a press release. The election was called over two years earlier than required by law. Polls showing that the UNC-led opposition coalition was likely to win the election were confirmed by the subsequent results.

The People's Partnership (PP) was a political coalition in Trinidad and Tobago among five political parties: the United National Congress (UNC), the Congress of the People (COP), the Tobago Organization of the People (TOP), Movement for Social Justice (MSJ) and National Joint Action Committee (NJAC). The political leader was Kamla Persad-Bissessar. The coalition was formed in advance of the 2010 general election attempting to form a multi-ethnic opposition bloc against the People's National Movement (PNM) government led by Patrick Manning. The coalition won the 2010 General Elections defeating the People's National Movement on May 24, 2010. On September 7, 2015, the coalition was defeated in the 2015 General Elections to the People's National Movement led by Keith Rowley. The coalition saw the departure of the Movement for Social Justice in 2012 and eventually disbanded on December 8, 2015.

Keith Christopher Rowley, is a Trinidadian politician serving as the seventh prime minister of Trinidad and Tobago, first elected into office on 9 September 2015 and again following the 2020 general election. He has led the People's National Movement (PNM) since May 2010 and was Leader of the Opposition from 2010 to 2015. He has also served as the Member of the House of Representatives for Diego Martin West since 1991. He is a volcanologist by profession, holding a doctorate in geology, specializing in geochemistry.

General elections were held in Trinidad and Tobago on 7 September 2015. The date of the general elections was announced by Prime Minister Kamla Persad-Bissessar on 13 June 2015. The result was a victory for the opposition People's National Movement, which received 52% of the vote and won 23 of the 41 seats in the House of Representatives.

On Monday November 28, 2016, local elections were held in Trinidad, the bigger of the two main islands of Caribbean island state Trinidad and Tobago. The elections were held slightly more than one month later than originally planned. They were held to select the membership of 14 local authorities, with representatives elected from 137 single-member districts across the country. The entire membership of Trinidad's local government was renewed as a result of these elections, with the previous set of local representatives having been elected in 2013. The elections came roughly a year following the 2015 parliamentary general election.
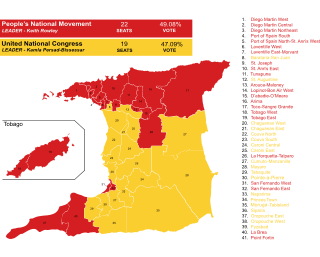
General elections were held in Trinidad and Tobago on Monday, 10 August 2020, to elect 41 members to the 12th Trinidad and Tobago Republican Parliament. It was the 14th election since gaining independence from the United Kingdom in 1962 and the 22nd national election in Trinidad and Tobago ever. Tracy Davidson-Celestine, political leader of the Tobago Council of the People's National Movement (PNM) became the first woman to lead a Tobagonian political party with representation in the House of Representatives. Additionally, two of the three largest parties elected in 2015, the United National Congress (UNC) and the Congress of the People (COP), were led by women.

House of Assembly elections were held in Tobago on 25 January 2021 where 12 members were elected in the eleventh election since the Assembly was established in 1980. This election marked the first time in history that both parties elected, the People's National Movement (PNM) and Progressive Democratic Patriots (PDP) won an equal number seats of 6-6, despite the PNM winning the popular vote, resulting in a deadlock and a constitutional crisis with both political parties and Prime Minister Keith Rowley seeking senior counsel advice on the way forward. This election was the first time after 20 years in power that the PNM lost its absolute majority. This election also marked the first time a female political leader was elected to the Assembly and the first time a woman led a major political party or a political party with representation in the Assembly, following the 2020 Tobago Council of the People's National Movement leadership election where Health Secretary, councillor and former Trinidad and Tobago Ambassador to Costa Rica and former Deputy Chief Secretary of Tobago Tracy Davidson-Celestine made history by being elected as the PNM's first female political leader at the regional or national level and one of the first bilingual political leaders in the country's history. If Davidson-Celestine and the PNM were to be elected with a majority to their sixth consecutive term in office, she would have made history, becoming the first female Chief Secretary of Tobago. The election was held alongside local by-elections in Trinidad in which the PNM and UNC retained two districts and the PNM losing one to the UNC.
The 2022 People's National Movement internal election, the last one for the PNM before the subsequent general election, took place over three days: November 26 and 27 and December 4, 2022. The current party leader and Prime Minister Keith Rowley had indicated he would most likely not seek to lead the party into the next general election. Rowley made these comments in his victory speech on the night of the 2020 Trinidad and Tobago general election, where the PNM secured a second mandate under his leadership but with the slimmest majority for a government in two decades. However, he announced that he would seek another term as the party's leader in October 2022. In the 2020 general election campaign, he indicated that he would have stood down had the PNM lost. The election followed the 2022 Tobago Council of the People's National Movement leadership election. Keith Rowley won re-election by an overwhelming majority with a low voter turnout with 9,111 out of 105,894 eligible party members voting.

Snap House of Assembly elections were held in Tobago on 6 December 2021 to elect all 15 members of the Tobago House of Assembly (THA). The election was called following a deadlock created by the January 2021 elections which resulted in a tie between the People's National Movement (PNM) and the Progressive Democratic Patriots (PDP), with both parties winning six seats. As a result, the number of seats in the legislature was increased from 12 to 15 to avoid ties.













