
Péter Medgyessy is a retired Hungarian politician who served as Prime Minister of Hungary from 27 May 2002 to 29 September 2004. On 25 August 2004, he resigned over disputes with coalition partner Alliance of Free Democrats, but remained as acting prime minister for a 30-day period as required by the Constitution, and a few additional days until his successor Ferenc Gyurcsány was confirmed by the National Assembly.

The Democratic Coalition is a social-liberal and social-democratic political party in Hungary led by former Prime Minister Ferenc Gyurcsány. Founded in 2010 as a faction within the Hungarian Socialist Party (MSZP), the Democratic Coalition split from the MSZP on 22 October 2011 and became a separate party. It has fifteen MPs in the National Assembly and four MEPs in the European Parliament.

The Jobbik – Conservatives, commonly known as Jobbik, is a conservative political party in Hungary.
The Fundamental Law of Hungary, the country's constitution, was adopted by parliament on 18 April 2011, promulgated by the president a week later and entered into force on 1 January 2012. It is Hungary's first constitution adopted within a democratic framework and following free elections.

Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 11 and 25 April 2010 to elect the members of the National Assembly. They were the sixth free elections since the end of the communist era. 386 Members of Parliament (MPs) were elected in a combined system of party lists and electoral constituencies. Electoral law in Hungary requires candidates to gather 500 signatures from citizens supporting their candidacy.

LMP – Hungary's Green Party is a green-liberal political party in Hungary. Founded in 2009, it was one of four parties to win seats in the National Assembly in the 2010 parliamentary election. It is a member of the European Green Party. The party's political position has been wildly described as centrist and centre-left. Other sources describe LMP and their voters as "hard to evaluate", populist, and inclusive of centre-right elements.

Éva Tétényi is a Hungarian politician, who served as the mayor of Esztergom between 2010 and 2014. Tétényi formerly worked as an architect.

Gergely Szilveszter Karácsony is a Hungarian politician, political scientist and current Mayor of Budapest. He previously served as member of the National Assembly (MP) from 2010 to 2014 and Mayor of Zugló from 2014 to 2019.

Gergely Gulyás is a Hungarian jurist, politician, the current Minister of the Prime Minister's Office since 2018. He is a member of the Fidesz party and has been a member of the National Assembly (MP) since 2010.

Together, officially Together – Party for a New Era, formerly also known as Together 2014, was a social-liberal political party in Hungary formed on 26 October 2012 for the 2014 Hungarian parliamentary election by Gordon Bajnai, the former Prime Minister of Hungary, to contest Viktor Orbán's government. Together was founded as a coalition of left-wing and liberal political movements and civil organizations that transformed itself into a party in March 2013.

An election of Members of the European Parliament from Hungary to the European Parliament was held on 25 May 2014.
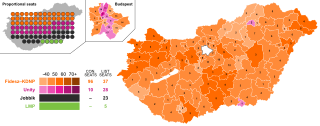
Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 6 April 2014. This parliamentary election was the 7th since the 1990 first multi-party election. The result was a victory for the Fidesz–KDNP alliance, preserving its two-thirds majority, with Viktor Orbán remaining Prime Minister. It was the first election under the new Constitution of Hungary which came into force on 1 January 2012. The new electoral law also entered into force that day. For the first time since Hungary's transition to democracy, the election had a single round. The voters elected 199 MPs instead of the previous 386 lawmakers.
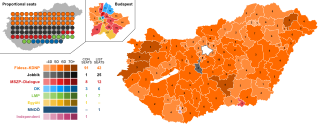
Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 8 April 2018. The elections were the second since the adoption of a new constitution, which came into force on 1 January 2012. The result was a victory for the Fidesz–KDNP alliance, preserving its two-thirds majority, with Viktor Orbán remaining Prime Minister. Orbán and Fidesz campaigned primarily on the issues of immigration and foreign meddling, and the election was seen as a victory for right-wing populism in Europe.

A referendum related to the European Union's migrant relocation plans was held in Hungary on 2 October 2016. The referendum was initiated by the government, under the provision of article 8 of the new constitution of 2012. It was commonly referred to as the kvótanépszavazás or kvótareferendum in the Hungarian media.

An indirect presidential election was held in Hungary on 13 March 2017. János Áder was elected President of Hungary for a second term.

Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 3 April 2022 to elect the National Assembly, coinciding with a referendum.
The following lists events that happened during 2018 in Hungary.

Fidesz–KDNP Party Alliance, formerly also known as the Alliance of Hungarian Solidarity, is a right-wing national conservative political alliance of two political parties in Hungary, the Fidesz – Hungarian Civic Alliance (Fidesz) and the Christian Democratic People's Party (KDNP). The two parties jointly contested every national election since the 2006 parliamentary election. The Fidesz–KDNP party alliance has governed Hungary since 2010, altogether obtaining a supermajority in each of the 2010, 2014, 2018, and 2022 national elections.
The 2018 protests in Hungary were massive demonstrations and protests held against the government of Viktor Orbán and his cabinet, triggered by the so-called "slave law" in December of that year. The first wave of demonstrations began in April-May. The series of anti-government demonstrations in December 2018 was a political movement against the measures of the fourth Orbán government, the direct precedents of which were the submission of the Overtime Act and the scandalous parliamentary day on 12 December 2018. On this day, members of the Jobbik, MSZP, LMP, DK and Dialogue in Parliament disrupted the legislature by whistling, shouting, scattering paper and preventing access to the presidential pulpit, thereby obstructing the vote. Protests erupted against the vote and the parliamentary session.
United for Hungary is a political alliance in Hungary that was formed to compete in the 2022 parliamentary election. The alliance lost the 2022 election.



















