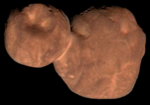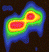
4769 Castalia is a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1.4 kilometers in diameter and was the first asteroid to be modeled by radar imaging. It was discovered on 9 August 1989, by American astronomer Eleanor Helin (Caltech) on photographic plates taken at Palomar Observatory in California. It is named after Castalia, a nymph in Greek mythology. It is also a Mars- and Venus-crosser asteroid.
4486 Mithra, is an eccentric asteroid and suspected contact-binary, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. It belongs to the Apollo group of asteroids and is a relatively slow rotator.

66391 Moshup, provisional designation 1999 KW4, is a binary asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group, approximately 1.3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 20 May 1999, by Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site in Socorro, New Mexico, United States. It is a Mercury-crosser that comes extremely close to the Sun at a perihelion of 0.2 AU.

163693 Atira (; provisional designation 2003 CP20) is a stony asteroid, dwelling in the interior of Earth's orbit. It is classified as a near-Earth object. Atira is a binary asteroid, a system of two asteroids orbiting their common barycenter. The primary component with a diameter of approximately 4.8 kilometers (3 miles) is orbited by a minor-planet moon that measures about 1 km (0.6 mi). Atira was discovered on 11 February 2003, by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States.

(450894) 2008 BT18 is a sub-kilometer asteroid and synchronous binary system, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It was discovered on 31 January 2008, by the LINEAR program at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, United States. The eccentric asteroid measures approximately 600 meters in diameter and has a composition of a basaltic achondrite.
(6491) 1991 OA is a highly eccentric, stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid, approximately half a kilometer in diameter. It was discovered on 16 July 1991, by American astronomer Henry E. Holt at the U.S. Palomar Observatory in California.
(467336) 2002 LT38, is a sub-kilometer asteroid and suspected tumbler, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group, approximately 240 meters (790 ft) in diameter. It was discovered on 12 June 2002, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States.
(7888) 1993 UC is a near-Earth minor planet in the Apollo group. It was discovered by Robert H. McNaught at the Siding Spring Observatory in Coonabarabran, New South Wales, Australia, on 20 October 1993. The asteroid has an observation arc of 34 years and has a well determined orbit. Its estimated size is 2.3 to 5.2 km.
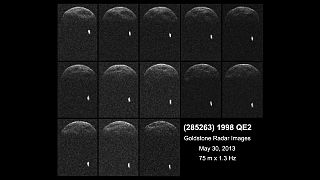
(285263) 1998 QE2, provisional designation 1998 QE2, is a dark asteroid and synchronous binary system, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Amor group, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 19 August 1998, by astronomers of the LINEAR program at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. Its sub-kilometer minor-planet moon was discovered by radar on 30 May 2013.

(192642) 1999 RD32, provisional designation: 1999 RD32, is an asteroid and suspected contact binary on an eccentric orbit, classified as a large near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 5 kilometers (3 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 8 September 1999, at a magnitude of 18, by astronomers of the LINEAR program using its 1-meter telescope at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, United States. The asteroid is likely of carbonaceous composition and has a rotation period of 17.08 hours.

(388188) 2006 DP14, provisional designation 2006 DP14, is a sub-kilometer sized, peanut-shaped asteroid on a highly eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. This contact binary was discovered on 23 February 2006, by astronomers of the LINEAR program at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. On 10 February 2014, it passed 6.25 lunar distances from Earth. The asteroid is approximately 400 meters in diameter and has a rotation period of 5.77 hours.

(436724) 2011 UW158, provisionally known as 2011 UW158, is a stony, walnut-shaped asteroid and fast rotator, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 300 meters in diameter. It was discovered on 25 October 2011, by Pan-STARRS at Haleakala Observatory on the island of Maui, Hawaii, in the United States.

(671294) 2014 JO25 is a near-Earth asteroid. It was discovered in May 2014 by astronomers at the Catalina Sky Survey near Tucson, Arizona - a project of NASA's NEO (Near Earth Object) Observations Program in collaboration with the University of Arizona.

(505657) 2014 SR339, provisional designation 2014 SR339, is a dark and elongated asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 970 meters (3,200 feet) in diameter. It was discovered on 30 September 2014, by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer telescope (WISE) in Earth's orbit. Closely observed at Goldstone and Arecibo in February 2018, it has a rotation period of 8.7 hours.

(164121) 2003 YT1, provisional designation 2003 YT1, is a bright asteroid and synchronous binary system on a highly eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 December 2003, by astronomers with the Catalina Sky Survey at the Catalina Station near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. The V-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 2.3 hours. Its 210-meter sized minor-planet moon was discovered at Arecibo Observatory in May 2004.

2017 YE5 is a binary pair of asteroids of approximately equal size and mass, each about 0.9 km (0.56 mi) in diameter. Classified as a near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous object of the Apollo group, 2017 YE5 was discovered by amateur astronomer Claudine Rinner at the Oukaïmeden Observatory on 21 December 2017. On 21 June 2018, the pair of asteroids passed within 15.5 lunar distances or approximately 6 million km (3.7 million mi) from Earth. During the close encounter, 2017 YE5 was resolved in high detail by concurrent radar observations by the Arecibo and Green Bank observatories, along with individual observations by the Goldstone Solar System Radar. 2017 YE5 is likely an extinct or dormant comet due to its distant elliptical orbit and dark red surface.

2002 NY40 is a sub-kilometer near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 800 meters (2,600 feet) in diameter. The contact binary with a bilobated, peanut-like shape was first observed on 14 July 2002 by the LINEAR automated system in New Mexico. On 18 August 2002, it passed Earth at a distance of 540,000 km. It was observed with adaptive optics by the Midcourse Space Experiment.

2020 BX12 is a sub-kilometer binary asteroid, classified as a near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous object of the Apollo group. It was discovered on 27 January 2020 by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System survey at the Mauna Loa Observatory during its approach to Earth of 0.02915 AU (4.361 million km; 11.34 LD). Radar observations of the asteroid were carried out by the Arecibo Observatory on 4 February 2020, revealing a natural satellite orbiting 360 m (1,180 ft) from the primary body.

(85990) 1999 JV6 (provisional designation 1999 JV6) is a sub-kilometer near-Earth asteroid and a potentially hazardous object of the Apollo group. It was discovered by astronomers of the LINEAR program at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico. 1999 JV6 is a contact binary object consisting of two distinct lobes, as seen in radar images from various observatories including Arecibo and Goldstone in January 2015.
2020 SL1 is a near-Earth asteroid of the Apollo group, discovered by the Pan-STARRS 1 survey at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii on 18 September 2020. With an estimated diameter of 0.9–2.0 km (0.56–1.24 mi), it is the largest potentially hazardous asteroid discovered in 2020.