
Enrico Letta is an Italian politician who served as Prime Minister of Italy from April 2013 to February 2014, leading a grand coalition of centre-left and centre-right parties. He was the leader of the Democratic Party (PD) from March 2021 to March 2023.

Mario Draghi is an Italian economist, academic, banker, and civil servant who served as the prime minister of Italy from February 2021 to October 2022. Prior to his appointment as prime minister, he served as President of the European Central Bank (ECB) between 2011 and 2019. Draghi was also Chair of the Financial Stability Board between 2009 and 2011, and Governor of the Bank of Italy between 2006 and 2011.

Sergio Mattarella is an Italian politician, jurist, academic, and lawyer who is currently serving as the 12th President of Italy since 2015. He is the longest-serving president in the history of the Italian Republic. Since Giorgio Napolitano's death in 2023, Mattarella has been the only living Italian president.

The Five Star Movement is a political party in Italy. Its leader and president is Giuseppe Conte, Prime Minister of Italy from 2018 until 2021. The M5S was founded on 4 October 2009 by Beppe Grillo, a political activist and comedian, and Gianroberto Casaleggio, a web strategist. The party is primarily described as populist, of the syncretic kind, due to its members' insistence that it has no place in the left–right political spectrum. The party is a proponent of green politics, direct democracy and broadly, progressivism.

The 2018 Italian general election was held on 4 March 2018 after the Italian Parliament was dissolved by President Sergio Mattarella on 28 December 2017. Voters were electing the 630 members of the Chamber of Deputies and the 315 elective members of the Senate of the Republic for the 18th legislature of the Italian Republic since 1948. The election took place concurrently with the Lombard and Lazio regional elections. No party or coalition gained an absolute majority in the parliament, even though the centre-right coalition won a plurality of seats as a coalition, and the Five Star Movement (M5S) won a plurality of seats as an individual party.

Forza Italia is a centre-right political party in Italy, whose ideology includes elements of liberal conservatism, Christian democracy, liberalism and populism. FI is a member of the European People's Party. Silvio Berlusconi was the party's leader and president until his death in 2023. The party has since been led by Antonio Tajani, who had been vice president and coordinatior and now functions as secretary. Other leading members include Elisabetta Casellati.

Luigi Di Maio is an Italian politician who has been serving as EU Special Representative for the Gulf region since 1 June 2023. Di Maio also served as Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2019 to 2022, as Deputy Prime Minister of Italy and Minister of Economic Development, Labour and Social Policies from 2018 to 2019, and as Vice President of the Chamber of Deputies in the 17th Italian legislature.
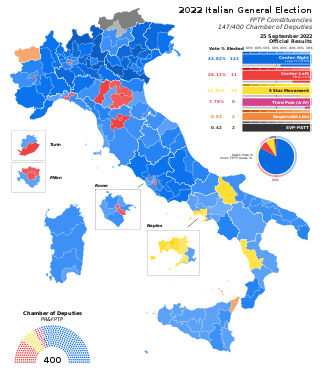
The 2022 Italian general election was a snap election held in Italy on 25 September 2022. After the fall of the Draghi government, which led to a parliamentary impasse, President Sergio Mattarella dissolved Parliament on 21 July, and called for new elections. Regional elections in Sicily were held on the same day. The results of the general election showed the centre-right coalition led by Giorgia Meloni's Brothers of Italy, a radical-right political party with neo-fascist roots, winning an absolute majority of seats in the Italian Parliament. Meloni was appointed Prime Minister of Italy on 22 October, becoming the first woman to hold the office.

Free and Equal was a left-wing electoral list and parliamentary group in the Chamber of Deputies and a sub-group in the Senate, the two houses of the Italian Parliament. LeU was launched on 3 December 2017 as a federation of political parties including Article 1, Italian Left and Possible. The leader of the alliance for the 2018 general election was Pietro Grasso, former President of the Senate and former anti-Mafia prosecutor. The three founding parties left the alliance in late 2018, but LeU continued to exist in Parliament. Following the 2021 Italian government crisis, LeU had a single minister, Roberto Speranza, in the national unity government of Prime Minister Mario Draghi.

In the 2018 Italian general election, no political group or party won an outright majority, resulting in a hung parliament. On 4 March, the centre-right coalition, in which Matteo Salvini's League emerged as the main political force, won a plurality of seats in the Chamber of Deputies and in the Senate, while the anti-establishment Five Star Movement (M5S) led by Luigi Di Maio became the party with the largest number of votes. The centre-left coalition, led by Matteo Renzi and the then-governing Democratic Party (PD), came third. Protracted negotiations were required before a government formation could be ultimated.

Giuseppe Conte is an Italian jurist, academic, and politician who served as prime minister of Italy from June 2018 to February 2021. He has been the president of the Five Star Movement (M5S) since August 2021.

The first Conte government was the 65th government of the Italian Republic. It was led by Giuseppe Conte, an independent, and it was in office from 1 June 2018 to 5 September 2019.

The 2019 Italian government crisis was a political event in Italy that occurred between August and September 2019. It includes the events that follow the announcement of the Minister of the Interior and leader of the League, Matteo Salvini, that he would revoke League's support of the cabinet and ask the President of the Republic to call a snap election. This provoked the resignation of Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte, and resulted in the formation of a new cabinet led by Conte himself.

The second Conte government was the 66th government of the Italian Republic and the second government led by Giuseppe Conte. The government was sworn in on 5 September 2019 to 13 February 2021.
Action is a liberal political party in Italy. Its leader is Carlo Calenda, a member of the European Parliament within the group of Renew Europe and former minister of Economic Development.

The 2021 Italian government crisis was a political event in Italy that began in January 2021 and ended the following month. It includes the events that follow the announcement of Matteo Renzi, leader of Italia Viva (IV) and former Prime Minister, that he would revoke IV's support to the Government of Giuseppe Conte.

Europeanists is a political party in Italy. Amid a government crisis triggered after Matteo Renzi announced that he would revoke Italia Viva's support to the government of Giuseppe Conte, Europeanists formed on 27 January 2021 as a component of a joint parliamentary group in the Italian Senate, with the aim to support Conte's cabinet.

The Draghi government was the 67th government of the Italian Republic, led by former President of the European Central Bank, Mario Draghi. It was in office between 13 February 2021 and 22 October 2022.

The 2022 Italian presidential election was held in Rome between 24 and 29 January 2022. The president of Italy was elected by a joint assembly composed of the Italian Parliament and regional representatives. The election process extended over multiple days, culminating in incumbent president Sergio Mattarella being confirmed for a second term, with a total of 759 votes on the eighth ballot. This was the second most votes ever received by a presidential candidate. Mattarella became the second president to be re-elected, his predecessor Giorgio Napolitano being the first.

Democratic Party – Democratic and Progressive Italy is the parliamentary group of the Democratic Party (PD) and minor allied parties in the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate of the Republic, formed in October 2022. Prior to the formation of the group, its name was that of the lead electoral list of the centre-left coalition in the 2022 Italian general election.




















