This article concerns the period 229 BC – 220 BC.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.
Year 222 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcellus and Calvus. The denomination 222 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 224 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Torquatus and Flaccus. The denomination 224 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The gens Atilia, sometimes written Atillia, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, which rose to prominence at the beginning of the fourth century BC. The first member of this gens to attain the consulship was Marcus Atilius Regulus, in 335 BC. The Atilii continued to hold the highest offices of the state throughout the history of the Republic, and well into imperial times.
Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus was a Roman general and statesman, who served as consul of the Roman Republic in 256 and 250 BC. He is remembered for his military successes; his military achievements, especially the Battle of Cape Ecnomus, significantly contributed to the victory of the Romans in the First Punic War.

The Battle of Telamon was fought between the Roman Republic and an alliance of Celtic tribes in 225 BC. The Romans, led by the consuls Gaius Atilius Regulus and Lucius Aemilius Papus, defeated the Celts led by the Gaesatae kings Concolitanus and Aneroëstes. This removed the Celtic threat from Rome and allowed the Romans to extend their influence over northern Italy.
The Battle of Clastidium was fought in 222 BC between a Roman army led by the consul Marcus Claudius Marcellus and the Insubres, a Celtic people in northern Italy. Florus writes that the Insubres were led by Viridomarus, or Britomartus, as the name varies in translation. The Romans won the battle, and in the process, Marcellus earned the spolia opima, one of the highest honors in ancient Rome, by killing the king in single combat. It was also notable as one of the few battles won by the Roman cavalry without any aid by the legions.
The Battle of Faesulae was fought in 225 BC between the Roman Republic and a group of Gauls living in Italy. The Gauls defeated the Romans, but later the same year, a decisive battle at Telamon had the opposite outcome.
Marcus Atilius Regulus was a Roman politician and statesman. He was consul in 227 and 217 BC and later censor in 214 BC. He was the son of his homonymous father who was consul in 267 and 256 BC.
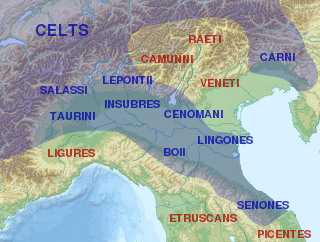
The Insubres or Insubri were an ancient Celtic population settled in Insubria, in what is now the Italian region of Lombardy. They were the founders of Mediolanum (Milan). Though completely Gaulish at the time of Roman conquest, they were the result of the fusion of pre-existing Ligurian and Celtic population with Gaulish tribes.
Aneroëstes was one of the two leaders of the Gaesatae, a group of Gaulish mercenaries who lived in the Alps near the Rhône and fought against the Roman Republic in the Battle of Telamon of 225 BC. He and his colleague Concolitanus were hired by the Boii and Insubres in response to the Roman colonisation of the formerly Gallic region of Picenum. After some initial success in Etruria, when faced with the army of the consul Lucius Aemilius Papus, Aneroëstes persuaded the Gauls to withdraw, but they were cut off at Telamon by the other consul, Gaius Atilius Regulus, and forced to fight a pitched battle.
The Gaesatae or Gaesati were a group of Gallic mercenary warriors who lived in the Alps near the river Rhône and fought against the Roman Republic at the Battle of Telamon in 225 BC.
Lucius Aemilius Papus was a Roman general and statesman. He jointly commanded the Roman armies which defeated the Gauls at the Battle of Telamon in 225 BC; his co-Consul, Gaius Atilius Regulus was killed during the battle. Papus was honoured with a triumph for this victory. He subsequently held several senior positions. He belonged to the patrician gens Aemilia.
Gaius Atilius Regulus was one of the two Roman consuls who fought a Celtic invasion of Italy in 225–224 BC; he was killed in battle and beheaded. Atilius came from a prominent family of consuls for four generations; the family originally hailed from southern Italy.

Over the course of nearly four centuries, the Roman Republic fought a series of wars against various Celtic tribes, whom they collectively described as Galli, or Gauls. Among the principal Gallic peoples described as antagonists by Greek and Roman writers were the Senones, Insubres, Boii, and Gaesatae.
The Battle of Silva Litana was an ambush that took place in a forest 75 miles northwest of the Roman city of Ariminum during the Second Punic War in 216 BC. The Gallic Boii surprised and destroyed a Roman army under the consul-elect Lucius Postumius Albinus. Of 25,000 Romans, only 10 survived, with a few being taken prisoner by the Gauls. The corpse of Postumius was decapitated and his skull was made into a gilded ceremonial cup by the Boii. News of this military disaster probably reached Rome after the defeat at Cannae in the fall of 216 BC or the spring election of consuls for 215 BC, triggering a renewed panic. The Romans were compelled to postpone military operations against the Gauls until the conclusion of the Second Punic War, sending only two legions to guard against additional Gallic attacks. However, the Boii and Insubres did not attempt to exploit their victory. Cisalpine Gaul remained in relative peace until 207 BC, when Hasdrubal Barca arrived there with his army from Spain.
The siege of Mutina in 218 BC constitutes one of the first episodes of the Second Punic War. Hannibal's diplomacy in Cisalpine Gaul persuaded the Gallic Boii and Insubres tribes to revolt and drive the Roman colonists out of Piacenza (Placentia) and push them as far as Modena (Mutina), which was then besieged.



