Related Research Articles

A paratrooper is a military parachutist—someone trained to parachute into a military operation, and usually functioning as part of an airborne forces. Military parachutists (troops) and parachutes were first used on a large scale during World War II for troop distribution and transportation. Paratroopers are often used in surprise attacks, to seize strategic objectives such as airfields or bridges.

Airborne forces are ground combat units carried by aircraft and airdropped into battle zones, typically by parachute drop. Parachute-qualified infantry and support personnel serving in airborne units are also known as paratroopers.

The 1st Airborne Division was an airborne infantry division of the British Army during the Second World War. The division was formed in late 1941 during the Second World War, after the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill, demanded an airborne force, and was initially under command of Major-General Frederick A. M. "Boy" Browning. The division was one of two airborne divisions raised by the British Army during the war, with the other being the 6th Airborne Division, created in May 1943, using former units of the 1st Airborne Division.

The 13th Airborne Division was an airborne forces formation of division-size of the United States Army that was active during World War II. The division was commanded for most of its existence by Major General Elbridge G. Chapman. It was officially activated in the United States in August 1943 at Fort Bragg in North Carolina, remaining active until February 1946, however it never saw combat.

The 17th Airborne Division, "The Golden Talons", was an airborne infantry division of the United States Army during World War II, commanded by Major General William M. Miley.

The 6th Airborne Division was an airborne infantry division of the British Army during the Second World War. Despite its name, the 6th was actually the second of two airborne divisions raised by the British Army during the war, the other being the 1st Airborne Division. The 6th Airborne Division was formed in the Second World War, in mid-1943, and was commanded by Major-General Richard N. Gale. The division consisted of the 3rd and 5th Parachute Brigades along with the 6th Airlanding Brigade and supporting units.

The Glider Badge was a special skills badge of the United States Army. According to the U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry, the badge was awarded to personnel who had "been assigned or attached to a glider or airborne unit or to the Airborne Department of the Infantry School; satisfactorily completed a course of instruction, or participated in at least one combat glider mission into enemy-held territory.

The 509th Infantry Regiment is an airborne infantry regiment of the United States Army. The unit was initially activated as a single battalion, the 504th Parachute Infantry Battalion, in October 1941 at Fort Benning, Georgia. Nicknamed "Geronimo", the 509th conducted the U.S. Army's first combat jump during World War II on 8 November 1942, flying 1,500 miles from England to seize Tafarquay airport in Oran, Algeria. The 509th made a total of five combat jumps during the war.

Glider infantry was a type of airborne infantry in which soldiers and their equipment were inserted into enemy-controlled territory via military glider. Initially developed in the late 1930s by Germany, glider infantry units were used extensively during World War II but are no longer used by any modern military.

The 2nd Parachute Brigade was an airborne forces brigade formed by the British Army during the Second World War.
The 1st Airborne Task Force was a short-lived Allied airborne unit that was active during World War II created for Operation Dragoon–the invasion of Southern France. Formed in July 1944, under the command of Major General Robert T. Frederick, it took part in the "Dragoon" landings on 15 August 1944, securing the area north-west of the landing beaches, before moving towards the French–Italian border as part of the United States Seventh Army. The unit was disbanded in November 1944.

The 551st Parachute Infantry Battalion was, for many years, a little-recognized airborne forces unit of the United States Army, raised during World War II, that fought in the Battle of the Bulge. Originally commissioned to take the French Caribbean island of Martinique, they were shipped instead to Western Europe. With an initial strength of 800 officers and enlisted men, the remaining 250 members of the Battalion were ordered on 7 January 1945 to attack the Belgian village of Rochelinval over open ground and without artillery support. During the successful assault the unit lost more than half its remaining men. The Battalion was inactivated on 27 January 1945 and the remaining 110 survivors were absorbed into the 82nd Airborne Division. Virtually nothing of the unit's history was known to the American public until the 1990s when renewed interest prompted its veterans to seek recognition for their costly success at Rochelinval. The battalion was awarded a Presidential Unit Citation in 2001 recognizing its accomplishment.

The 6th Airlanding Brigade was an airborne infantry brigade of the British Army during the Second World War. Created during May 1943, the brigade was composed of three glider infantry battalions and supporting units, and was assigned to the 6th Airborne Division, alongside the 3rd and 5th Parachute Brigades.
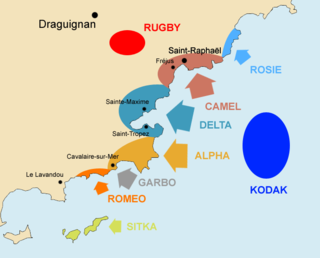
The British 2nd Parachute Brigade was part of the Operation Rugby airborne landings in August 1944. The operation was carried out by an ad hoc airborne formation called the 1st Airborne Task Force. Operation Rugby was itself part of the Operation Dragoon invasion of Southern France by the American 7th Army. The airborne task force landed in the River Argens valley with the objective of preventing German reinforcements from reaching the landing beaches. The landings were mainly an American operation and the brigade was the only British Army formation involved.
The Allied invasion of Italy, a phase of the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, took place on 3 September at Reggio di Calabria, and on 9 September 1943 at Taranto and Salerno. Allied naval forces landed American and Commonwealth troops on the beaches of southern Italy where they faced resistance from Axis forces.

The 11th Parachute Battalion was an airborne infantry battalion of the Parachute Regiment, raised by the British Army in World War II.

The 1st Airlanding Light Regiment was an airborne forces unit of the British Army's Royal Artillery during the Second World War.

The 193rd Glider Infantry Regiment was an airborne infantry regiment of the United States Army during World War II. It was part of the 17th Airborne Division and fought during the Battle of the Bulge.

The 194th Glider Infantry Regiment was a Glider infantry regiment of the United States Army that served in World War II. It was a part of the 17th Airborne Division, and saw active combat service until its deactivation in 1945.
References
Buckeridge, Justin P. Bolt From the Blue: 550th Airborne Battalion 1941–1945 Battery Press 1978