Related Research Articles

The Irish House of Commons was the lower house of the Parliament of Ireland that existed from 1297 until the end of 1800. The upper house was the House of Lords. The membership of the House of Commons was directly elected, but on a highly restrictive franchise, similar to the unreformed House of Commons in contemporary Great Britain. Catholics were disqualified from sitting in the Irish parliament from 1691, even though they comprised the vast majority of the Irish population.

Emily FitzGerald, Duchess of Leinster, known before 1747 as Lady Emily Lennox, from 1747 to 1761 as The Countess of Kildare and from 1761 to 1766 as The Marchioness of Kildare, was the second of the famous Lennox sisters, daughters of Charles Lennox, 2nd Duke of Richmond.

Marquess of Donegall is a title in the Peerage of Ireland held by the head of the Chichester family, originally from Devon, England. Sir John Chichester sat as a Member of Parliament and was High Sheriff of Devon in 1557. One of his sons, Sir Arthur Chichester, was Lord Deputy of Ireland from 1605 to 1616. In 1613, he was raised to the Peerage of Ireland as Baron Chichester, of Belfast in County Antrim. When he died childless in 1625 the barony became extinct.

The Society of United Irishmen was a sworn association in the Kingdom of Ireland formed in the wake of the French Revolution to secure "an equal representation of all the people" in a national government. Despairing of constitutional reform, and in defiance both of British Crown forces and of Irish sectarian division, in 1798 the United Irishmen instigated a republican rebellion. Their suppression was a prelude to the abolition of the Irish Parliament in Dublin and to Ireland's incorporation in a United Kingdom with Great Britain. An attempt, following the Acts of Union, to revive the movement and renew the insurrection led to an abortive rising in Dublin in 1803.

Castleblayney is a town in County Monaghan, Ireland. The town had a population of 3,607 as of the 2016 census. Castleblayney is near the border with County Armagh in Northern Ireland, and lies on the N2 road from Dublin to Derry and Letterkenny.

John Foster, 1st Baron Oriel PC (Ire) was an Anglo-Irish politician and peer who thrice served as Chancellor of the Exchequer of Ireland and also served as the last speaker of the Irish House of Commons.
The Public Record Office of Northern Ireland (PRONI) is situated in Belfast, Northern Ireland. It is a division within the Engaged Communities Group of the Department for Communities (DfC).

The history of Ireland from 1691–1800 was marked by the dominance of the Protestant Ascendancy. These were Anglo-Irish families of the Anglican Church of Ireland, whose English ancestors had settled Ireland in the wake of its conquest by England and colonisation in the Plantations of Ireland, and had taken control of most of the land. Many were absentee landlords based in England, but others lived full-time in Ireland and increasingly identified as Irish.. During this time, Ireland was nominally an autonomous Kingdom with its own Parliament; in actuality it was a client state controlled by the King of Great Britain and supervised by his cabinet in London. The great majority of its population, Roman Catholics, were excluded from power and land ownership under the penal laws. The second-largest group, the Presbyterians in Ulster, owned land and businesses but could not vote and had no political power. The period begins with the defeat of the Catholic Jacobites in the Williamite War in Ireland in 1691 and ends with the Acts of Union 1800, which formally annexed Ireland in a United Kingdom from 1 January 1801 and dissolved the Irish Parliament.

The Lords Justices were deputies who acted collectively in the absence of the chief governor of Ireland as head of the executive branch of the Dublin Castle administration. Lords Justices were sworn in at a meeting of the Privy Council of Ireland.
Hugh McShane O'Neill was an early modern Irish nobleman and rebel associated with the McShanes of Glenconkeyne and Killetra. This group was also called the "Wild Clan Shanes of Killetragh" or the "McShane-O'Neills". His parentage is disputed however he is claimed by some as being either a grandson or great-grandson of Conn O'Neill, 1st Earl of Tyrone, and Gearoid Mór Fitzgerald, 8th Earl of Kildare, and of the primary line of the O'Neill of Tyrone clan.

William Conolly, also known as Speaker Conolly, was an Irish Whig politician, Commissioner of Revenue, lawyer and landowner. He was an influential figure in Irish politics, serving as Speaker of the Irish House of Commons between 1715 and his death.
William Clere Leonard Brendan Parsons, 7th Earl of Rosse, is an Anglo-Irish peer. He is also 10th Baronet Parsons, of Birr Castle.
McShane is a patronymic surname originating in Ireland. Also appears in Scotland and England. The surname evolved from the given name Shane, a derivative of John, of Hebrew origin. Some of the earliest historical records regarding the surname are documented through Hugh McShane O'Neill of the royal O'Neill dynasty.

Carrickfergus is a barony in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is bounded on the south-east by Belfast Lough, and otherwise surrounded by the barony of Belfast Lower. It is coextensive with the civil parish of Carrickfergus or St Nicholas and corresponds to the former county of the town of Carrickfergus, a county corporate encompassing Carrickfergus town.

William James Conolly was an Irish landowner and Whig politician who sat in the Irish House of Commons from 1727 to 1754 and in the British House of Commons from 1734 to 1754.
David George Boyce (1942–2020), also known as George Boyce, was a Northern Irish historian who specialised in Irish history.
Eighteenth-Century Ireland or Iris an dá chultúr, is an annual, peer-reviewed academic journal of eighteenth century Ireland published on behalf of the Eighteenth-Century Ireland Society. The journal was established in 1986. Articles are in English, Irish, or French.
George Evans, 3rd Baron Carbery, known as Hon. George Evans from 1749 to 1759, was an Irish peer. He probably built the house later enlarged as the present Laxton Hall.
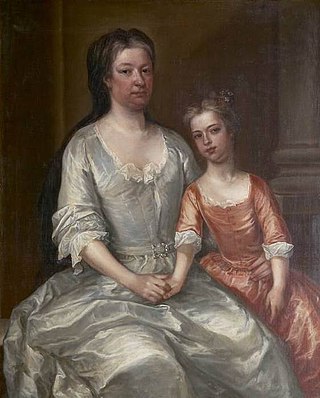
Katherine Conolly was an Irish political hostess, landowner, and philanthropist.

Martha "Matty" McTier was an advocate for women's health and education, and a supporter of democratic reform, whose correspondence with her brother William Drennan and other leading United Irishmen documents the political radicalism and tumult of late eighteenth-century Ireland.
References
- ↑ A.P.W. Malcomson, The Pursuit of the Heiress; Aristocratic Marriage in Ireland 1740-1840, Ulster Historical Foundation (publisher's note).
- ↑ Cormac Ó Gráda, Rough Justice, Dublin Review of Books
- ↑ RIA
- ↑ "University of Limerick honour Irish archivist in conferring ceremony". www.limerickleader.ie. Retrieved 18 January 2023.