Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that the solid is volatile. The compound is colourless, but most samples appear yellow. This is most likely due to the presence of the impurity OsO2, which is yellow-brown in colour. In biology, its property of binding to lipids has made it a widely-used stain in electron microscopy.

The Sharpless epoxidation reaction is an enantioselective chemical reaction to prepare 2,3-epoxyalcohols from primary and secondary allylic alcohols. The oxidizing agent is tert-butyl hydroperoxide. The method relies on a catalyst formed from titanium tetra(isopropoxide) and diethyl tartrate.
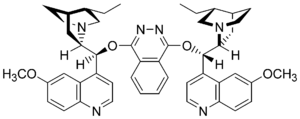
Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation is the chemical reaction of an alkene with osmium tetroxide in the presence of a chiral quinine ligand to form a vicinal diol. The reaction has been applied to alkenes of virtually every substitution, often high enantioselectivities are realized, with the chiral outcome controlled by the choice of dihydroquinidine (DHQD) vs dihydroquinine (DHQ) as the ligand. Asymmetric dihydroxylation reactions are also highly site selective, providing products derived from reaction of the most electron-rich double bond in the substrate.
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to:
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.
In organic chemistry, the Michael reaction or Michael addition describes a reaction between any Michael donor and any Michael acceptor. It belongs to the larger class of conjugate additions and is widely used for the mild formation of C–C bonds. Many asymmetric variants exist and depending on the conditions, Michael Additions can be diastereoselective and/or enantioselective.

(E)-Stilbene, commonly known as trans-stilbene, is an organic compound represented by the condensed structural formula C6H5CH=CHC6H5. Classified as a diarylethene, it features a central ethylene moiety with one phenyl group substituent on each end of the carbon–carbon double bond. It has an (E) stereochemistry, meaning that the phenyl groups are located on opposite sides of the double bond, the opposite of its geometric isomer, cis-stilbene. Trans-stilbene occurs as a white crystalline solid at room temperature and is highly soluble in organic solvents. It can be converted to cis-stilbene photochemically, and further reacted to produce phenanthrene.
Dihydroxylation is the process by which an alkene is converted into a vicinal diol. Although there are many routes to accomplish this oxidation, the most common and direct processes use a high-oxidation-state transition metal. The metal is often used as a catalyst, with some other stoichiometric oxidant present. In addition, other transition metals and non-transition metal methods have been developed and used to catalyze the reaction.

The Peterson olefination is the chemical reaction of α-silyl carbanions with ketones to form a β-hydroxysilane (2) which eliminates to form alkenes (3).
The aza-Baylis–Hillman reaction or aza-BH reaction in organic chemistry is a variation of the Baylis–Hillman reaction and describes the reaction of an electron deficient alkene, usually an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, with an imine in the presence of a nucleophile. The reaction product is an allylic amine. The reaction can be carried out in enantiomeric excess of up to 90% with the aid of bifunctional chiral BINOL and phosphinyl BINOL compounds, for example in the reaction of n-(4-chloro-benzylidene)-benzenesulfonamide with methyl vinyl ketone (MVK) in cyclopentyl methyl ether and toluene at -15°C.
The Rubottom oxidation is a useful, high-yielding chemical reaction between silyl enol ethers and peroxyacids to give the corresponding α-hydroxy carbonyl product. The mechanism of the reaction was proposed in its original disclosure by A.G. Brook with further evidence later supplied by George M. Rubottom. After a Prilezhaev-type oxidation of the silyl enol ether with the peroxyacid to form the siloxy oxirane intermediate, acid-catalyzed ring-opening yields an oxocarbenium ion. This intermediate then participates in a 1,4-silyl migration to give an α-siloxy carbonyl derivative that can be readily converted to the α-hydroxy carbonyl compound in the presence of acid, base, or a fluoride source.
Asymmetric catalytic oxidation is a technique of oxidizing various substrates to give an enantiopure product using a catalyst.
The Upjohn dihydroxylation is an organic reaction which converts an alkene to a cis vicinal diol. It was developed by V. VanRheenen, R. C. Kelly and D. Y. Cha of the Upjohn Company in 1976. It is a catalytic system using N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMO) as stoichiometric re-oxidant for the osmium tetroxide. It is superior to previous catalytic methods.
The Milas hydroxylation is an organic reaction converting an alkene to a vicinal diol, and was developed by Nicholas A. Milas in the 1930s. The cis-diol is formed by reaction of alkenes with hydrogen peroxide and either ultraviolet light or a catalytic osmium tetroxide, vanadium pentoxide, or chromium trioxide.
The Lemieux–Johnson or Malaprade–Lemieux–Johnson oxidation is a chemical reaction in which an olefin undergoes oxidative cleavage to form two aldehyde or ketone units. The reaction is named after its inventors, Raymond Urgel Lemieux and William Summer Johnson, who published it in 1956. The reaction proceeds in a two step manner, beginning with dihydroxylation of the alkene by osmium tetroxide, followed by a Malaprade reaction to cleave the diol using periodate. Excess periodate is used to regenerate the osmium tetroxide, allowing it to be used in catalytic amounts. The Lemieux–Johnson reaction ceases at the aldehyde stage of oxidation and therefore produces the same results as ozonolysis.

Oxoammonium-catalyzed oxidation reactions involve the conversion of organic substrates to more highly oxidized materials through the action of an N-oxoammonium species. Nitroxides may also be used in catalytic amounts in the presence of a stoichiometric amount of a terminal oxidant. Nitroxide radical species used are either 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) or derivatives thereof.
Epoxidation with dioxiranes refers to the synthesis of epoxides from alkenes using three-membered cyclic peroxides, also known as dioxiranes.
The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and a carbon electrophile such as an aldehyde. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as a tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product. It is named for Anthony B. Baylis and Melville E. D. Hillman, two of the chemists who developed this reaction while working at Celanese. This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction, as K. Morita had published earlier work on it.

Potassium osmate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2[OsO2(OH)4]. This diamagnetic purple salt contains osmium in the VI (6+) oxidation state. When dissolved in water a pink solution is formed but when dissolved in methanol, the salt gives a blue solution. The salt gained attention as a catalyst for the asymmetric dihydroxylation of olefins.
In homogeneous catalysis, C2-symmetric ligands refer to ligands that lack mirror symmetry but have C2 symmetry. Such ligands are usually bidentate and are valuable in catalysis. The C2 symmetry of ligands limits the number of possible reaction pathways and thereby increases enantioselectivity, relative to asymmetrical analogues. C2-symmetric ligands are a subset of chiral ligands. Chiral ligands, including C2-symmetric ligands, combine with metals or other groups to form chiral catalysts. These catalysts engage in enantioselective chemical synthesis, in which chirality in the catalyst yields chirality in the reaction product.