An oligopeptide, often just called peptide, consists of two to twenty amino acids and can include dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and pentapeptides. Some of the major classes of naturally occurring oligopeptides include aeruginosins, cyanopeptolins, microcystins, microviridins, microginins, anabaenopeptins, and cyclamides. Microcystins are best studied, because of their potential toxicity impact in drinking water. A review of some oligopeptides found that the largest class are the cyanopeptolins (40.1%), followed by microcystins (13.4%).

Spirulina is a biomass of cyanobacteria that can be consumed by humans and animals. The three species are Arthrospira platensis, A. fusiformis, and A. maxima.

Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthases.

Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they can poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning.
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be made by bacteria inside these organisms. While there exist a wide range of peptides that are not synthesized by ribosomes, the term nonribosomal peptide typically refers to a very specific set of these as discussed in this article.

Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin by humans, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).
Aphanizomenon flos-aquae is a brackish and freshwater species of cyanobacteria found around the world, including the Baltic Sea and the Great Lakes.

Dadiah (Minangkabau) or dadih (Indonesian) a traditional fermented milk popular among people of West Sumatra, Indonesia, is made by pouring fresh, raw, unheated, buffalo milk into a bamboo tube capped with a banana leaf and allowing it to ferment spontaneously at room temperature for two days.
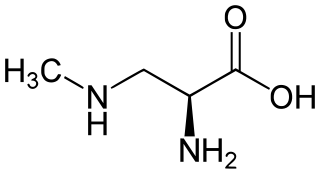
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria. BMAA is a neurotoxin. Its potential role in various neurodegenerative disorders is the subject of scientific research.

Anatoxin-a, also known as Very Fast Death Factor (VFDF), is a secondary, bicyclic amine alkaloid and cyanotoxin with acute neurotoxicity. It was first discovered in the early 1960s in Canada, and was isolated in 1972. The toxin is produced by multiple genera of cyanobacteria and has been reported in North America, South America, Central America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Symptoms of anatoxin-a toxicity include loss of coordination, muscular fasciculations, convulsions and death by respiratory paralysis. Its mode of action is through the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAchR) where it mimics the binding of the receptor's natural ligand, acetylcholine. As such, anatoxin-a has been used for medicinal purposes to investigate diseases characterized by low acetylcholine levels. Due to its high toxicity and potential presence in drinking water, anatoxin-a poses a threat to animals, including humans. While methods for detection and water treatment exist, scientists have called for more research to improve reliability and efficacy. Anatoxin-a is not to be confused with guanitoxin, another potent cyanotoxin that has a similar mechanism of action to that of anatoxin-a and is produced by many of the same cyanobacteria genera, but is structurally unrelated.

Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena, among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of Nodularia spumigena are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Cyanobacteria are composed of many toxic substances, most notably of microcystins and nodularins: the two are not easily differentiated. A significant homology of structure and function exists between the two, and microcystins have been studied in greater detail. Because of this, facts from microcystins are often extended to nodularins.
Microbial toxins are toxins produced by micro-organisms, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, dinoflagellates, and viruses. Many microbial toxins promote infection and disease by directly damaging host tissues and by disabling the immune system. Endotoxins most commonly refer to the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or lipooligosaccharide (LOS) that are in the outer plasma membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. The botulinum toxin, which is primarily produced by Clostridium botulinum and less frequently by other Clostridium species, is the most toxic substance known in the world. However, microbial toxins also have important uses in medical science and research. Currently, new methods of detecting bacterial toxins are being developed to better isolate and understand these toxins. Potential applications of toxin research include combating microbial virulence, the development of novel anticancer drugs and other medicines, and the use of toxins as tools in neurobiology and cellular biology.

Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a toxin produced by cyanobacteria. It is the most toxic of the microcystins.

Planktothrix is a diverse genus of filamentous cyanobacteria observed to amass in algal blooms in water ecosystems across the globe. Like all Oscillatoriales, Planktothrix species have no heterocysts and no akinetes. Planktothrix are unique because they have trichomes and contain gas vacuoles unlike typical planktonic organisms. Previously, some species of the taxon were grouped within the genus Oscillatoria, but recent work has defined Planktothrix as its own genus. A tremendous body of work on Planktothrix ecology and physiology has been done by Anthony E. Walsby, and the 55.6 kb microcystin synthetase gene which gives these organisms the ability to synthesize toxins has been sequenced. P. agardhii is an example of a type species of the genus. P. agardhii and P. rubescens are commonly observed in lakes of the Northern Hemisphere where they are known producers of potent hepatotoxins called microcystins.

Cyclamides are a class of oligopeptides produced by cyanobacteria algae strains such as Microcystis aeruginosa. Some of them can be toxic.
Microcystis is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa. Many members of a Microcystis community can produce neurotoxins and hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Communities are often a mix of toxin-producing and nonproducing isolates.

Microcystis aeruginosa is a species of freshwater cyanobacteria that can form harmful algal blooms of economic and ecological importance. They are the most common toxic cyanobacterial bloom in eutrophic fresh water. Cyanobacteria produce neurotoxins and peptide hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Microcystis aeruginosa produces numerous congeners of microcystin, with microcystin-LR being the most common. Microcystis blooms have been reported in at least 108 countries, with the production of microcystin noted in at least 79.

In biochemistry, non-coded or non-proteinogenic amino acids are distinct from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids which are naturally encoded in the genome of organisms for the assembly of proteins. However, over 140 non-proteinogenic amino acids occur naturally in proteins and thousands more may occur in nature or be synthesized in the laboratory. Chemically synthesized amino acids can be called unnatural amino acids. Unnatural amino acids can be synthetically prepared from their native analogs via modifications such as amine alkylation, side chain substitution, structural bond extension cyclization, and isosteric replacements within the amino acid backbone. Many non-proteinogenic amino acids are important:
Canadian Reference Materials (CRM) are certified reference materials of high-quality and reliability produced by the National Metrology Institute of Canada – the National Research Council Canada. The NRC Certified Reference Materials program is operated by the Measurement Science and Standards portfolio and provides CRMs for environmental, biotoxin, food, nutritional supplement, and stable isotope analysis. The program was established in 1976 to produce CRMs for inorganic and organic marine environmental analysis and remains internationally recognized producer of CRMs.
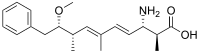
Cyanopeptolins (CPs) are a class of oligopeptides produced by Microcystis and Planktothrix algae strains, and can be neurotoxic. The production of cyanopeptolins occurs through nonribosomal peptides synthases (NRPS).