Cooperative binding occurs in molecular binding systems containing more than one type, or species, of molecule and in which one of the partners is not mono-valent and can bind more than one molecule of the other species. In general, molecular binding is an interaction between molecules that results in a stable physical association between those molecules.

In the fields of biochemistry and pharmacology an allosteric regulator is a substance that binds to a site on an enzyme or receptor distinct from the active site, resulting in a conformational change that alters the protein's activity, either enhancing or inhibiting its function. In contrast, substances that bind directly to an enzyme's active site or the binding site of the endogenous ligand of a receptor are called orthosteric regulators or modulators.
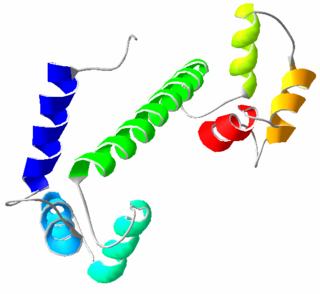
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases.

The N-methyl-D-aspartatereceptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and predominantly Ca2+ ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA and kainate receptors. Depending on its subunit composition, its ligands are glutamate and glycine (or D-serine). However, the binding of the ligands is typically not sufficient to open the channel as it may be blocked by Mg2+ ions which are only removed when the neuron is sufficiently depolarized. Thus, the channel acts as a "coincidence detector" and only once both of these conditions are met, the channel opens and it allows positively charged ions (cations) to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is thought to be very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and mediating learning and memory functions.

An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist.

In biochemistry and molecular biology, a binding site is a region on a macromolecule such as a protein that binds to another molecule with specificity. The binding partner of the macromolecule is often referred to as a ligand. Ligands may include other proteins, enzyme substrates, second messengers, hormones, or allosteric modulators. The binding event is often, but not always, accompanied by a conformational change that alters the protein's function. Binding to protein binding sites is most often reversible, but can also be covalent reversible or irreversible.

Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals including peptides and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.

The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Accurate regulation of GABAergic transmission through appropriate developmental processes, specificity to neural cell types, and responsiveness to activity is crucial for the proper functioning of nearly all aspects of the central nervous system (CNS). Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions.

In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from Latin ligare, which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure.
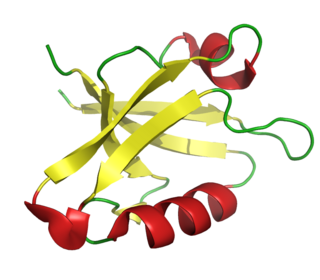
The PDZ domain is a common structural domain of 80-90 amino-acids found in the signaling proteins of bacteria, yeast, plants, viruses and animals. Proteins containing PDZ domains play a key role in anchoring receptor proteins in the membrane to cytoskeletal components. Proteins with these domains help hold together and organize signaling complexes at cellular membranes. These domains play a key role in the formation and function of signal transduction complexes. PDZ domains also play a highly significant role in the anchoring of cell surface receptors to the actin cytoskeleton via mediators like NHERF and ezrin.

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction.
Allosteric enzymes are enzymes that change their conformational ensemble upon binding of an effector which results in an apparent change in binding affinity at a different ligand binding site. This "action at a distance" through binding of one ligand affecting the binding of another at a distinctly different site, is the essence of the allosteric concept. Allostery plays a crucial role in many fundamental biological processes, including but not limited to cell signaling and the regulation of metabolism. Allosteric enzymes need not be oligomers as previously thought, and in fact many systems have demonstrated allostery within single enzymes. In biochemistry, allosteric regulation is the regulation of a protein by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site.

The sigma-1 receptor (σ1R), one of two sigma receptor subtypes, is a chaperone protein at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that modulates calcium signaling through the IP3 receptor. In humans, the σ1 receptor is encoded by the SIGMAR1 gene.

The calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a Class C G-protein coupled receptor which senses extracellular levels of calcium ions. It is primarily expressed in the parathyroid gland, the renal tubules of the kidney and the brain. In the parathyroid gland, it controls calcium homeostasis by regulating the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH). In the kidney it has an inhibitory effect on the reabsorption of calcium, potassium, sodium, and water depending on which segment of the tubule is being activated.
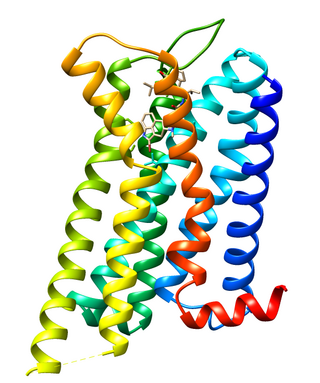
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the DRD2 gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, including those of Solomon H. Snyder and Philip Seeman used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined.
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimuli. Some of them, like benzodiazepines or alcohol, function as psychoactive drugs. The site that an allosteric modulator binds to is not the same one to which an endogenous agonist of the receptor would bind. Modulators and agonists can both be called receptor ligands.

Therapeutic Target Database (TTD) is a pharmaceutical and medical repository constructed by the Innovative Drug Research and Bioinformatics Group (IDRB) at Zhejiang University, China and the Bioinformatics and Drug Design Group at the National University of Singapore. It provides information about known and explored therapeutic protein and nucleic acid targets, the targeted disease, pathway information and the corresponding drugs directed at each of these targets. Detailed knowledge about target function, sequence, 3D structure, ligand binding properties, enzyme nomenclature and drug structure, therapeutic class, and clinical development status. TTD is freely accessible without any login requirement at https://idrblab.org/ttd/.

Catabolite Control Protein A (CcpA) is a master regulator of carbon metabolism in gram-positive bacteria. It is a member of the LacI/GalR transcription regulator family. In contrast to most LacI/GalR proteins, CcpA is allosterically regulated principally by a protein-protein interaction, rather than a protein-small molecule interaction. CcpA interacts with the phosphorylated form of Hpr and Crh, which is formed when high concentrations of glucose or fructose-1,6-bisphosphate are present in the cell. Interaction of Hpr or Crh modulates the DNA sequence specificity of CcpA, allowing it to bind operator DNA to modulate transcription. Small molecules glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate are also known allosteric effectors, fine-tuning CcpA function.

Ruth Nussinov is an Israeli-American biologist born in Rehovot who works as a professor in the Department of Human Genetics, School of Medicine at Tel Aviv University and is the senior principal scientist and principal investigator at the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health. Nussinov is also the editor in chief of the Current Opinion in Structural Biology and formerly of the journal PLOS Computational Biology.
Arthur Christopoulos is an Australian Professor of Analytical Pharmacology at Monash University. He was a Councillor of the International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology from 2018 to 2022. In 2019 he was appointed Dean of Monash University's Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences and from 2021 to 2023 he served as the inaugural Director of Monash University's Neuromedicines Discovery Centre. He was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science in 2021.















