ABR, RhoGEF and GTPase activating protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABR gene. [5]
ABR, RhoGEF and GTPase activating protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABR gene. [5]
The ABR activator of RhoGEF and GTPase, also symbolized as ABR, gene is located on Chromosome 11 and has a reported 13 alternatively spliced transcript variants. [6] This gene is found to have ubiquitous expression within 23 human tissues, including the heart and brain. [7] The protein encoded by ABR shares homology with the Breakpoint Cluster Region (BCR) gene located on chromosome 22 and has shown to share similar protein functions. [8] Additionally, the protein encoded by this gene contains a GTPase-activating protein domain, a domain found in members of the Rho family of GTP-binding proteins. The ABR gene is an inhibitor of ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1), a protein found to influence cell growth, motility of the cell, and maintain adhesion to neighboring epithelial cells. [9] Recent papers suggest ABR has tumor suppressor properties in Leukemia because of its role as a RAC1 inhibitor and is being researched as a potential therapy treatment in Leukemia patients. [10] Other studies suggest ABR plays an important role in vestibular morphogenesis. [11]
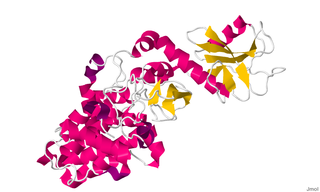
Chimerin 1 (CHN1), also known as alpha-1-chimerin, n-chimerin, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CHN1 gene.
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small signaling G proteins, and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic kingdoms, including yeasts and some plants. Three members of the family have been studied in detail: Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. All G proteins are "molecular switches", and Rho proteins play a role in organelle development, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell movement, and other common cellular functions.

Cell division control protein 42 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDC42 gene. Cdc42 is involved in regulation of the cell cycle. It was originally identified in S. cerevisiae (yeast) as a mediator of cell division, and is now known to influence a variety of signaling events and cellular processes in a variety of organisms from yeast to mammals.

FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain-containing protein 1 (FGD1) also known as faciogenital dysplasia 1 protein (FGDY), zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 3 (ZFYVE3), or Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor FGD1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGD1 gene that lies on the X chromosome. Orthologs of the FGD1 gene are found in dog, cow, mouse, rat, and zebrafish, and also budding yeast and C. elegans. It is a member of the FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing family.

Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor TIAM1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TIAM1 gene.
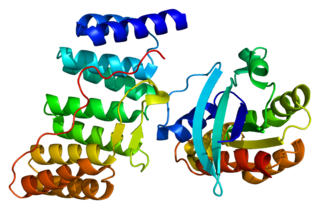
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 3 (Rac3) is a G protein that in humans is encoded by the RAC3 gene. It is an important component of intracellular signalling pathways. Rac3 is a member of the Rac subfamily of the Rho family of small G proteins. Members of this superfamily appear to regulate a diverse array of cellular events, including the control of cell growth, cytoskeletal reorganization, and the activation of protein kinases.

Rho GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ARHGAP1 gene.

RhoGEF domain describes two distinct structural domains with guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity to regulate small GTPases in the Rho family. Rho small GTPases are inactive when bound to GDP but active when bound to GTP; RhoGEF domains in proteins are able to promote GDP release and GTP binding to activate specific Rho family members, including RhoA, Rac1 and Cdc42.

Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGEF7 gene.

Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 6 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ARHGEF6 gene.

Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGDIA gene.

Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGEF12 gene. This protein is also called RhoGEF12 or Leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (LARG).

RhoG is a small monomeric GTP-binding protein, and is an important component of many intracellular signalling pathways. It is a member of the Rac subfamily of the Rho family of small G proteins and is encoded by the gene RHOG.

Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 2 (Dock2) is a protein encoded in the human by the DOCK2 gene. Dock2 is a large protein involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-A subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which function as activators of small G-proteins. Dock2 specifically activates isoforms of the small G protein Rac.

Rho GTPase-activating protein 32 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RICS gene. RICS has two known isoforms, RICS that are expressed primarily at neurite growth cones, and at the post synaptic membranes, and PX-RICS which is more widely expressed in the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and endosomes. The only known domain of the RICS is the RhoGAP domain, whilst PX-RICS has an additional Phox homology and SH3 domain.

Dedicator of cytokinesis protein (Dock7) is a large protein encoded in the human by the DOCK7 gene, involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-C subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which function as activators of small G-proteins. Dock7 activates isoforms of the small G protein Rac.

Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 4 (Dock4), is a large protein encoded in the human by the DOCK4 gene, involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-B subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which function as activators of small G-proteins. Dock4 activates the small G proteins Rac and Rap1.

Cdc42 effector protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDC42EP2 gene.

Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 6 (Dock6), also known as Zir1 is a large protein encoded in the human by the DOCK6 gene, involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-C subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors which function as activators of small G-proteins.

The Rho GTPase activating protein 31 is encoded in humans by the ARHGAP31 gene. It is a Cdc42/Rac1 GTPase regulator.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.