
Congo red is an organic compound, the sodium salt of 3,3′-([1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(4-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid). It is an azo dye. Congo red is water-soluble, yielding a red colloidal solution; its solubility is greater in organic solvents. The use of Congo red in the textile industry has long been abandoned, primarily because of its carcinogenic properties, but it is still used for histological staining.

Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.

An acid dye is a dye that is typically applied to a textile at low pH. They are mainly used to dye wool, not cotton fabrics. Some acid dyes are used as food colorants, and some can also be used to stain organelles in the medical field.

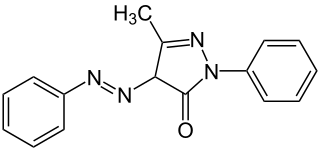
Mordant red 19 is an organic compound with the chemical formula C16H13ClN4O5S. It is classified as an azo dye.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated carbon act as a nucleophile. In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic.
Trypan blue is an azo dye. It is a direct dye for cotton textiles. In biosciences, it is used as a vital stain to selectively colour dead tissues or cells blue.

Sudan III is a lysochrome diazo dye. It is structurally related to azobenzene.
A substantive dye or direct dye is a dye that adheres to its substrate, typically a textile, by non-ionic forces.
Solvent Black 3 is an azo dye. It is a non-fluorescent, relatively thermostable lysochrome diazo dye used for staining of neutral triglycerides and lipids on frozen sections and some lipoproteins on paraffin sections. It has the appearance of a dark brown to black powder with maximum absorption at 596–605 nm and melting point 120–124 °C. It stains blue-black.
Sudan Yellow 3G, also known as Solvent Yellow 16, C.I. disperse yellow and C.I. 12700, is a yellow azo dye. It is soluble in fats and oils.

Sulfanilic acid (4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid) is an organic compound with the formula H3NC6H4SO3. It is an off-white solid. It is a zwitterion, which explains its high melting point. It is a common building block in organic chemistry.

Acid Orange 7, also known as 2-naphthol orange is an azo dye. It is used for dyeing wool.

Direct Blue 1 is an organic compound that is one of many azo dyes. This salt is used as a substantive dye for textiles with high contents of cellulose, i.e. cotton. It is prepared by the azo coupling of the aminonaphthalene and diazotized derivative of o-dianisidine.

Acid red 88 is an azo dye. Due to its intense colour, solid samples appear almost black. It is used to dye cotton textiles red. A closely related acid dye is Acid Red 13.
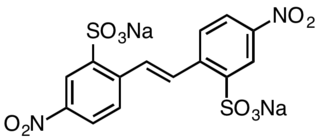
Disodium 4,4′-dinitrostilbene-2,2′-disulfonate is an organic compound with the formula (O2NC6H3(SO3Na)CH)2. This salt is a common precursor to a variety of textile dyes and optical brighteners
Direct Blue 15 is an organic compound that is classified as an azo dye. It is a dark blue water soluble solid. It is a popular substantive dye, which means that it useful for dying cotton and related cellulosic materials. It is produced by azo coupling of o-dianisidine with the appropriate naphthalene disulfonate.

N-Ethyl-N-(2-chloroethyl)aniline is the organic compound with the formula C6H5N(Et)(CH2CH2Cl) (Et = ethyl). It is a low-melting colorless solid that is an alkylating agent. The compound is a precursor to several cationic azo dyes via reaction of the chloroethyl group with tertiary amines or pyridine followed by azo coupling. Examples of derived dyes include C. I. Basic Red 18, Maxilon Red 2GL, and Yoracryl Red 2G.
Basic Red 18 is a cationic azo dye used for coloring textiles. The chromophore is the cation, which contains many functional groups, but most prominently the quaternary ammonium center.
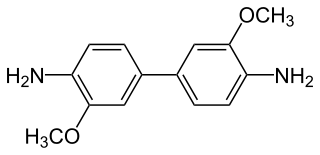
o-Dianisidine is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3O)(H2N)C6H3]2. A colorless or white solid, it is a bifunctional compound derived via the benzidine rearrangement from o-anisidine.













