
Acne, also known as acne vulgaris, is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide.

Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Dandruff is a milder form of the condition without inflammation.

The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.

Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), sometimes known as acne inversa or Verneuil's disease, is a long-term dermatological condition characterized by the occurrence of inflamed and swollen lumps. These are typically painful and break open, releasing fluid or pus. The areas most commonly affected are the underarms, under the breasts, and the groin. Scar tissue remains after healing. HS may significantly limit many everyday activities, for instance, walking, hugging, moving, and sitting down. Sitting disability may occur in patients with lesions in sacral, gluteal, perineal, femoral, groin or genital regions; and prolonged periods of sitting down itself can also worsen the condition of the skin of these patients.

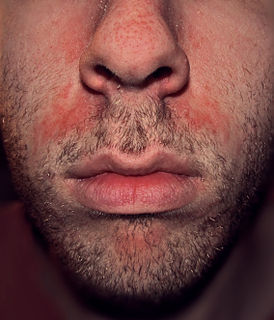
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarged nose may occur in severe disease, a condition known as rhinophyma.

Acne keloidalis nuchae is a destructive scarring folliculitis that occurs almost exclusively on the occipital scalp of people of African descent, primarily men.
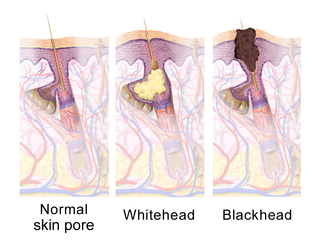
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word "comedo" comes from the Latin comedere, meaning "to eat up", and was historically used to describe parasitic worms; in modern medical terminology, it is used to suggest the worm-like appearance of the expressed material.

Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) presents with itchy red small bumps on sun-exposed skin, particularly face, neck, forearms and legs. It generally appears 30 minutes to a few hours after sun exposure and may last between one and 14 days. The bumps may become small blisters or plaques and may appear bloody. It tends not leave scarring.
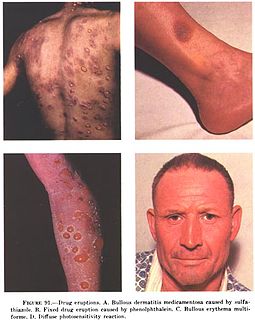
In medicine, a drug eruption is an adverse drug reaction of the skin. Most drug-induced cutaneous reactions are mild and disappear when the offending drug is withdrawn. These are called "simple" drug eruptions. However, more serious drug eruptions may be associated with organ injury such as liver or kidney damage and are categorized as "complex". Drugs can also cause hair and nail changes, affect the mucous membranes, or cause itching without outward skin changes.
Madarosis is a condition that results in the loss of eyelashes, and sometimes eyebrows. The term "madarosis" is derived from the ancient Greek "madaros", meaning "bald". It originally was a disease of only losing eyelashes but it currently is the loss of both eyelashes and eyebrows. Eyebrows and eyelashes are both important in the prevention of bacteria and other foreign objects from entering the eye. A majority of patients with madarosis have leprosy, and it was reported that 76% of patients with varying types of leprosy had madarosis.
Acne conglobata is a highly inflammatory disease presenting with comedones, nodules, abscesses, and draining sinus tracts.
Acne aestivalis also known as acne mallorca, is a special kind of polymorphous light eruption induced by ultra violet A radiation. This condition is said to be seasonal, usually affecting people in springtime and goes away in autumn when there is less sun light. This photo induced skin reaction leads to a monomorphous eruption that consists of multiple, uniform, red, papular lesions. This skin reaction is classified as a delayed-type hypersensitivity because the onset is 24–72 hours after sun exposure. The condition equally affects men and women between the ages of 20–40 years old with no prior history of acne vulgaris. The eruption is unusual because it spares the face but it affects the lateral aspects of the upper arms, shoulder girdle, back, and chest. This condition's pathogenesis is not very well understood but scientists believe it an unfortunate side effect that results from a strong immune response to potentially cancer-causing cell damage.

Neonatal acne, also known as acne neonatorum, is an acneiform eruption that occurs in newborns or infants within the first 4-6 weeks of life, and presents with open and closed comedones on the cheeks, chin and forehead.
Halogen acne is caused by iodides, bromides and fluorides (halogens) that induce an acneiform eruption similar to that observed with steroids.
Acne mechanica is an acneiform eruption that has been observed after repetitive physical trauma to the skin such as rubbing, occurring from clothing or sports equipment. In addition to those mechanisms, the skin not getting enough exposure to air also contributes to the formation of acne mechanica. It is often mistaken as a rash that forms on sweaty skin that is constantly being rubbed, but in reality, it is a breakout of acne mechanica. The term "acne" itself describes the occurrence in which hair follicles in the skin get clogged by oil, dead skin cells, dirt and bacteria, or cosmetic products and create a pimple. Pimples can vary in type, size, and shape, but the sole basis of them occurring is the same - the oil gland in the pore becomes clogged and sometimes infected, which creates pus in order to fight the infection and subsequently causes the development of swollen, red lesions on the skin.
Acne miliaris necrotica is a rare condition consisting of follicular vesicopustules, sometimes occurring as solitary lesions that are usually very itchy. The condition affects middle aged and elderly individuals. Affected areas can include the scalp, frontal hairline, face, and chest.
Infantile acne is a form of acneiform eruption that occurs in infants from 6 weeks to 1 year of age. Typical symptoms include inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions, papules and pustules most commonly present on the face. No cause of infantile acne has been established but it may be caused by increased sebaceous gland secretions due to elevated androgens, genetics and the fetal adrenal gland causing increased sebum production. Infantile acne can resolve by itself by age 1 or 2 however treatment options include topical benzyl peroxide, topical retinoids and topical antibiotics in most cases.
Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (CGPD), is a rare benign granulomatous skin disease of unknown cause. The disorder was first described in 1970 by Gianotti in a case series of five children. CGPD is more common in boys than girls.










