
Daunorubicin, also known as daunomycin, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Specifically it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and Kaposi's sarcoma. It is administered by injection into a vein. A liposomal formulation known as liposomal daunorubicin also exists.

Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is also used for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. It is used by mouth or injection into a vein.

Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the form of its hydrochloride salt to treat ovarian cancer, lung cancer and other cancer types.
Topoisomerase inhibitors are chemical compounds that block the action of topoisomerases, which are broken into two broad subtypes: type I topoisomerases (TopI) and type II topoisomerases (TopII). Topoisomerase plays important roles in cellular reproduction and DNA organization, as they mediate the cleavage of single and double stranded DNA to relax supercoils, untangle catenanes, and condense chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. Topoisomerase inhibitors influence these essential cellular processes. Some topoisomerase inhibitors prevent topoisomerases from performing DNA strand breaks while others, deemed topoisomerase poisons, associate with topoisomerase-DNA complexes and prevent the re-ligation step of the topoisomerase mechanism. These topoisomerase-DNA-inhibitor complexes are cytotoxic agents, as the un-repaired single- and double stranded DNA breaks they cause can lead to apoptosis and cell death. Because of this ability to induce apoptosis, topoisomerase inhibitors have gained interest as therapeutics against infectious and cancerous cells.

DNA topoisomerase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TOP1 gene. It is a DNA topoisomerase, an enzyme that catalyzes the transient breaking and rejoining of a single strand of DNA.

6-Diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON) is a glutamine antagonist, which was isolated originally from Streptomyces in a sample of Peruvian soil. This diazo compound is biosynthesized from lysine by three enzymes in bacteria. It is one of the most famous non-proteinogenic amino acid and was characterized in 1956 by Henry W Dion et al., who suggested a possible use in cancer therapy. This antitumoral efficacy was confirmed in different animal models. DON was tested as chemotherapeutic agent in different clinical studies, but was never approved. In 2019, DON was shown to kill tumor cells while reversing disease symptoms and improve overall survival in late-stage experimental glioblastoma in mice, when combined with calorie-restricted ketogenic diet.

Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors are a class of medical drugs that are mainly used to treat advanced cancers. They function by inhibiting one or more of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes, which are part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This signal pathway regulates cellular functions such as growth and survival. It is strictly regulated in healthy cells, but is always active in many cancer cells, allowing the cancer cells to better survive and multiply. PI3K inhibitors block the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and thus slow down cancer growth. They are examples of a targeted therapy. While PI3K inhibitors are an effective treatment, they can have very severe side effects and are therefore only used if other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
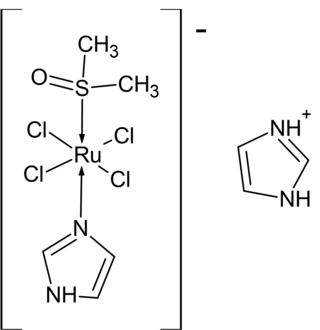
NAMI-A is the imidazolium]] salt of the coordination complex [RuCl4(dmso)(C3N2H4)]− where dmso is dimethylsulfoxide and C3N2H4 is imidazole Together with KP1019 and BOLD-100, NAMI-A has been investigated as an anticancer agent.
Angiokinase inhibitors are a new therapeutic target for the management of cancer. They inhibit tumour angiogenesis, one of the key processes leading to invasion and metastasis of solid tumours, by targeting receptor tyrosine kinases. Examples include nintedanib, afatinib and motesanib.
Onartuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.

Tasquinimod is an experimental drug currently being investigated for the treatment of solid tumors. Tasquinimod has been mostly studied in prostate cancer, but its mechanism of action suggests that it could be used to treat other cancers. Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), formerly called hormone-resistant or hormone-refractory prostate cancer, is prostate cancer that grows despite medical or surgical androgen deprivation therapy. Tasquinimod targets the tumor microenvironment and counteracts cancer development by inhibiting angiogenesis and metastasis and by modulating the immune system. It is now in phase III development, following successful phase II trial outcomes.

Isatuximab, sold under the brand name Sarclisa, is a monoclonal antibody (mAb) medication for the treatment of multiple myeloma.

Saracatinib (AZD-0530) is an experimental drug being developed by AstraZeneca. It acts as a dual kinase inhibitor, with selective actions as a Src inhibitor and a Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitor.
FOLFOXIRI is a chemotherapy regimen for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. The role of FOLFOXIRI in colorectal cancer has been reviewed.

Melphalan flufenamide, sold under the brand names Pepaxto and Pepaxti, is an anticancer medication used to treat multiple myeloma.
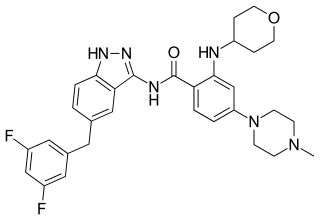
Entrectinib, sold under the brand name Rozlytrek, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer and NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors. It is a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), of the tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) A, B and C, C-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK).

Etirinotecan pegol is a drug developed by Nektar Therapeutics for the treatment of certain kinds of breast cancer with brain metastases. The European Medicines Agency refused to grant it a marketing authorisation in 2017.

Irosustat is an orally active, irreversible, nonsteroidal inhibitor of steroid sulfatase (STS) and member of the aryl sulfamate ester class of drugs that was under development by Sterix Ltd and Ipsen for the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, and endometrial cancer but has not yet been marketed. The drug was first designed and synthesized in the group of Professor Barry V L Potter at the Department of Pharmacy & Pharmacology, University of Bath, working together with Professor Michael J. Reed at Imperial College, London and its initial development was undertaken through the university spin-out company Sterix Ltd and overseen by Cancer Research UK (CRUK). Results of the "first-in-class" clinical trial in breast cancer of an STS inhibitor in humans were published in 2006 and dose optimisation studies and further clinical data have been reported.

Indisulam is a chloroindolyl sulfonamide cell cycle inhibitor that exhibits antitumor activity in vitro and in an animal model. This compound affects cell cycle progression in human tumor cells and is being studied for the treatment of cancers such as melanomas and blood-borne cancers such as leukemia.

Lurbinectedin, sold under the brand name Zepzelca, is a medication used for the treatment of small cell lung cancer.
















