| Acrochaetiales | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rhodochorton purpureum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Archaeplastida |
| Division: | Rhodophyta |
| Class: | Florideophyceae |
| Subclass: | Nemaliophycidae |
| Order: | Acrochaetiales Feldmann [1] |
| Families | |
| Acrochaetiales | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rhodochorton purpureum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Archaeplastida |
| Division: | Rhodophyta |
| Class: | Florideophyceae |
| Subclass: | Nemaliophycidae |
| Order: | Acrochaetiales Feldmann [1] |
| Families | |
Acrochaetiales contains two families and six genera: [1]

Porphyra is a coldwater seaweed that grows in cold, shallow seawater. More specifically, it belongs to red algae phylum of laver species, comprising approximately 70 species. It grows in the intertidal zone, typically between the upper intertidal zone and the splash zone in cold waters of temperate oceans. In East Asia, it is used to produce the sea vegetable products nori and gim. There are considered to be 60 to 70 species of Porphyra worldwide and seven around Britain and Ireland where it has been traditionally used to produce edible sea vegetables on the Irish Sea coast. Porphyra is a chief source of plant-based vitamin B12.

Chordariaceae is a family of brown algae. Members of this family are may be filamentous, crustose with fused cells at the base, or they may be terete and differentiated into a central medulla and an outer photosynthetic cortex. They have a sporphytic thallus usually aggregated to form a pseudo-parenchyma.

Saccharina is a genus of 24 species of Phaeophyceae. It is found in the north Atlantic Ocean and the northern Pacific Ocean at depths from 8 m to 30 m.

Saccharina japonica is a marine species of the Phaeophyceae plant, a type of kelp or seaweed, which is extensively cultivated on ropes between the seas of China, Japan and Korea. It is widely eaten in East Asia. A commercially important species, S. japonica is also called ma-konbu (真昆布) in Japanese, dasima (다시마) in Korean and hǎidài (海带) in Chinese. Large harvests are produced by rope cultivation which is a simple method of growing seaweeds by attaching them to floating ropes in the ocean.
Onslowiaceae is the only family in order Onslowiales in the brown algae. The family contains only the genera Onslowia and Verosphacela.
Nemoderma is the only genus in the family Nemodermataceae and order Nemodermatales of the brown algae. The genus contains only a single species, Nemoderma tingitanum.

Rhodomelaceae is estimated to be the largest red algae family, with about 125 genera and over 700 species.

Rhodymenia is a genus of red algae, containing the following species:

Laurencia is a genus of red algae that grow in temperate and tropical shore areas, in littoral to sublittoral habitats, at depths up to 65 m (213 ft).

Hapalidiaceae is a family of red alga belonging to the order Corallinales.
The Mesotaeniaceae are a small family of unicellular green algae known as the "saccoderm desmids". The Mesotaeniaceae appear to be sister or ancestral to the Zygnemataceae. The desmids are a deep branching group of Zygnemataceae. Spirotaenia was found to be a basal green alga.
Sirodotia Kylin (1912) is a genus of freshwater red alga which was described by Kylin in 1912. The family Batrachospermaceae belongs to the order Batrachospermales and has six well known genera namely Batrachospermum, Kumanoa, Sirodotia, Nothocladus, Tuomeya, and Sheathia. The morphology of the gametophyte of Batrachospermum, Sirodotia, Tuomeya, and Nothocladus are more are less similar to each other. Necchi and Entwisle (1990) proposed to delimit them from generic level to section level of genus Batrachospermum. Sheathia was the member of genus Batrachospermum and has risen to generic level. phylogenetic studies revealed a distinctive genus level of the above with full support in bootstrap analysis and Sirodotia has been raised to generic level.
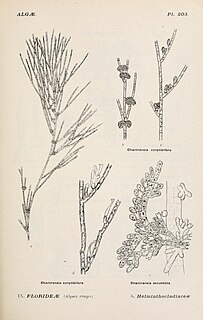
Acrochaetium is a genus of marine red alga.

Batrachospermaceae is a family of fresh water red algae (Rhodophyta). Genera within the Batrachospermaceae generally have a "Lemanea-type" life history with carpospores germinating to produce chantransia. Sporophyte phase with meiosis occurs in an apical cell to produce the gametophyte stage. Pit connections have two pit plug cap layers with the other layer enlarged. This family of freshwater red algae is uniaxial, meaning each filament with a single apical cell. The genera included within Batrachospermaceae are listed in the table below.

Phyllophoraceae is a family of red algae in the order Gigartinales.

Timothy John Entwisle, is an Australian botanist, much of whose research work is in phycology (algae). See for example the articles. He was awarded a Ph.D. from La Trobe University in 1986 for work on the taxonomy of Vaucheria.
Entwisleia is a genus in the red algae family, Entwisleiaceae. There is just one species in this genus, Entwisleia bella, from southeastern Tasmania and represents both a new family and a new order in the Nemaliophycidae.

Crouania is a genus of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the Callithamniaceae family. The name of the genus honours the Crouan brothers, Pierre-Louis Crouan and Hippolyte-Marie Crouan. It was first described by Jacob Georg Agardh in 1842, and the type species is Crouania attenuata.