 |
|---|
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is divided into cantons, which group the communes (=municipalities). A dozen of the communes have official city status, and one, Luxembourg City, is further divided into quarters (unofficial subdivision).
Contents

 |
|---|
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is divided into cantons, which group the communes (=municipalities). A dozen of the communes have official city status, and one, Luxembourg City, is further divided into quarters (unofficial subdivision).

Luxembourg was divided into three districts until October 2015:
There are a total of 12 cantons, which were previously a subdivision of the districts but are now the first-level subdivision of Luxembourg.
The communes (municipalities) are the lowest administrative division in Luxembourg.
12 communes have legal city status, some since the early Middle Ages. The City of Luxembourg, the nation's capital, is the largest city in the country.
Below the official administrative level of the commune, Luxembourg City has further unofficial administrative subdivisions, known as quarters. The twenty-four quarters of Luxembourg City are a de facto subdivision without legal basis used to simplify public administration.
Administrative divisions are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divided. Such a unit usually has an administrative authority with the power to take administrative or policy decisions for its area.
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French comté denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count (earl) or a viscount. Literal equivalents in other languages, derived from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including comté, contea, contado, comtat, condado, Grafschaft, graafschap, and zhupa in Slavic languages; terms equivalent to 'commune' or 'community' are now often instead used.
An arrondissement is any of various administrative divisions of France, Belgium, Haiti, certain other Francophone countries, as well as the Netherlands.
Belgium comprises 581 municipalities, 300 of them grouped into five provinces in Flanders and 262 others in five provinces in Wallonia, while the remaining 19 are in the Brussels Capital Region, which is not divided in provinces. In most cases, the municipalities are the smallest administrative subdivisions of Belgium, but in municipalities with more than 100,000 inhabitants, on the initiative of the local council, sub-municipal administrative entities with elected councils may be created. As such, only Antwerp, having over 500,000 inhabitants, became subdivided into nine districts. The Belgian arrondissements, an administrative level between province and municipality, or the lowest judicial level, are in English sometimes called districts as well.

A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.

The administrative divisions of France are concerned with the institutional and territorial organization of French territory. These territories are located in many parts of the world. There are many administrative divisions, which may have political, electoral (districts), or administrative objectives. All the inhabited territories are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council and their citizens have French citizenship and elect the President of France.
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared with other administrative divisions such as counties, departments, or provinces. Internationally, the most politically important cantons are the Swiss cantons. As the constituents of the Swiss Confederation, theoretically and historically, they are semi-sovereign states.

Municipalities are the lowest level of administrative division in Switzerland. Each municipality is part of one of the Swiss cantons, which form the Swiss Confederation. In most cantons, municipalities are also part of districts or other sub-cantonal administrative divisions.

Districts of Switzerland are a political subdivision for cantons. In the federally constituted Switzerland, each canton is completely free to decide its own internal organisation. Therefore, there exists a variety of structures and terminology for the subnational entities between canton and municipality, loosely termed districts. Most cantons are divided into Bezirke. They are also termed Ämter, Amtsbezirke, district or distretto. The Bezirke generally provide only administration and court organization. However, for historical reasons districts in cantons Graubünden and Schwyz are their own legal entities with jurisdiction over tax and often have their own Landsgemeinde.
The 12 cantons of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg are subdivisions at the first level of local administrative unit (LAU-1) in the European Union's Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics for Eurostat purposes. They were subdivisions of the three districts of Luxembourg until 2015, when the district level of government was abolished. The cantons are in turn subdivided into 100 communes.
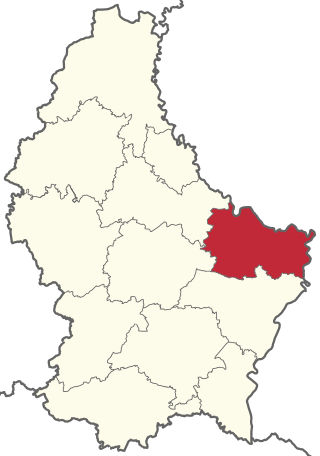
Echternach is a canton in the east of Luxembourg. Its capital is Echternach.

An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.

A municipiu is a level of administrative subdivision in Romania and Moldova, roughly equivalent to city in some English-speaking countries.

Romania's administration is relatively centralized and administrative subdivisions are therefore fairly simplified.

Luxembourg's 100 communes conform to LAU Level 2 and are the country's lowest administrative divisions.
The Swiss Confederation comprises the 26 cantons of Switzerland.

The administrative division of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The territory of Poland is divided into voivodeships (provinces); these are further divided into powiats, and these in turn are divided into gminas. Major cities normally have the status of both gmina and powiat. Poland currently has 16 voivodeships, 380 powiats, and 2,478 gminas.
Administrative divisions of the Kingdom of Cambodia have several levels. Cambodia is divided into 24 provinces and the special administrative unit and capital of Phnom Penh. Though a different administrative unit, Phnom Penh is at provincial level, so de facto Cambodia has 25 provinces and municipalities.
Subdivisions of the canton of Ticino, Switzerland, are the 108 comuni grouped into 38 circoli, which in turn form a part or the whole of one of the eight districts.