Related Research Articles
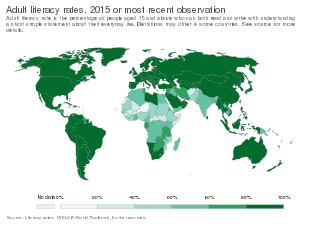
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, humans in literate societies have sets of practices for producing and consuming writing, and they also have beliefs about these practices. Reading, in this view, is always reading something for some purpose; writing is always writing something for someone for some purpose. Beliefs about reading and writing and their value for society and for the individual always influence the ways literacy is taught, learned, and practiced.

Adult education, distinct from child education, is a practice in which adults engage in systematic and sustained self-educating activities in order to gain new forms of knowledge, skills, attitudes, or values. It can mean any form of learning adults engage in beyond traditional schooling, encompassing basic literacy to personal fulfillment as a lifelong learner, and to ensure the fulfillment of an individual.
The history of education in Africa can be roughly divided into pre- and post- colonial periods. Since the introduction of formal education to Africa by European colonists, African education, particularly in West and Central Africa, is characterised by both traditional African teachings and European-style schooling systems. The state of education reflects not only the effects of colonialism, but instability resulting from and exacerbated by armed conflicts in many regions of Africa as well as fallout from humanitarian crises such as famine, lack of drinking water, and outbreaks of diseases such as malaria and Ebola, among others. Although the quality of education and the quantity of well-equipped schools and teachers has steadily increased since the onset of the colonial period, there are still numerous inequalities evident in the existing educational systems based on region, economic status, and gender.

Molly Melching is the founder and Creative Director of the Tostan Community Empowerment Program (CEP). Tostan is a non-governmental organization (NGO) headquartered in Dakar, Senegal whose mission is to empower African communities to bring about sustainable development and positive social transformation based on respect for human rights. Her website, Tostan.org, states "Tostan implements a holistic, three-year empowering education program in African national languages that has engaged over 3,500 rural communities in eight African countries on themes of democracy, human rights, health, literacy, and project management skills". These themes include the abandonment of female genital cutting, the abolishment of child/forced marriage, and female empowerment in leadership positions such as leadership positions in countries across West and East Africa.
Family literacy is a method of education. Relatively new, family literacy is being put into practice in the United States, Canada, and South Africa.
Human rights education (HRE) is the learning process that seeks to build up knowledge, values, and proficiency in the rights that each person is entitled to. This education teaches students to examine their own experiences from a point of view that enables them to integrate these concepts into their values, decision-making, and daily situations. According to Amnesty International, HRE is a way to empower people, training them so their skills and behaviors will promote dignity and equality within their communities, societies, and throughout the world.

The All Pakistan Women's Association, or APWA, as it is commonly known, is a voluntary, non-profit and non-political Pakistani organisation whose fundamental aim is the promotion of moral, social and economic welfare of the women of Pakistan.

Tostan is a US-registered 501(c)(3) international non-governmental organization headquartered in Dakar, Senegal. The organization's mission is "to empower communities to develop and achieve their vision for the future and inspire large-scale movements leading to dignity for all" in several West African countries, including Senegal, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, The Gambia, Mali, and Mauritania.
The Barli Development Institute for Rural Women in Indore is a Baháʼí inspired, though independent residential vocational education school providing programs for women in the vicinity of the city of Indore, India in the state of Madhya Pradesh as well as a base for outreach/non-residential training centers.
The UNESCO Confucius Prize for Literacy recognizes the activities of outstanding individuals, governments or governmental agencies and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) working in literacy serving rural adults and out-of-school youth, particularly women and girls. The Prize was established in 2005 through the support of the Government of the People's Republic of China in honour of the great Chinese scholar Confucius. It is part of the International Literacy Prizes, which UNESCO awards every year in recognition of excellence and inspiring experiences in the field of literacy throughout the world. The Confucius Prize offers two awards of US$20,000 each, a medal and a diploma, as well as a study visit to literacy project sites in China.
Environmental adult education is recognized as a "hybrid outgrowth of the environmental movement and adult education, combining an ecological orientation with a learning paradigm to provide a vigorous educational approach to environmental concerns."
Post-literacy or post-literacy education is a concept used in continuing education and adult education programs aimed at recently literate or "neo-literate" adults and communities, largely in the developing world. Unlike continuing education or further education, which covers secondary or vocational topics for adult learners, post-literacy programs provide skills which might otherwise be provided in primary education settings. Post-literacy education aims to solidify literacy education, provide resources and media aimed at the newly literate, and also may create systems of non-formal education to serve these communities. Projects include providing formal continuing education, providing written materials relevant to economic development to newly literate members of developing societies, and leveraging radio and other non-written media to increase access to educational material in informal settings.

Open educational practices (OEP) are part of the broader open education landscape, including the openness movement in general. It is a term with multiple layers and dimensions and is often used interchangeably with open pedagogy or open practices. OEP represent teaching and learning techniques that draw upon open and participatory technologies and high-quality open educational resources (OER) in order to facilitate collaborative and flexible learning. Because OEP emerged from the study of OER, there is a strong connection between the two concepts. OEP, for example, often, but not always, involve the application of OER to the teaching and learning process. Open educational practices aim to take the focus beyond building further access to OER and consider how in practice, such resources support education and promote quality and innovation in teaching and learning. The focus in OEP is on reproduction/understanding, connecting information, application, competence, and responsibility rather than the availability of good resources. OEP is a broad concept which can be characterised by a range of collaborative pedagogical practices that include the use, reuse, and creation of OER and that often employ social and participatory technologies for interaction, peer-learning, knowledge creation and sharing, empowerment of learners, and open sharing of teaching practices.

The World Literacy Foundation(WLF) is a global not-for-profit that works to lift young people out of poverty through literacy. Founded in Melbourne, Australia in 2003, the World Literacy Foundation operates on the principle that education is a basic human right. It aims to eradicate global illiteracy through the promotion of literacy and the provision of educational resources.
Anil Bordia was an Indian educationist, social activist and former civil servant, widely respected for his contributions to the Indian education sector. The Government of India honoured him, in 2010, with Padma Bhushan, the third highest civilian award, for his services to the fields of education and literature on education.
Global citizenship education (GCED) is a form of civic learning that involves students' active participation in projects that address global issues of a social, political, economic, or environmental nature. The two main elements of GCE are 'global consciousness'; the moral or ethical aspect of global issues, and 'global competencies', or skills meant to enable learners to participate in changing and developing the world. The promotion of GCE was a response by governments and NGOs to the emergence of supranational institution, regional economic blocs, and the development of information and communications technologies. These have all resulted in the emergence of a more globally oriented and collaborative approach to education. GCE addresses themes such as peace and human rights, intercultural understanding, citizenship education, respect for diversity and tolerance, and inclusiveness.

The Instituto Nacional para la Educación de los Adultos, abbreviated INEA, is a decentralized public organization of the Mexican federal public administration, grouped in the sector coordinated by the Ministry of Education Public, with legal personality and its own patrimony, created by presidential decree on August 31, 1981.

Climate change education (CCE) is education that aims to address and develop effective responses to climate change. It helps learners understand the causes and consequences of climate change, prepares them to live with the impacts of climate change and empowers learners to take appropriate actions to adopt more sustainable lifestyles. Climate change and climate change education are global challenges that can be anchored in the curriculum in order to provide local learning and widen up mindset shits on how climate change can be mitigated. In such as case CCE is more than climate change literacy but understanding ways of dealing with climate
Social Impact Media Awards is an annual media competition run by a non-profit impact media agency SIMA Studios. SIMA Studios curates and distributes documentaries and creative media projects.

Sustainable Development Goal 4 is about quality education and is among the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in September 2015. The full title of SDG 4 is "Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all".
References
- 1 2 3 "The Winners of the UNESCO international literacy prizes, 2008" (PDF).
- ↑ "Missions and objectives". Archived from the original on 2011-09-04.
- ↑ "UNESCO Award for Literacy". Archived from the original on 4 September 2011. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ↑ "Ethiopia has won the UNESCO International Literacy Prize of 2008". Archived from the original on 2011-07-26.
- ↑ "Women are the Future of Mankind - UNESCO magazine" (PDF). Retrieved 21 March 2024.