
The government of Ethiopia is the federal government of Ethiopia. It is structured in a framework of a federal parliamentary republic, whereby the prime minister is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. The prime minister is chosen by the lower chamber of the Federal Parliamentary Assembly. Federal legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament. The judiciary is more or less independent of the executive and the legislature. They are governed under the 1995 Constitution of Ethiopia. There is a bicameral parliament made of the 108-seat House of Federation and the 547-seat House of Peoples' Representatives. The House of Federation has members chosen by the regional councils to serve five-year terms. The House of Peoples' Representatives is elected by direct election, who in turn elect the president for a six-year term.

The Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front was an ethnic federalist political coalition in Ethiopia that existed from 1988 to 2019. It consisted of four political parties: Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF), Amhara Democratic Party (ADP), Oromo Democratic Party (ODP) and Southern Ethiopian People's Democratic Movement (SEPDM). After leading the overthrow of the People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, it dominated Ethiopian politics from 1991 to 2019. In November 2019, the EPRDF was dissolved, and Prime Minister and EPDRF chairman Abiy Ahmed merged three of the constituent parties into his new Prosperity Party, which was officially founded on 1 December 2019.

The Tigray People's Liberation Front, also known as the Tigrayan People's Liberation Front, is a left-wing ethnic nationalist, paramilitary group, and the former ruling party of Ethiopia. It was classified as a terrorist organization by the Ethiopian government during the Tigray War until its removal from the list in 2023. In older and less formal texts and speech it is known as Woyane or Weyané.

Asaita (Amharic: አሳይታ, Asayəta; Afar: Aysaqiita), known historically as Aussa (Awsa), is a town in northeastern Ethiopia, and until 2007 served as the capital of the Afar Region of Ethiopia. Located in the Afambo woreda, part of the region's Awsi Rasu zone, the town has a latitude and longitude of 11°34′N41°26′E and an elevation of 300 metres (980 ft).

The Afar, also known as the Danakil, Adali and Odali, are a Cushitic ethnic group inhabiting the Horn of Africa. They primarily live in the Afar Region of Ethiopia and in northern Djibouti, as well as the entire southern coast of Eritrea. The Afar speak the Afar language, which is part of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. Afars are the only inhabitants of the Horn of Africa whose traditional territories border both the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden.

The Amhara Democratic Party (ADP), formerly known as the Amhara National Democratic Movement (ANDM), was a political party in Ethiopia. The party was one of four members of the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) that ruled Ethiopia at the time. In 2012, the party chairman was Demeke Mekonnen, who replaced Addisu Legesse in 2010. In November 2019, prime minister Abiy Ahmed, holding the role of EPRDF chair, unified the constituent parties of the coalition into a new party called Prosperity Party.

The Gambela Peoples’ Democratic Movement, also known as the Gambela People’s Democratic Movement or Gambella Peoples’ Unity Democratic Movement, was a political party in the Gambela Region of Ethiopia. It was the regional ally of the ruling EPRDF coalition.
The Ethiopian Democratic Union or EDU, also known as Teranafit, was one of the political parties that formed in opposition to the Derg regime of Ethiopia. It merged with the Ethiopian Democratic Party to form the Ethiopian Democratic Unity Party.

The Ethiopian Civil War was a civil war in Ethiopia and present-day Eritrea, fought between the Ethiopian military junta known as the Derg and Ethiopian-Eritrean anti-government rebels from 12 September 1974 to 28 May 1991.
Elidar is a woreda in Afar Region, Ethiopia. Part of the Administrative Zone 1, Elidar is bordered on the south by the Awash River which separates it from Asayita, on the west by Dubti, on the northwest by Kori, on the north by the Administrative Zone 2, on the northeast by Eritrea, and on the east by Djibouti. Towns in Elidar include Bure, Diche Oto, Elidar and Manda.

The Afar Revolutionary Democratic Unity Front is an Afar political party in Ethiopia, founded in 1993. It had been a member of the United Ethiopian Democratic Forces (UEDF) coalition opposition party.

Bitwoded Sultan Alimirah Hanfare was Sultan of Aussa from 1944 until his death in 2011. He ascended to the throne after his predecessor and uncle, Mohammad Yayyo.

The Transitional Government of Ethiopia (TGE) was an era established immediately after the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) seized power from the Marxist-Leninist People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (PDRE) in 1991. During the transitional period, Meles Zenawi served as the president of the TGE while Tamrat Layne was prime minister. Among other major shifts in the country's political institutions, it was under the authority of the TGE that the realignment of provincial boundaries on the basis of ethnolinguistic identity occurred. The TGE was in power until 1995, when it transitioned into the reconstituted Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia that remains today.
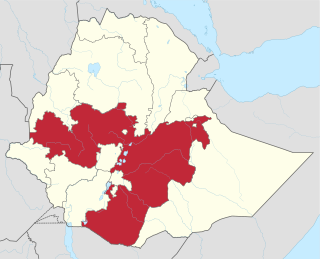
The Oromo conflict is a protracted conflict between the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) and the Ethiopian government. The Oromo Liberation Front formed to fight the Ethiopian Empire to liberate the Oromo people and establish an independent state of Oromia. The conflict began in 1973, when Oromo nationalists established the OLF and its armed wing, the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA). These groups formed in response to prejudice against the Oromo people during the Haile Selassie and Derg era, when their language was banned from public administration, courts, church and schools, and the stereotype of Oromo people as a hindrance to expanding Ethiopian national identity.

The Prosperity Party is a ruling political party in Ethiopia that was established on 1 December 2019 as a successor to the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front by incumbent Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed.

Tigrayan nationalism is an ethnic nationalism that advocates the interests of Tigrayan people in Ethiopia. Inspired predominantly by the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) with its predecessor Tigray Liberation Front (TLF), this type of nationalism holds that Tigrayans are an independent group with unique ancestry, heritage, history and culture outside Ethiopia. As such, they claim Tigray is the source of Ethiopian civilization and utterly a benefactor of state-building without other local ethnic groups. Tigrayan nationalists accuse Amharas of imposing their cultural, economic and political hegemony over Tigrayans.

The fallof the Derg was a military campaign that resulted in the defeat of the ruling Marxist–Leninist military junta, the Derg, by the rebel coalition Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) on 28 May 1991 in Addis Ababa, ending the Ethiopian Civil War. The Derg took power after deposing Emperor Haile Selassie and the Solomonic dynasty, an imperial dynasty of Ethiopia that began in 1270. The Derg suffered from insurgency with different factions, and separatist rebel groups since their early rule, beginning with the Ethiopian Civil War. The 1983–1985 famine, the Red Terror, and resettlement and villagization made the Derg unpopular with the majority of Ethiopians tending to support insurgent groups like the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) and Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF).
The 1995 Ethiopian Federal Constitution formalizes an ethnic federalism law aimed at undermining long-standing ethnic imperial rule, reducing ethnic tensions, promoting regional autonomy, and upholding unqualified rights to self-determination and secession in a state with more than 80 different ethnic groups. But the constitution is divisive, both among Ethiopian nationalists who believe it undermines centralized authority and fuels interethnic conflict, and among ethnic federalists who fear that the development of its vague components could lead to authoritarian centralization or even the maintenance of minority ethnic hegemony. Parliamentary elections since 1995 have taken place every five years since enactment. All but one of these have resulted in government by members of the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) political coalition, under three prime ministers. The EPRDF was under the effective control of the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF), which represents a small ethnic minority. In 2019 the EPRDF, under Abiy, was dissolved and he inaugurated the pan-ethnic Prosperity Party which won the 2021 Ethiopian Election, returning him as prime minister. But both political entities were different kinds of responses to the ongoing tension between constitutional ethnic federalism and the Ethiopian state's authority. Over the same period, and all administrations, a range of major conflicts with ethnic roots have occurred or continued, and the press and availability of information have been controlled. There has also been dramatic economic growth and liberalization, which has itself been attributed to, and used to justify, authoritarian state policy.
This list details about chronological aspect of the Derg, the military junta that ruled Ethiopia from 1974 to 1987 by decade.

The Ethiopian Student Movement was a period of radical Marxist–Leninist student activism and movement in Ethiopia from the mid-1960s to the 1974 revolution. The first demonstration occurred in 1965 by university student, led by Marxist–Leninist motivation chanting "Land to the Tiller" and "Is poverty a crime?". The student uprisings continued in 1966 until 1969. The movement also called for the abolition of monarchy under Emperor Haile Selassie and feudalism in Ethiopia.















