
Agriculture is a major industry in the United States, which is a net exporter of food. As of the 2017 census of agriculture, there were 2.04 million farms, covering an area of 900 million acres (1,400,000 sq mi), an average of 441 acres per farm.
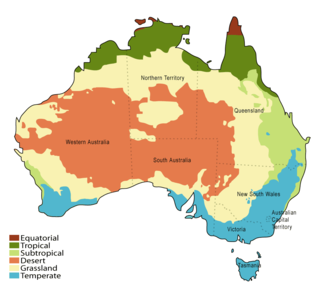
Although Australia is mostly arid, the nation is a major agricultural producer and exporter, with over 325,300 employed in agriculture, forestry and fishing as of February 2015. Agriculture and its closely related sectors earn $155 billion-a-year for a 12% share of GDP. Farmers and grazers own 135,997 farms, covering 61% of Australia's landmass. Across the country there is a mix of irrigation and dry-land farming. The success of Australia to become a major agricultural power despite the odds is facilitated by its policies of long-term visions and promotion of agricultural reforms that greatly increased the country's agricultural industry.

Agriculture in Russia is an important part of the economy of the Russian Federation. The agricultural sector survived a severe transition decline in the early 1990s as it struggled to transform from a command economy to a market-oriented system. Following the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, large collective and state farms – the backbone of Soviet agriculture – had to contend with the sudden loss of state-guaranteed marketing and supply channels and a changing legal environment that created pressure for reorganization and restructuring. In less than ten years, livestock inventories declined by half, pulling down demand for feed grains, and the area planted to grains dropped by 25%.

Agriculture in Belarus can be divided into two segments: livestock production and crop production. Crop production slightly outweighs livestock production in the country's product mix, accounting for around 55% of gross agricultural output since 1995. Agriculture accounted for 7.9% GDP in 2013, while over the same year that sector accounted for only 3% GDP in the EU.

Canada is one of the largest agricultural producers and exporters in the world. As with other developed nations, the proportion of the population agriculture employed and agricultural GDP as a percentage of the national GDP fell dramatically over the 20th century, but it remains an important element of the Canadian economy. A wide range of agriculture is practised in Canada, from sprawling wheat fields of the prairies to summer produce of the Okanagan valley. In the federal government, overview of Canadian agriculture is the responsibility of the Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food.

Roughly one-third of Iran's total surface area is suited for farmland, but because of poor soil and lack of adequate water distribution in many areas, most of it is not under cultivation. Only 12% of the total land area is under cultivation but less than one-third of the cultivated area is irrigated; the rest is devoted to dryland farming. Some 92 percent of agricultural products depend on water. The western and northwestern portions of the country have the most fertile soils. Iran's food security index stands at around 96 percent.

Agriculture in Kyrgyzstan is a significant sector of the economy. According to the CIA World Factbook, it comprises 18% of the total GDP and occupies 48% of the total labor force. Only 6.8% of the total land area is used for crop cultivation, but 44% of the land is used as pastures for livestock. Because of the many mountains of Kyrgyzstan, animal husbandry remains a significant part of the agricultural economy.

For millennia, agriculture has played an important role in the Chinese economy and society. By the time the People's Republic of China was established in 1949, virtually all arable land was under cultivation; irrigation and drainage systems constructed centuries earlier and intensive farming practices already produced relatively high yields. But little prime virgin land was available to support population growth and economic development. However, after a decline in production as a result of the Great Leap Forward (1958–60), agricultural reforms implemented in the 1980s increased yields and promised even greater future production from existing cultivated land.

Armenia has 2.1 million hectares of agricultural land, 72% of the country's land area. Most of this, however, is mountain pastures, and cultivable land is 480,000 hectares, or 16% of the country's area. In 2006, 46% of the work force was employed in agriculture, and agriculture contributed 21% of the country's GDP. In 1991 Armenia imported about 65 percent of its food.

Agriculture in Portugal is based on small to medium-sized family-owned dispersed units; however, the sector also includes larger-scale intensive farming export-oriented agrobusinesses backed by companies. The extent of cooperative organisation has been reaching a greater importance with globalization. Portugal produces a wide variety of products, including green vegetables, rice, corn, wheat, barley, olives, oilseeds, nuts, cherries, bilberry, table grapes and edible mushrooms. Forestry has also played an important economic role among the rural communities and industry. In 2013, the gross agricultural product accounted for 2.4% of the GDP. Portugal is the largest world producer of both cork and carob, as well as the third largest exporter of chestnut and the third largest European producer of pulp. Portugal is among the top ten largest olive oil producers in the world and is the fourth biggest exporter. The country is also one of the world's largest exporters of wine, being reputed for its fine wines. The land area of slightly more than 9.2 million hectares was classified as follows : 2,755 arable land and permanent crops, 530 permanent pasture, 3,640 forest and woodland, and 2,270 other land.

Agriculture in Morocco employs about 40% of the nation's workforce. Thus, it is the largest employer in the country. In the rainy sections of the northwest, barley, wheat, and other cereals can be raised without irrigation. On the Atlantic coast, where there are extensive plains, olives, citrus fruits, and wine grapes are grown, largely with water supplied by artesian wells. Livestock are raised and forests yield cork, cabinet wood, and building materials. Part of the maritime population fishes for its livelihood. Agadir, Essaouira, El Jadida, and Larache are among the important fishing harbors. Both the agriculture and fishing industries are expected to be severely impacted by climate change.

Agriculture in Jordan contributed substantially to the economy at the time of Jordan's independence, but it subsequently suffered a decades-long steady decline. In the early 1950s, agriculture constituted almost 40 percent of GNP; on the eve of the Six-Day War, it was 17 percent.

The share of agriculture in Austria in the Austrian economy declined steadily after World War II, agriculture continues to represent an important element of the economy because of its social and political significance. The Chamber of Agriculture remains on an equal level with the chambers of commerce and labor, although its members produce only a fraction of the GDP that industrial and commercial workers produce.

Like the rest of the economy, agriculture in Estonia has been in great flux since the degeneration of the collective and state farm systems.
Prior to World War II, agriculture in Bulgaria was the leading sector in the Bulgarian economy. In 1939, agriculture contributed 65 percent of Net material product (NMP), and four out of every five Bulgarians were employed in agriculture. The importance and organization of Bulgarian agriculture changed drastically after the war, however. By 1958, the Bulgarian Communist Party (BCP) had collectivized a high percentage of Bulgarian farms; in the next three decades, the state used various forms of organization to improve productivity, but none succeeded. Meanwhile, private plots remained productive and often alleviated agricultural shortages during the Todor Zhivkov era.
Poland's agricultural sector is vital for European and Global market because it produces a variety of agricultural, horticultural and animal origin products. The surface area of agricultural land in Poland is 15.4 million ha, which constitutes nearly 50% of the total area of the country.

Agriculture in Spain is important to the national economy. The primary sector activities accounting for agriculture, husbandry, fishing and silviculture represented a 2.7% of the Spanish GDP in 2017, with an additional 2.5% represented by the agrofood industry.
In 2018, Latvia produced 1.4 million tons of wheat; 426 thousand tons of potatoes; 306 thousand tons of barley; 229 thousand tons of rapeseed; 188 thousand tons of oat; 81 thousand tons of rye; 80 thousand tons of beans; and smaller quantities of other agricultural products.

Moldova is an agrarian-industrial state, with agricultural land occupying 2,499,000 hectares in a total area of 3,384,600 hectares. It is estimated that 1,810,500 of these hectares are arable. Moldova is located in Eastern Europe, and is landlocked, bordering Romania and Ukraine. Moldova's agricultural sector benefits from a geographical proximity to large markets, namely the European Union. As a share of GDP, agriculture has declined from 56% in 1995 to 13.8% in 2013. Data from 2015 estimated that agriculture accounted for 12% of Moldova's GDP. Agriculture as a sector is export-oriented, with the composition of Moldova's total exports containing agriculture and the agri-food sector as a main component. 70% of agri-food exports in 2012 included beverages, edible fruits and nuts, oilseeds, vegetable preparations and cereals. Here, fruits, vegetables and nuts were attributed to 33% of Moldova's exports for 2011–2013. Moldova is also one of the top ten apple exporters in the world. However, because of the long-term emphasis on fruit, vegetables are often imported.

Agriculture in Finland is characterized by the northern climate and self-sufficiency in most major agricultural products. Its economic role is declining in terms of GNP and employment in primary production, but together with the food industry and forestry with which it is linked, it forms a significant part of the Finnish economy. The number of farms has steadily declined for the last decades. Between 2000 and 2012 their number fell from almost 80,000 in 2000 to about 60,000, while the amount of arable land has slightly increased to a total of almost 2.3 million hectares. Agriculture employed 125,000 people in 2010, which is a drop of 30 percent from 2000.



















