
A grain elevator is a facility designed to stockpile or store grain. In the grain trade, the term "grain elevator" also describes a tower containing a bucket elevator or a pneumatic conveyor, which scoops up grain from a lower level and deposits it in a silo or other storage facility.

Agricore United was a farmer-directed agribusiness in Canada. It supplied crop nutrition and crop protection products, and offered grain handling and marketing services. It was created on November 1, 2001 by the merger of Agricore and United Grain Growers. It was headquartered in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Its shares were publicly traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) under the symbol "AU" until June 15, 2007, when it was taken over by the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool. Agri-business giant Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) had a 28% stake in the company at the time of the takeover.
Warner is a village in Alberta, Canada. It is surrounded by the County of Warner No. 5, approximately 65 km (40 mi) south of Lethbridge. Warner is a farming community. Warner is situated at the intersection of Highway 4 and Highway 36, about 38 km north of the Montana border and Interstate 15. Warner's nearest neighbours are the towns of Stirling and Milk River.

The Saskatchewan Wheat Pool was a grain handling, agri-food processing and marketing company based in Regina, Saskatchewan. The Pool created a network of marketing alliances in North America and internationally which made it the largest agricultural grain handling operation in the province of Saskatchewan. Before becoming Viterra, SWP had operated 276 retail outlets and more than 100 grain handling and marketing centres. The Saskatchewan Wheat Pool operated under the name of AgPro in the prairie provinces of Manitoba and Alberta. Begun as a co-operative in the 1920s, the company became a publicly traded corporation in the 1990s. After the 2007 takeover of its competitor, Winnipeg-based Agricore United, the Pool name was retired. The merged company operated under the name Viterra until 2013, when it was acquired by Glencore International.

Maybutt, also known as "New Stirling" or "New Town", is a former locality in the County of Warner No. 5, Alberta, Canada. The community is situated 1 km north of the Village of Stirling just off the CANAMEX Corridor between Lethbridge and the Canada–US border. The community has become a bedroom community to Lethbridge, with many newer acreages being developed in the area. The footprint of Maybutt is defined by its historic boundary roads, Young St., Sunnyside Ave., Front St. & Lorne Ave, and Etzikom Ave. York St., First Ave. and Second Ave. are the only interior streets left of the original street grid of Maybutt.

A wheat pool is a co-operative that markets grain on behalf of its farmer-members.

Raley, Alberta is an unincorporated community in Cardston County, Alberta, Canada. The population of Raley was 5 in 1966. The community is located about 4 km north of Highway 3, and about 15 km east of the Town of Cardston. Raley is named after C. Raley, of Lethbridge.
The Warner elevator row is a group of four historic wood-cribbed grain elevators standing in a row from south to north alongside the Canadian Pacific Railway line from Great Falls, Montana to Lethbridge, Alberta at the east entrance of the village of Warner, Alberta, Canada. At one time, the row had at least seven elevators.

The Canadian Grain Elevator Discovery Centre is a set of restored grain elevators located in Nanton, Alberta, Canada. The centre's goal is to preserve examples of old grain elevators to educate visitors about the town's, and Alberta's, agricultural history.

The Alberta Central Railway Museum is a railway museum located south-east of the City of Wetaskiwin, in Central Alberta, Canada. The main building was designed as a scaled-down version of the City's 1907 Canadian Pacific Railway depot. The depot includes a waiting room, baggage room and telegraph office, as well as exhibits and railroad artifacts. Railroad equipment includes locomotives, a sleeper car, passenger coach, freight equipment, cabooses, freight cars and a snowplough. Attractions include a model train layout of the original Wetaskiwin railyard. The museum also features a 1906 Alberta Grain Co. grain elevator which was moved from Hobbema. The elevator is known to be Alberta's second-oldest grain elevator in the Province. Rides are given on a one-mile loop of track.

The Scandia Eastern Irrigation District Museum is an open-air museum in Southern Alberta, Canada. The museum includes a historic 1925 Alberta Wheat Pool grain elevator, Bow Slope Stockyard, and displays of how irrigation has affected the prosperity of the area. The museum is part of Eastern Irrigation District Historical Park, which also includes a blacksmith shop, barn, general store, stock yards and river ferry.
The Krause Milling Co grain elevator and flour mill site complex is composed of a 1929 grain elevator, drive shed, office/powerhouse, storage building and foundation of the 1929 flour mill, in the center of Radway, Alberta.

The Ritchie Mill is the oldest surviving flour mill in the province of Alberta.
The Prairie Elevator Museum is a former Alberta Wheat Pool grain elevator that has been restored and converted into a community gift shop and tea house. The elevator stands within the Hamlet of Acadia Valley, Alberta, next to the defunct Canadian National Railway track bed.

St. Albert Grain Elevator Park is an open-air museum which features two historic grain elevators and a reconstructed railway station.

The Saskatchewan Grain Growers' Association (SGGA) was a farmer's association that was active in Saskatchewan, Canada in the early 20th century. It was a successor to the Territorial Grain Growers' Association, and was formed in 1906 after Saskatchewan became a province. It provided a voice for farmers in their struggle with grain dealers and the railways, and was influential in obtaining favorable legislation. The association initially resisted calls to create a farmer-owned marketing company. Later it did support formation of the Saskatchewan Co-operative Elevator Company. The SGGA helped the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool, a cooperative marketing organization, to become established in 1924. In 1926 the SGGA merged with the more radical Farmers' Union of Canada, which had earlier split from the SGGA, to create the United Farmers of Canada,

Edward Alexander Partridge was a Canadian teacher, farmer, agrarian radical, businessman and author. He was born in Ontario but moved to Saskatchewan where he taught and then became a farmer. He was active in the Territorial Grain Growers' Association (TGGA), founded in 1902, which addressed various problems with the Western Canada grain market. He founded the cooperative Grain Growers' Grain Company, the predecessor of the United Grain Growers, and the Grain Growers' Guide, a widely distributed weekly paper. His "Partridge Plan" was a broad and visionary proposal for addressing a wide range of farmers' issues, eliminating many abuses caused by the near-monopoly of grain elevator companies, and resulted in important reforms by the provincial governments. Patridge was named a National Historic Person in 2018.
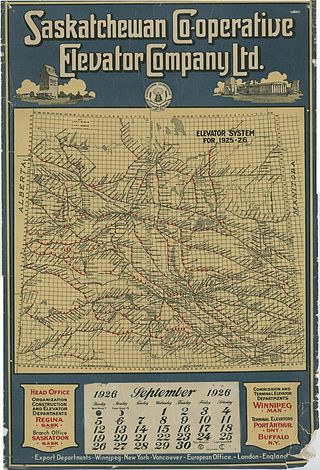
The Saskatchewan Co-operative Elevator Company (SCEC) was a farmer-owned enterprise that provided grain storage and handling services to farmers in Saskatchewan, Canada between 1911 and 1926, when its assets were purchased by the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool.















