
The Great Plains, sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located just to the east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. It is the western part of the Interior Plains, which also include the mixed grass prairie, the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. Great Plains or Western Plains is also used to describe the ecoregion of the Great Plains, or alternatively the western portion of the Great Plains.

Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the area referred to as the Interior Lowlands of Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east.

Silphidae is a family of beetles that are known commonly as large carrion beetles, carrion beetles or burying beetles. There are two subfamilies: Silphinae and Nicrophorinae. Nicrophorines are sometimes known as sexton beetles. The number of species is relatively small at around two hundred. They are more diverse in the temperate region although a few tropical endemics are known. Both subfamilies feed on decaying organic matter such as dead animals. The subfamilies differ in which uses parental care and which types of carcasses they prefer. Silphidae are considered to be of importance to forensic entomologists because when they are found on a decaying body they are used to help estimate a post-mortem interval.

Trogidae, sometimes called hide beetles, is a family of beetles with a distinctive warty or bumpy appearance. Found worldwide, the family includes about 300 species contained in four or five genera.

The Loess Hills are a formation of wind-deposited loess soil in the westernmost parts of Iowa and Missouri, and the easternmost parts of Nebraska and Kansas, along the Missouri River.

Omus dejeani is a species of flightless tiger beetle (Cicindelidae) that is found from British Columbia almost to northern California in dense, coastal forests. It is the largest species of the genus, at between 15 and 20 mm.
Saint Helena, Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha, as well the other uninhabited islands nearby, are a haven for wildlife in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. The islands are or were home to much endemic flora and fauna, especially invertebrates, and many endemic fish species are found in the reef ecosystems off the islands. The islands have been identified by BirdLife International as Important Bird Areas for both their endemic landbirds and breeding seabirds.

Amblycheila is a genus of flightless, nocturnal tiger beetles. There are eight species distributed across the southwestern United States and Mexico.

The plains pocket gopher is one of 35 species of pocket gophers, so named in reference to their externally located, fur-lined cheek pouches. They are burrowing animals, found in grasslands and agricultural land across the Great Plains of North America, from Manitoba to Texas. Pocket gophers are the most highly fossorial rodents found in North America.

The olive-backed pocket mouse is a species of rodent in the family Heteromyidae. It is found in the central Great Plains of Canada and the United States where it is widespread and relatively common; the IUCN considers it to be of "least concern".

Ipomoea leptophylla, the bush morning glory, bush moonflower or manroot, is a species of flowering plant in the bindweed family, Convolvulaceae.

Cicindela limbalis, the common claybank tiger beetle, is a species of tiger beetle. The length of the beetle is 12–16 millimeters (0.5–0.6 in). The beetle's back is reddish purple and sometimes may be dull green or brown. The species can commonly be found on steep, moist bare clay soil. The beetle can live for 3 years.
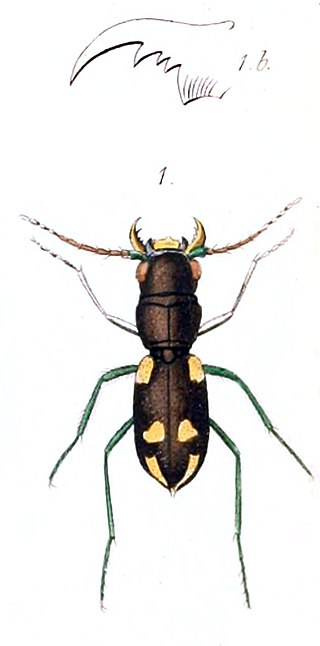
Apteroessa grossa is a species of tiger beetles in the family Cicindelidae, the sole species in the genus Apteroessa and described on the basis of a specimen from the Coromandel region (Tranquebar) in southern India. It is somewhat large and robust, and is among the few tiger beetles with highly reduced wings making them flightless. There are three known specimens in museums, with varying degrees of damage. The species has not been seen in the wild after its description in the 18th century and is thought to be extremely local in distribution.
The ecology of the Great Plains is diverse, largely owing to their great size. Differences in rainfall, elevation, and latitude create a variety of habitats including short grass, mixed grass, and tall-grass prairies, and riparian ecosystems.
Amblycheila picolominii is a species of nocturnal tiger beetle in the genus Amblycheila. Its common name is the plateau giant tiger beetle. It was discovered in 1839.
Amblycheila hoversoni, also known as the South Texas giant tiger beetle, is a flightless and nocturnal tiger beetle species found in south and west-central Texas, United States. First described in 1990, it is the largest tiger beetle species in the Western Hemisphere.

Amblycheila schwarzi, also known as the Mojave giant tiger beetle, is a flightless and nocturnal tiger beetle species found in the southern United States. A. schwarzi was first described by German entomologist Walther Horn in 1904.

Holcaspis brevicula, the Eyrewell ground beetle, is a species of carabid beetle native to New Zealand, one of a number of small black flightless beetles in the genus Holcaspis that inhabit the dry eastern lowlands of the South Island. H. brevicula is very rare—only ten specimens have ever been collected—and critically endangered: the species was found only in Eyrewell Forest, a single plantation of exotic pine trees currently being converted into dairy farms.

Climate change in South Dakota encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of South Dakota.

Rivacindela hudsoni is an Australian species of the family Cicindelinae or "tiger beetle" and is the fastest-running known insect. The genus Rivacindela is contentiously treated as a subgenus of the broader Cicindela and are typically found in saline habitats such as dry salt lakes and salt streams and are flightless. The species was discovered in South Australia and described in 1997, with an adult form of approximately 20–21mm in length and a running speed of 2.49 m/s, or 120 body lengths per second.















