
A parasitic disease, also known as parasitosis, is an infectious disease caused or transmitted by a parasite. Many parasites do not cause diseases as it may eventually lead to death of both organism and host. Parasites infecting human beings are called human parasites. Parasitic diseases can affect practically all living organisms, including plants and mammals. The study of parasitic diseases is called parasitology.

The Juan Fernández fur seal is the second smallest of the fur seals, second only to the Galápagos fur seal. They are found only on the Pacific Coast of South America, more specifically on the Juan Fernández Islands and the Desventuradas Islands. There is still much that is unknown about this species. Scientists still do not know the average life span of this species, or the diet and behavior of males apart from the breeding season.

Hookworm infection is an infection by a type of intestinal parasite known as a hookworm. Initially, itching and a rash may occur at the site of infection. Those only affected by a few worms may show no symptoms. Those infected by many worms may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and tiredness. The mental and physical development of children may be affected. Anemia may result.

Necator americanus is a species of hookworm commonly known as the New World hookworm. Like other hookworms, it is a member of the phylum Nematoda. It is an obligatory parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine of human hosts. Necatoriasis—a type of helminthiasis—is the term for the condition of being host to an infestation of a species of Necator. Since N. americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale are the two species of hookworms that most commonly infest humans, they are usually dealt with under the collective heading of "hookworm infection". They differ most obviously in geographical distribution, structure of mouthparts, and relative size.

Ancylostoma is a genus of nematodes that includes some species of hookworms.

Ancylostoma duodenale is a species of the roundworm genus Ancylostoma. It is a parasitic nematode worm and commonly known as the Old World hookworm. It lives in the small intestine of hosts such as humans, cats and dogs, where it is able to mate and mature. Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus are the two human hookworm species that are normally discussed together as the cause of hookworm infection. They are dioecious. Ancylostoma duodenale is abundant throughout the world, including Southern Europe, North Africa, India, China, southeast Asia, some areas in the United States, the Caribbean, and South America.
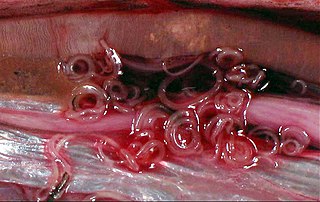
The Chromadorea are a class of the roundworm phylum, Nematoda. They contain a single subclass (Chromadoria) and several orders. With such a redundant arrangement, the Chromadoria are liable to be divided if the orders are found to form several clades, or abandoned if they are found to constitute a single radiation.

The Strongylida suborder includes many of the important nematodes found in the gastrointestinal tracts of ruminants, horses, and swine, as well as the lungworms of ruminants and the hookworms of dogs and cats.

Charles Wardell Stiles was an American parasitologist born in Spring Valley, New York. He was notable for working on a campaign against hookworm infestation in the American South, where it had been found to cause high rates of anemia, a debilitating disease.

Arthur Looss was a German zoologist and parasitologist. Looss was born in 1861 in Chemnitz, and was educated both there and in Łódź, Poland. Thereafter, he studied at the University of Leipzig, where he received a doctorate for his study of trematodes.

Ancylostomiasis is a hookworm disease caused by infection with Ancylostoma hookworms. The name is derived from Greek ancylos αγκύλος "crooked, bent" and stoma στόμα "mouth".
Necatoriasis is the condition of infection by Necator hookworms, such as Necator americanus. This hookworm infection is a type of helminthiasis (infection) which is a type of neglected tropical disease.

Amoscanate (INN), also known as nithiocyamine, is an experimental anthelmintic agent of the arylisothiocyanate class which was found to be highly effective in animals against the four major species of schistosomes which infect humans, and is also highly active against hookworm infection. However, significant liver toxicity was seen in lab animals at higher doses. The ether analogue of amoscanate, nitroscanate, is used in veterinary medicine as an anthelmintic.
Human parasites include various protozoa and worms.

Hookworm vaccine is a vaccine against hookworm. No effective vaccine for the disease in humans has yet been developed. Hookworms, parasitic nematodes transmitted in soil, infect approximately 700 million humans, particularly in tropical regions of the world where endemic hookworms include Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. Hookworms feed on blood and those infected with hookworms may suffer from chronic anaemia and malnutrition. Helminth infection can be effectively treated with benzimidazole drugs, and efforts led by the World Health Organization have focused on one to three yearly de-worming doses in schools because hookworm infections with the heaviest intensities are most common in school-age children. However, these drugs only eliminate existing adult parasites and re-infection can occur soon after treatment. School-based de-worming efforts do not treat adults or pre-school children and concerns exist about drug resistance developing in hookworms against the commonly used treatments, thus a vaccine against hookworm disease is sought to provide more permanent resistance to infection.

Ancylostoma braziliense is a species of hookworm belonging to the genus Ancylostoma. It is an intestinal parasite of domestic cats and dogs. Severe infection is often fatal to these pets, especially in puppies and kittens. The infection is particularly endemic in the southern United States. It is most often confused with the zoonotic hookworm species Ancylostoma ceylanicum because of their uncanny resemblance.

The Ancylostomatidae are a family of worms that includes the hookworms.
Hookworms were an English five-piece neo-psychedelic rock band from Leeds/Halifax that formed in 2010. Between 2010 and 2018 the band released 3 studio albums and became known for their live shows.
Ancylostoma ceylanicum is a parasitic roundworm belonging to the genus Ancylostoma. It is a hookworm both of humans and of other mammals such as dogs, cats, and golden hamsters. It is the only zoonotic hookworm species that is able to produce symptomatic infections in humans, with the majority of cases being in Southeast Asia.

Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera Ancylostoma and Necator. In other animals the main parasites are species of Ancylostoma.











