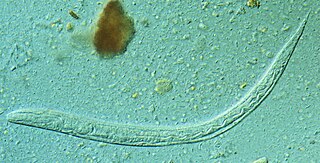
Strongyloides stercoralis is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term threadworm can also refer to nematodes of the genus Enterobius, otherwise known as pinworms.

Trichinosis, also known as trichinellosis, is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the Trichinella type. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of larvae to muscle, which occurs about a week after being infected, can cause swelling of the face, inflammation of the whites of the eyes, fever, muscle pains, and a rash. Minor infection may be without symptoms. Complications may include inflammation of heart muscle, central nervous system involvement, and inflammation of the lungs.

Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria Leptospira. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild to severe. Weil's disease, the acute, severe form of leptospirosis, causes the infected individual to become jaundiced, develop kidney failure, and bleed. Bleeding from the lungs associated with leptospirosis is known as "severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome".

Toxocariasis is an illness of humans caused by larvae of either the dog roundworm, the cat roundworm or the fox roundworm. Toxocariasis is often called visceral larva migrans (VLM). Depending on geographic location, degree of eosinophilia, eye and/or pulmonary signs, the terms ocular larva migrans (OLM), Weingarten's disease, Frimodt-Møller's syndrome, and eosinophilic pseudoleukemia are applied to toxocariasis. Other terms sometimes or rarely used include nematode ophthalmitis, toxocaral disease, toxocarose, and covert toxocariasis. This zoonotic, helminthic infection is a rare cause of blindness and may provoke rheumatic, neurologic, or asthmatic symptoms. Humans normally become infected by ingestion of embryonated eggs from contaminated sources.
Gnathostomiasis is the human infection caused by the nematode (roundworm) Gnathostoma spinigerum and/or Gnathostoma hispidum, which infects vertebrates.

Swine influenza is an infection caused by any one of several types of swine influenza viruses. Swine influenza virus (SIV) or swine-origin influenza virus (S-OIV) is any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As of 2009, the known SIV strains include influenza C and the subtypes of influenza A known as H1N1, H1N2, H2N1, H3N1, H3N2, and H2N3.

Trichinella spiralis is a viviparous nematode parasite, occurring in rodents, pigs, bears, hyenas and humans, and is responsible for the disease trichinosis. It is sometimes referred to as the "pork worm" due to it being typically encountered in undercooked pork products. It should not be confused with the distantly related pork tapeworm.

Ascaris suum, also known as the large roundworm of pig, is a parasitic nematode that causes ascariasis in pigs. While roundworms in pigs and humans are today considered as two species with different hosts, cross-infection between humans and pigs is possible; some researchers have thus argued they are the same species. Ascariasis is associated with contact to pigs and pig manure in Denmark.

Trichinella is the genus of parasitic roundworms of the phylum Nematoda that cause trichinosis. Members of this genus are often called trichinella or trichina worms. A characteristic of Nematoda is the one-way digestive tract, with a pseudocoelom.

Paragonimiasis is a food-borne parasitic infection caused by the lung fluke, most commonly Paragonimus westermani. It infects an estimated 22 million people yearly worldwide. It is particularly common in East Asia. More than 30 species of trematodes (flukes) of the genus Paragonimus have been reported; among the more than 10 species reported to infect humans, and only 8 bringing about infections in humans, the most common is P. westermani, the oriental lung fluke.

Taeniasis is an infection within the intestines by adult tapeworms belonging to the genus Taenia. There are generally no or only mild symptoms. Symptoms may occasionally include weight loss or abdominal pain. Segments of tapeworm may be seen in the stool. Complications of pork tapeworm may include cysticercosis.
Sparganosis is a parasitic infection caused by the plerocercoid larvae of the genus Spirometra including S. mansoni, S. ranarum, S. mansonoides and S. erinacei. It was first described by Patrick Manson from China in 1882, and the first human case was reported by Charles Wardell Stiles from Florida in 1908. The infection is transmitted by ingestion of contaminated water, ingestion of a second intermediate host such as a frog or snake, or contact between a second intermediate host and an open wound or mucous membrane. Humans are the accidental hosts in the life cycle, while dogs, cats, and other mammals are definitive hosts. Copepods are the first intermediate hosts, and various amphibians and reptiles are second intermediate hosts.
Aujeszky's disease, usually called pseudorabies in the United States, is a viral disease in swine that has been endemic in most parts of the world. It is caused by Suid herpesvirus 1 (SuHV-1). Aujeszky's disease is considered to be the most economically important viral disease of swine in areas where classical swine fever has been eradicated. Other mammals, such as cattle, sheep, goats, cats, dogs, and raccoons, are also susceptible. The disease is usually fatal in these animal species.
Mycobacterium caprae is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycobacterium and a member of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Prior to 2003, the species was referred to as Mycobacterium tuberculosis subsp. caprae. It is also synonymous with the name Mycobacterium bovis subsp. caprae.
Reverse zoonosis, also known as zooanthroponosis, and sometimes anthroponosis, refers to pathogens reservoired in humans that are capable of being transmitted to non-human animals.

Capillaria aerophila is a nematode parasite found in the respiratory tract of foxes, dogs, and various other carnivorous mammals. A few cases of human infestation have also been reported. Though it is sometimes called a "lungworm", this term usually refers to other species of nematodes. Infestation by C. aerophila is referred to as "pulmonary capillariasis", "bronchial capillariasis," or (rarely) "thominxosis." This parasite has a direct life cycle, meaning that the life cycle can be completed in a single host. C. aerophila usually causes only minor clinical symptoms, such as irritation of the respiratory tract and coughing. However, secondary bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, including pneumonia, may develop in heavy infestations. Treatment with anthelmintics, such as levamisole or fenbendazole, is usually sufficient to cure C. aerophila infestations.

Capillaria hepatica is a parasitic nematode which causes hepatic capillariasis in rodents and numerous other mammal species, including humans. The life cycle of C. hepatica may be completed in a single host species. However, the eggs, which are laid in the liver, must mature outside of the host body prior to infecting a new host. So the death of the host in which the adults reach sexual maturity, either by being eaten or dying and decomposing, is necessary for completion of the life cycle.

Trichinella britovi is a nematode parasite responsible for a zoonotic disease called trichinellosis. Currently, eight species of Trichinella are known, only three of which cause trichinellosis, and Trichinella britovi is one of them. Numerous mammal species, as well as birds and crocodiles, can harbor the parasite worldwide, but the sylvatic cycle is mainly maintained by wild carnivores.
Taenia asiatica, commonly known as Asian taenia or Asian tapeworm, is a parasitic tapeworm of humans and pigs. It is one of the three species of Taenia infecting humans and causes taeniasis. Discovered only in 1980s from Taiwan and other East Asian countries as an unusual species, it is so notoriously similar to Taenia saginata, the beef tapeworm, that it was for a time regarded as a slightly different strain. But anomaly arose as the tapeworm is not of cattle origin, but of pigs. Morphological details also showed significant variations, such as presence of rostellar hooks, shorter body, and fewer body segments. The scientific name designated was then Asian T. saginata. But the taxonomic consensus turns out to be that it is a unique species. It was in 1993 that two Korean parasitologists, Keeseon S. Eom and Han Jong Rim, provided the biological bases for classifying it into a separate species. The use of mitochondrial genome sequence and molecular phylogeny in the late 2000s established the taxonomic status.

Alaria is a genus of flatworms, or trematodes, in the family Diplostomidae.











