Related Research Articles

The master race is a pseudoscientific concept in Nazi ideology in which the putative "Aryan race" is deemed the pinnacle of human racial hierarchy. Members were referred to as "Herrenmenschen".
Loving v. Virginia, 388 U.S. 1 (1967), was a landmark civil rights decision of the U.S. Supreme Court which ruled that laws banning interracial marriage violate the Equal Protection and Due Process Clauses of the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. Beginning in 2013, the decision was cited as precedent in U.S. federal court decisions ruling that restrictions on same-sex marriage in the United States were unconstitutional, including in the Supreme Court decision Obergefell v. Hodges (2015).
The one-drop rule was a legal principle of racial classification that was prominent in the 20th-century United States. It asserted that any person with even one ancestor of black ancestry is considered black. It is an example of hypodescent, the automatic assignment of children of a mixed union between different socioeconomic or ethnic groups to the group with the lower status, regardless of proportion of ancestry in different groups.

Madison Grant was an American lawyer, zoologist, anthropologist, and writer known for his work as a conservationist, eugenicist, and advocate of scientific racism. Grant is less noted for his far-reaching achievements in conservation than for his pseudoscientific advocacy of Nordicism, a form of racism which views the "Nordic race" as superior.
The Pioneer Fund is an American non-profit foundation established in 1937 "to advance the scientific study of heredity and human differences". The organization has been described as racist and white supremacist in nature. The Southern Poverty Law Center classifies the Pioneer Fund as a hate group. One of its first projects was to fund the distribution in US churches and schools of Erbkrank, a Nazi propaganda film about eugenics.

In 1924, the Virginia General Assembly enacted the Racial Integrity Act. The act reinforced racial segregation by prohibiting interracial marriage and classifying as "white" a person "who has no trace whatsoever of any blood other than Caucasian". The act, an outgrowth of eugenicist and scientific racist propaganda, was pushed by Walter Plecker, a white supremacist and eugenicist who held the post of registrar of the Virginia Bureau of Vital Statistics.

Harry Hamilton Laughlin was an American educator and eugenicist. He served as the superintendent of the Eugenics Record Office from its inception in 1910 to its closure in 1939, and was among the most active individuals influencing American eugenics policy, especially compulsory sterilization legislation.

The Byrd machine, or Byrd organization, was a political machine of the Democratic Party led by former Governor and U.S. Senator Harry F. Byrd (1887–1966) that dominated Virginia politics for much of the 20th century. From the 1890s until the late 1960s, the Byrd organization effectively controlled the politics of the state through a network of courthouse cliques of local constitutional officers in most of the state's counties.

Roger Pearson is a British anthropologist, eugenicist, white supremacist, political organiser for the extreme right, and publisher of political and academic journals.

Walter Ashby Plecker was an American physician and public health advocate who was the first registrar of Virginia's Bureau of Vital Statistics, serving from 1912 to 1946. He was a leader of the Anglo-Saxon Clubs of America, a white supremacist organization founded in Richmond, Virginia, in 1922. A eugenicist and proponent of scientific racism, Plecker drafted and lobbied for the passage of the Racial Integrity Act of 1924 by the Virginia legislature; it institutionalized the one-drop rule.

The Passing of the Great Race: Or, The Racial Basis of European History is a 1916 racist and pseudoscientific book by American lawyer, anthropologist, and proponent of eugenics Madison Grant (1865–1937). Grant expounds a theory of Nordic superiority, claiming that the "Nordic race" is inherently superior to other human "races". The theory and the book were praised by Adolf Hitler and other Nazis.
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced racial segregation, "Jim Crow" being a pejorative term for an African American. Such laws remained in force until 1965. Formal and informal segregation policies were present in other areas of the United States as well, even as several states outside the South had banned discrimination in public accommodations and voting. Southern laws were enacted by white-dominated state legislatures (Redeemers) to disenfranchise and remove political and economic gains made by African Americans during the Reconstruction era. Such continuing racial segregation was also supported by the successful Lily-white movement.
The House Behind the Cedars is a 1927 silent race film directed, written, produced and distributed by the noted director Oscar Micheaux. It was loosely adapted from the 1900 novel of the same name by African-American writer Charles W. Chesnutt, who explored issues of race, class and identity in the post-Civil War South. No print of the film is known to exist, and it is considered lost. Micheaux remade the film in 1932 under the title Veiled Aristocrats.

John Powell was an American pianist, ethnomusicologist and composer. Along with Annabel Morris Buchanan, he helped found the White Top Folk Festival, which promoted music of the people in the Appalachian Mountains. A firm believer in segregation and white supremacy, Powell also helped found the Anglo-Saxon Clubs of America, which soon had numerous posts in Virginia. He contributed to the drafting and passage of the Racial Integrity Act of 1924, which institutionalized the one-drop rule by classifying as black (colored) anyone with African ancestry.
Theodore Lothrop Stoddard was an American historian, journalist, political scientist and white supremacist. Stoddard wrote several books which advocated eugenics, white supremacy, Nordicism, and scientific racism, including The Rising Tide of Color Against White World-Supremacy (1920). He advocated a racial hierarchy which he believed needed to be preserved through anti-miscegenation laws. Stoddard's books were once widely read both inside and outside the United States.

Eugenics, the set of beliefs and practices which aims at improving the genetic quality of the human population, played a significant role in the history and culture of the United States from the late 19th century into the mid-20th century. The cause became increasingly promoted by intellectuals of the Progressive Era.
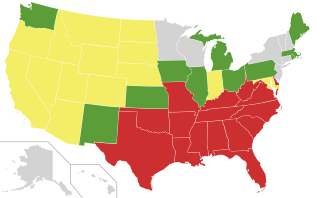
In the United States, many U.S. states historically had anti-miscegenation laws which prohibited interracial marriage and, in some states, interracial sexual relations. Some of these laws predated the establishment of the United States, and some dated to the later 17th or early 18th century, a century or more after the complete racialization of slavery. Nine states never enacted anti-miscegenation laws, and 25 states had repealed their laws by 1967. In that year, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in Loving v. Virginia that such laws are unconstitutional under the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
The history of eugenics is the study of development and advocacy of ideas related to eugenics around the world. Early eugenic ideas were discussed in Ancient Greece and Rome. The height of the modern eugenics movement came in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.

Earnest Sevier Cox was an American Methodist preacher, political activist and white supremacist. He is best known for his political campaigning for stricter segregation between blacks and whites in the United States through tougher anti-miscegenation laws, for his advocacy for "repatriation" of African Americans to Africa, and for his book White America. He is also noted for having mediated collaboration between white southern segregationists and African American separatist organizations such as UNIA and the Peace Movement of Ethiopia to advocate for repatriation legislation, and for having been a personal friend of black racial separatist Marcus Garvey.
Ivey Foreman Lewis was an American botanist and geneticist who served for two decades as dean of the University of Virginia and helped found the Virginia Academy of Science. A proponent of eugenics throughout his career, in his final years, Lewis and his sister Nell Battle Lewis gained national attention for their opposition to racial desegregation in public education, especially the United States Supreme Court decisions in Brown v. Board of Education.
References
- ↑ David E. Whisnant. All That Is Native and Fine: The Politics of Culture in an American Region. UNC Press Books, Aug 1, 1995 pp. 240-43
- ↑ J. Douglas Smith. The Campaign for Racial Purity and the Erosion of Paternalism in Virginia, 1922-1930: "Nominally White, Biologically Mixed, and Legally Negro" The Journal of Southern History, Vol. 68, No. 1 (Feb., 2002), pp. 65-106
- ↑ Lombardo, P. A. (1987). Miscegenation, Eugenics, and Racism: Historical Footnotes to Loving v. Virginia. UC Davis L. Rev., 21, 421.
- ↑ Kushner, D. Z. (2006). John Powell: his racial and cultural ideologies. MinAd: The Online Journal of the Israel Musicology Society, 5(1).
- ↑ Sherman, R. B. (1988). " The Last Stand": The Fight for Racial Integrity in Virginia in the 1920s. The Journal of Southern History, 69-92.
- ↑ Lombardo, Paul (2000). Eugenic Laws Against Race Mixing. Image Archive on the American Eugenics Movement, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.