
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
Monosaccharides, also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built. Simply, this is the structural unit of carbohydrates.
In chemistry, a pentose is a monosaccharide with five carbon atoms. The chemical formula of many pentoses is C
5H
10O
5, and their molecular weight is 150.13 g/mol.

Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.
An aldose is a monosaccharide with a carbon backbone chain with a carbonyl group on the endmost carbon atom, making it an aldehyde, and hydroxyl groups connected to all the other carbon atoms. Aldoses can be distinguished from ketoses, which have the carbonyl group away from the end of the molecule, and are therefore ketones.

Phenolphthalein ( feh-NOL(F)-thə-leen) is a chemical compound with the formula C20H14O4 and is often written as "HIn", "HPh", "phph" or simply "Ph" in shorthand notation. Phenolphthalein is often used as an indicator in acid–base titrations. For this application, it turns colorless in acidic solutions and pink in basic solutions. It belongs to the class of dyes known as phthalein dyes.

Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans.
Furfural is an organic compound with the formula C4H3OCHO. It is a colorless liquid, although commercial samples are often brown. It has an aldehyde group attached to the 2-position of furan. It is a product of the dehydration of sugars, as occurs in a variety of agricultural byproducts, including corncobs, oat, wheat bran, and sawdust. The name furfural comes from the Latin word furfur, meaning bran, referring to its usual source. Furfural is only derived from dryed biomass. In addition to ethanol, acetic acid, and sugar, furfural is one of the oldest organic chemicals available readily purified from natural precursors.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
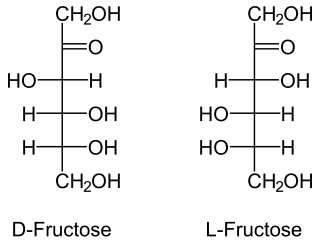
In organic chemistry, a ketose is a monosaccharide containing one ketone group per molecule. The simplest ketose is dihydroxyacetone, which has only three carbon atoms. It is the only ketose with no optical activity. All monosaccharide ketoses are reducing sugars, because they can tautomerize into aldoses via an enediol intermediate, and the resulting aldehyde group can be oxidised, for example in the Tollens' test or Benedict's test. Ketoses that are bound into glycosides, for example in the case of the fructose moiety of sucrose, are nonreducing sugars.

Molisch's test is a sensitive chemical test, named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch, for the presence of carbohydrates, based on the dehydration of the carbohydrate by sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to produce an aldehyde, which condenses with two molecules of a phenol, resulting in a violet ring.
In chemistry, a chemical test is a qualitative or quantitative procedure designed to identify, quantify, or characterise a chemical compound or chemical group.

Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), also known as 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural, is an organic compound formed by the dehydration of reducing sugars. It is a white low-melting solid which is highly soluble in both water and organic solvents. The molecule consists of a furan ring, containing both aldehyde and alcohol functional groups.
The Kiliani–Fischer synthesis, named for German chemists Heinrich Kiliani and Emil Fischer, is a method for synthesizing monosaccharides. It proceeds via synthesis and hydrolysis of a cyanohydrin, followed by reduction of the intermediate acid to the aldehyde, thus elongating the carbon chain of an aldose by one carbon atom while preserving stereochemistry on all the previously present chiral carbons. The new chiral carbon is produced with both stereochemistries, so the product of a Kiliani–Fischer synthesis is a mixture of two diastereomeric sugars, called epimers. For example, D-arabinose is converted to a mixture of D-glucose and D-mannose.
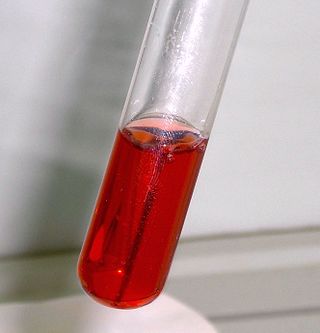
Seliwanoff’s test is a chemical test which distinguishes between aldose and ketose sugars. If the sugar contains a ketone group, it is a ketose. If a sugar contains an aldehyde group, it is an aldose. This test relies on the principle that, when heated, ketoses are more rapidly dehydrated than aldoses. It is named after Theodor Seliwanoff, the chemist who devised the test. When added to a solution containing ketoses, a red color is formed rapidly indicating a positive test. When added to a solution containing aldoses, a slower forming light pink is observed instead.
Bial's test is a chemical test for the presence of pentoses originally developed for the diagnosis of Pentosuria. It is named after Manfred Bial, a German physician. The components include orcinol, hydrochloric acid, and ferric chloride. A pentose, if present, will be dehydrated to form furfural which then reacts with the orcinol to generate a colored substance. The solution will turn bluish and a precipitate may form. The solution shows two absorption bands, one in the red between Fraunhofer lines B and C and the other near the D line. An estimate of the relevant wavelengths can be made by referring to the Fraunhofer lines article.
Chemical tests in mushroom identification are methods that aid in determining the variety of some fungi. The most useful tests are Melzer's reagent and potassium hydroxide.
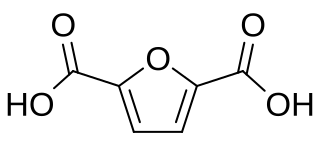
2,5-Furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) is an organic chemical compound consisting of two carboxylic acid groups attached to a central furan ring. It was first reported as dehydromucic acid by Rudolph Fittig and Heinzelmann in 1876, who produced it via the action of concentrated hydrobromic acid upon mucic acid. It can be produced from certain carbohydrates and as such is a renewable resource, it was identified by the US Department of Energy as one of 12 priority chemicals for establishing the “green” chemistry industry of the future. Furan-2,5-dicarboxylic acid (FDCA) has been suggested as an important renewable building block because it can substitute for terephthalic acid (PTA) in the production of polyesters and other current polymers containing an aromatic moiety.

Methoxymethylfurfural is an organic compound derived from dehydration of sugars and subsequent etherification with methanol. This colorless liquid is soluble in a wide range of solvents including lower alcohols. The molecule is a derivative of furan, containing both aldehyde and ether (methoxymethyl) functional groups. MMF has been detected in the leaves and roots of Chilean Jaborosa magellanica (Solanaceae). It has a typical odor suggestive of maraschino cherries. MMF can be made from a wide range of carbohydrate containing feedstocks including sugar, starch and cellulose using a chemical catalytic process and is a potential "carbon-neutral" feedstock for fuels and chemicals.

Carbon snake is a demonstration of the dehydration reaction of sugar by concentrated sulfuric acid. With concentrated sulfuric acid, granulated table sugar (sucrose) performs a degradation reaction which changes its form to a black solid-liquid mixture. The carbon snake experiment can sometimes be misidentified as the black snake, "sugar snake", or "burning sugar" reaction, all of which involve baking soda rather than sulfuric acid.











